* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electricity-review-assignment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
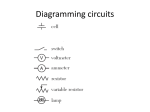
Electricity Review Assignment 1. Explain the meaning of the word “STATIC”. Now, explain what static electricity is. The word static means still. Static electricity involves the build up of electrons on the surface of an insulating material. The electrons remain “still” until they are discharged by coming near another object. Static electricity is the IMBALANCE of electrons between 2 objects. 2. What is the difference between a positive charge and a negative charge? An object has a negative charge if it has gained extra electrons and now has more electrons than protons. An object will have a positive charge if the object has lost electrons. There will now be more prtotons than electrons so the object has a positive charge. 3. What are the 3 laws of electrostatics? Negative and Negative charges will repel Positive and Positive charges will repel A negative and a positive charge will attract 4. Explain the difference between a conductor and an insulator. An insulator is a material that holds its electrons very tightly and therefore will not let additional electrons pass through it easily. A conductor is a material that has loose electrons and when additional electrons are forced into the material, they can pass the electrons through the material with very little resistence. 5. List the 4 basic components of an electrical circuit system. Component Description __SOURCE____ A source is where the electrical energy comes from or where it is generated battery, plug-in __LOAD______ A load is the object that converts the electrical energy into some other form of energy A conductor is the material that allows the electricity to move around the path or circuit A control will allow or disallow the flow of the current light, stove element __CONDUCTOR_ _CONTROL_______ Examples copper wire switch 6. Wire Resistor Cell Variable resistor Lamp (2 ways) 7. What are an ammeter, a galvanometer and voltmeter? Explain what they measure and the units that they measure in. These are devices that measure electrical values. Ammeter – measures current in Amperes (A) Galvanometer – also measures current (but weaker current) in Amperes or small versions (ex. mA) Voltmeter – measures voltage. The unit for voltage is volts (V) 8. What is resistance? Explain the idea of resistance using a diagram to illustrate what you understand about this concept. Resistance is provided by objects that impede the flow of electrons. Good diagram examples could be like a bottle neck of traffic or the pinching off of a hose. 9. Explain how a toaster works, according to the idea of resistance. A toaster receives a supply of electrons traveling from the power source through its power cord (conductor). The heating elements in the toaster act as a resistor and when the electrons reach it, the material resists their flow. Some of the electrons undergo an energy transformation, converting to heat and light. The heat cooks your toast. 10. What is a variable resistor? Provide two examples. A variable resistor is a resistor in which the user can control how much current is being resisted. If there is very little resistance, the object will not release as many electrons as (heat, light, sound, motion, etc..). If there is lots of resistance, the object will need to release more electrons in one of the above forms. Examples – dimmer switch, dial on a toaster that determines how dark your toast gets, the volume knob of a stereo, etc… 11. According to Georg Ohm, what is the relationship between current, voltage and resistance? How can it be calculated? There is a direct relationship between voltage and current. If one goes up, so does the other. There is an inversely proportional relationship between current and resistance. If one goes up, the other one must go down. The Formula for Ohm’s Law is V=I x R 12. Explain how an electric cell works. What 2 components help make up an electrical cell? An electric cell has 2 main parts – 2 different metals (electrodes) and a conducting liquid/paste (electrolyte) It will convert chemical energy into electrical energy. When the circuit is connect, IONS form from the electrodes and take part in chemical reactions with the electrolyte. One of the electrodes will tend to lose electrons and the other will gain electrons. The electrons will travel through the circuit and power the load (device) in the circuit. 13. According to our lab work, did the types of metals or the type of solution affect the amount of voltage generated in our wet cells more? What solutions worked the best and what metals worked the best? The type of metals had a bigger impact than the type of liquid. 14. What is the difference between AC and DC electricity? DC means direct current. It will travel one direction. This is the type you have in a battery AC means alternating current. The current will travel both ways (a certain number of times per second). This is what the wall socket (household power) uses. 15. What are fuses and what are circuit breakers? Fuses and Circuit Breakers are safety devices that prevent too much current from flowing into the electronic device. A fuse has a type of metal that acts a resistor. If the metal receives too much current, it will melt and interrupt the circuit (similar to a switch) A circuit breaker is the same idea as a fuse, except it uses metals that will expand when there is too much current. It will then trigger a spring which will flip the breaker so there is no longer a connected current. 16. Calculations - Using Ohm’s Law, find the missing value a) A circuit has a load that resists the flow of current by 12 ohms. The amount of current is 4 Amperes. What is the voltage through the circuit? V= ? I=4A R = 12 ohms V= I x R V = 4 x 12 V = 48 Volts b) A circuit is powered from a 240V plug in. If there is a 3 A current, what was the resistance of the load? V = 240V I=3A R=? V = IxR 240 = 3 x R divide by 3 80 = R R = 80 ohms or R= I V R = 240 3 R = 80 ohms c) A car has a 12V battery. If the current is 15 A going to the starter, what is the resistance? V = 12 V I = 15 A R=? V=IxR 12= 15xR divide by 15 0.8 = R or R = 0.8 ohms 17. List the top 3 sources of electrical energy in Saskatchewan. (text page 278) # 1 coal = 46% #2 gas = 25% #3 hydro = 23% R= I V R = 12 15 R = 0.8 ohms 18. Describe how either a hydroelectric dam works….or …. Describe how a coal based electrical generating station works. Hydroelectric – A Hydroelectric power station uses the movement of water to generate power. The water is held back by a dam. The water is forced to flow through the penstock which makes it pass by a turbine which the water turns. The spinning of the turbine will allow the generator to convert the mechanical (movement) energy into electricity. (Electrical energy) A coal generating station works in much the same way, except it is the pressure of steam that turns the turbine. Crushed coal is burns to heat water. The water will turn into high pressure steam which will travel through pipes to turn the turbine. The spinning of the turbine allows the generator to change the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Cost calculations will be on the website This is the sheet that says Calculation review for exam. You have it already.