* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KS4 Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
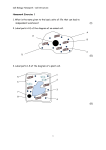
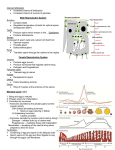
KS4 Biology B13a / Side 1 Structure of the male reproduction system Label the following diagram: Complete the following table: Structure Function Testis Carries sperm from testes to urethra Scrotum Coiled tube where sperm is stored Urethra Transfers sperm into vagina Produces fluid containing nutrients for sperm, makes up semen Ureter Produces alkaline fluid to add to sperm to make semen 1. Why are the testes located outside of the body protected by the scrotal sacs? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13a / Side 2 2. What is the function of the fluids produced by the prostate gland and seminal vesicle? 3. Outline the route taken by ejaculated sperm from their site of production to the oviduct of the female. 4. How does a condom work as a contraceptive? 5. Label the following diagram of a sperm cell: a) Sperm are extremely adapted to their function; describe in what ways they have become specialized. b) How many sperms are needed to fertilize an egg cell? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13a / Side 3 Structure of the Female Reproductive system Label the following diagram of the female reproductive system: Complete the following table: Structure Function Ovaries Connect ovaries to uterus, where fertilization occurs Uterus Narrow neck of uterus, dilates during labor Vagina 1. The uterus is said to be the most powerful muscle in the body. Why does it need to be so powerful? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13a / Side 4 2. What happens to the egg cell once it is released from the ovaries? 3. Fill in the missing words in the following paragraph: An egg is released by one of the two _______________ approximately every 28 _______________. It passes into the end of the _______________ and moves slowly downward. If _______________ is to take place the egg must be met by a _______________ before or just after it reaches the _______________. Sperm are produced in the tubules of the _______________ in vast quantities. Ejaculation forces the sperm from the _______________ into the sperm duct and leaves the body through the _______________. Millions of ejaculated sperm is deposited into the _______________ from here they make their journey to the egg cell. Thousands of sperms may reach the egg but only _______________ enters it. _______________ occurs when the sperm nucleus fuses with the egg nucleus to form a _______________. This is the moment of conception. Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13b / Side 1 Adolescence Adolescence or puberty is the transition from a sexually immature child into a sexually mature adult. The average age for the onset of puberty is 12 – 13 in girls and 13 – 15 in boys. Hormones control development of sexual characteristics in the male and female. Complete the following table; use your textbook for assistance: Male Female Hormone Site of production Function of hormone These two hormones also bring characteristics) in boys and girls. about bodily changes (secondary sexual List these changes in the table below: Boys Sha Tin College Girls Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13c / Side 1 Ovulation and the menstrual cycle One of the changes that occur in girls during puberty is the start of her menstrual periods. The length of the cycle varies but on average it occurs about every 28 days. The diagram below illustrates the events that occur during the menstrual cycle. Essentially during the menstrual cycle an egg cell is matured and released from one of the ovaries and the lining of the uterus is thickened to prepare for implantation of a zygote, a fertilized egg cell. Use the diagram above and your textbook to help you answer the following questions: 1. Describe what happens during menstruation or a period. 2. What is ovulation and when does it occur during the menstrual cycle? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13c / Side 2 3. At the same time as the egg is developing the lining of the uterus is becoming thicker with blood vessels. What is the purpose of this thick lining? 4. What is an empty follicle called? 5. What happens to the egg cell and the uterus if fertilization does not take place? 6. During what days in the menstrual cycle do you think the woman is the most likely to get pregnant if she has sexual intercourse? Explain your answer? 7. Name the two hormones that play a major role in the menstrual cycle. 8. When females reach the age of about 50 years old ovulation no longer occurs and menstruation ceases, what is this phase known as? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13d / Side 1 1. Complete the missing terms in the boxes using the following words: Implantation Ovulation Fertilization Cell division 2. Match the correct term with the definitions. a. Vagina Embryo sinks into the soft uterus lining b. Zygote Release of an egg from one of the ovaries c. Implantation A fertilized egg cell d. Fertilization Release of semen out of the urethra through the penis e. Ovulation Male and female nuclei fuse together f. Oviduct Where sperm is deposited during sexual intercourse g. Ejaculation Where fertilization takes place Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13e / Side 1 Pregnancy Following successful implantation of the embryo into the lining of the uterus the placenta develops. The embryo and the placenta is now called a foetus. The placenta is a temporary organ that allows the blood systems of the fetus and the mother to come in close contact without actually mixing. 