* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SUMMER REVIEW PACKET (for those coming into Pre
Survey
Document related concepts
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
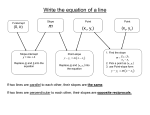
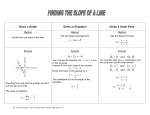
6 Pre-Calculus Review Assignment (Summer 201 ) Name: ____________________________ This assignment is made up of several types of problems from the Prerequisite chapter in Pre-Calculus. This is not a required assignment but is recommended for you to be sure you are ready for Pre-Calculus next year. Reviewing this material ahead of time will help us move on to NEW content earlier and will help you to be more successful in this class. We will use the textbook: Demana: Pre-Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic, 7th edition Visit www.phschool.com/home.html to access the book online. In the web codes box, enter aze-0640 (NOTE: this is the 8th edition, but the same book we use). Materials for this class: 3 ring binder/folder Notebook/Looseleaf paper 1 subject Notebook TI-83 plus or TI-84 plus graphing calculator recommended – watch for sales this summer! Section P.1 1.) Use the distributive property to write the expanded for 2 x 2 x . _____________________ 2.) Use the distributive property to write the factored form of 2 x3 4 x 2 . ______________________ 3.) Convert from inequality to interval notation: x 4 . ______________________ 4.) Convert from interval to inequality notation: [ -5, 8 ) ______________________ In exercises 5 & 6, simplify the expression. Assume that denominators are not zero. uv 2 3 5.) 2 3 vu ___________ 6.) 3x 2 y 3 2 _____________ Section P.2 7.) Given the points (-4, 3) and (5, -1). a.) Find the distance between the points. ______________________ b.) Find the midpoint of the line segment determined by the points. ______________________ 8.) Let (3, 5) be the midpoint of the line segment with endpoints (-1,1) and (a, b). Determine a and b. ______________________ 9.) Write the standard form of the equation of a circle with radius 5 and center at (-2, 7). ______________________ Section P.3 10.) Find the slope of the line through the points (-1, -2) and (4, -5). ______________________ 11.) Find an equation in point-slope form for the line through the point (2, -1) and slope m = -2/3. ______________________ In exercises 12 - 14, solve each equation algebraically. 12.) 3x – 4 = 6x + 5 ______________________ 13.) (5 - 2y) – 3(1 - y) = y + 1 14.) x2 x5 1 3 2 3 ______________________ ______________________ In exercises 15 - 16, solve the inequality and draw a number line to graph the solution and write the solution in interval notation. 15.) 5x + 1 2x - 4 ______________________ 16.) 3x 5 -1 4 ______________________ Section P.4 In exercises #17 - 22, find an equation for the line. Use the indicated form of the line. 17.) The line through (3, -2) with slope m = 4/5. (general form) ______________________ 18.) The line through the points (-1, -4) and (3, 2). (slope-intercept form) ______________________ 19.) The line through (-2, 4) with slope m = 0. ______________________ 20.) The line 3x – 4y = 7 (slope-intercept form) ______________________ 21.) The line through (2, -3) and parallel to the line 2x + 5y = 3. (general form) ______________________ 22.) The line through (2, -3) and perpendicular to the line 2x + 5y = 3. (slope-intercept form) ______________________ In exercises 23 - 24, solve each equation algebraically. 23.) x(2x + 5) = 4(x + 7) ______________________ 24.) 4 x 1 3 ______________________ Section P.5 In exercises 25-31, solve each equation algebraically. (Quadratics that can be solved by factoring should be solved by factoring). 25.) 16 x 2 24 x 7 0 ______________________ 26.) 6 x 2 7 x 3 ______________________ 27.) 4 x 2 20 x 25 0 ______________________ 28.) 9 x 2 12 x 4 0 ______________________ 29.) 3(3x 1) 21 2 ______________________ 30.) x 2 4 x 3 0 ______________________ 31.) Use the quadratic formula to solve the equation 3x 2 4 x 1 0 ______________________ In exercises 32 & 33, use factoring to solve the equation. 32.) 3x3 19 x 2 14 x 0 ______________________ 33.) x3 2 x 2 4 x 8 0 ______________________ Section P.6 Perform the indicated operation, and write your answer in standard form a + bi. 34.) 2 5i 3 2i 35.) 4 i 3 5i ______________________ ______________________ 36.) Multiply 4 7i by its conjugate 37.) 2 6i 3i ______________________ ______________________ 38.) Solve the equation 4 x 2 6 x 5 x 1 _____________________ Section P.7 Solve the inequalities algebraically. Write your solutions using interval notation. 39.) 5x 2 0 ______________________ 40.) x 5 6 4 ______________________ Solve the inequalities graphically. Sketch the graph in the space provided. Write your solutions using interval notation. 41.) 2 x3 2 x 5 ______________________ FORMULAS (These will not be given to you on the test – you need to know them!) 1.) Distance Formula: 2.) Midpoint Formula: d x2 x1 y2 y1 2 x x y y2 M 1 2 , 1 2 2 y2 y1 x2 x1 3.) Slope Formula: m 4.) Point-Slope Form: y y1 m( x x1 ) 5.) Slope-intercept Form: y mx b 6.) General Form: Ax By C 0 7.) Quadratic Formula: x b b2 4ac 2a 2