* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar Ch 2: Nouns Review
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian numbers wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
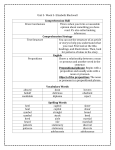
Grammar Ch 2: Nouns Review A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. A common noun is a general name for a person, place, thing, or idea. They are usually not capitalized. (town) A proper noun is the name of a particular person, place, thing, or idea. They are always capitalized. (Savannah) A concrete noun names a thing that can be seen, heard, smelled, touched, or tasted. (thunder, feather, table, rainbow…) An abstract noun names an idea, feeling, quality, or characteristic. (beauty, honor, laughter, greed…) A collective noun is a word that names a group of people or things. (class, pack, family, herd….) A singular noun names one person, place, thing, or idea. (child) A plural noun names more than one person, place, thing, or idea. (children) A possessive noun shows ownership or relationship. (Reggie’s dog, the Smiths’ vacation) Noun Singular Plural ending in –s Plurals not ending in –s Rule Add an apostrophe and –s Add an apostrophe Add an apostrophe and –s Possessive bird’s family eggs’ colors men’s hats A compound noun is made of two or more words used together as a single noun. (watermelon, sixteen-year-old, swimming pool) A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The most common linking verbs ar eforms of the verb be. (is, am, are, was, were, been, being) **also refer to your Writer’s Guide (bright yellow) A predicate noun renames or defines the subject after a linking verb. (My sister is the captain) A direct object names the receiver of the action of the action verb. (Hector kicked the football) An indirect object tells to whom or what or for whom or what an action is done. (The coach gave the team their awards) A noun or pronoun that follows a preposition is the object of the preposition. (My uncle ran in the marathon. He competed for the trophy.) A preposition is a word that shows a relationship between a noun or pronoun and some other word in the sentence. A preposition is always followed by an object, either a noun or a pronoun. (The worm is on the apple. The worm is beside the apple. The worm is under the apple. The worm is in the apple.) Common prepositions: about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, as, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in , inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, over, past, through, to, toward, under, until, up, with, within, without **also refer to your Writer’s Guide (bright yellow)