1. In the above diagram, label the structures and colour the mother’s blood red and the embryo’s blood blue. 2. One of the main jobs of the placenta is to allow the diffusion of substances between the foetal and mother’s blood systems and vice versa. Complete the table below. Substances diffusing from: Mother to foetus Sha Tin College Foetus to mother Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13e / Side 2 3. Give two reasons why the maternal and foetal circulations are separated. Inside of the uterus the foetus is surrounded by a fluid filled membrane. 4. Label the following diagram. What is the function of structure B in the diagram above? 5. What is the function of the amniotic fluid? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13f / Side 1 Labour and Birth Pregnancy lasts between 38 – 40 weeks, at the end of the period the baby is ready to be born and is about 3 kg in weight and 50 cm length. There are three stages of labour: A. B. C. Amnion ruptures and the cervix widens/dilates to a diameter of 10 cm. Strong powerful contractions of the uterine muscle push the bay out of the uterus through the cervix and vagina. The placenta and umbilical cord are expelled after the baby is born, this is known as the afterbirth. 1. Babies are usually born headfirst. What advantages are there in being born in this position? 2. Some babies are born under weight even though they are born at the right time. Suggest factors that can affect the birth weight of the baby. Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13g / Side 1 HIV virus HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that severely damages the immune system by infecting and destroying certain white blood cells. AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is the final, life-threatening stage of infection of HIV. At the end of 2002 it is estimated that 42 million people are living with HIV/AIDS and 19 million have already died since the beginning of the epidemic in the 1980s. While there are new and improved treatments for HIV, there is no cure, and because of the nature of the virus, developing a preventive vaccine is problematic. 1) Go to the following website and take a quiz to test how much you know about the transmission of HIV. http://www.unicef.org/voy/learning/learhome.html Use the following website to help you answer the questions below. http://w3.whosea.org/hivaids/factsheet.htm 2) List four ways in which HIV is transmitted (spread from person to person) 1. 2. 3. 4. 3) A common misconception amongst students is that HIV can be spread from an infected person by using the same cutlery or bath as them and that mosquitoes carry the virus. State some other myths that you have heard about on how HIV can be spread. 4) Suggest how the spread of HIV can be prevented. 1. 2. 3. Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13h / Side 1 World population of Humans The population of the world surged from 2.4 billion in 1950 to 6.1 billion 50 years later. The annual increase is about 94 million people; about 260,000 people are added to the world population each day. As you see the Human population has been growing at an alarming rate with birth rates remaining high and death rates falling. Rapid population growth directly affects the global ecosystem placing a greater demand on the space needed to sustain large numbers of people. 1. Suggest reasons why the world’s population has been rapidly increasing. ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 2. The population growth rate in developed countries in the United States and Europe is less than 1% but in developing countries such as India and Nigeria the rate is more than double. What is the impact of a rapidly growing population in developing countries such as these? 3. Since 1979 China has enforced a controversial one-child policy in its efforts to control rapid population growth. Apart from such a stringent family planning measure, suggest other ways that population growth can be limited. Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13i / Side 1 Review questions 1. The diagram shows part of the female reproductive system a. Use an S to mark on the diagram the place where sperm are released during intercourse and an F to show where fertilization usually occurs. b. Explain how the structure of a sperm enables it to travel from S to F. 2. A few weeks after fertilization, the fertilized egg becomes an embryo, which is surrounded by amniotic fluid. a. Label structure F in the diagram Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17 KS4 Biology B13i / Side 2 b. Describe two functions of the amniotic fluid c. Describe how the oxygen level in the blood of the embryo is maintained. 3. The diagram below shows the relative levels of the two hormones, oestrogen and hormone Q, during a woman’s menstrual cycle. a. What effect does the build up of oestrogen have from day 9 to day 14? b. Name hormone Q c. Where is hormone Q produced? d. What would be indicated if high levels of hormone Q continued beyond day 24? Sha Tin College Science Department - June 17