* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.2 PowerPoint 4.11.16
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
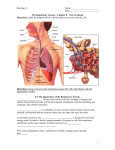
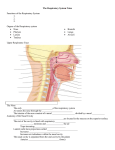
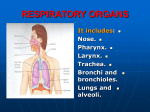
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 4.11 .16 MAJOR ORGANS N___ P_____ L_____ T______ B_____ B__________ L____ TRACTS _____ Respiratory Tract Nose Mouth Nasal cavity Pharynx Larynx _____ Respiratory Tract Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs ZONES _________ Zone Everything except the exchange N___ M____ N____ ______ P______ L_____ T______ B______ B__________ ___________ Zone Where the respiration actually takes place Lungs Alveoli UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Filter and remove foreign particles Humidify and control temperature of inspired air Produce sound (voice) Sense of _____ (olfactory sense) Aid in immunity Conduct air to lowest respiratory tract UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT _____ Only part of respiratory system that is external to the body Openings are called nostrils or nares _____ Cavity ______ the nose Split into ____ and _____ by the nasal septum Mucus membrane lined to filter air Front of nasal cavity, inside each nostril, is the _________ region Contains oily cilia: trap particles __________ receptors Along roof of nasal cavity UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nasal cavity (contd) Rest of nasal cavity is called the __________ cavity This region warms the air, but is lined with thinly lined veins These are the causes of ___________ __________ 3 uneven bones that extend through the nasal cavity Increase _________ area to filter air CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING 1. What structures make up the respiratory system? 2. What are the functions of the upper respiratory tract? 3. What structures make up the lower respiratory tract? 4. What is the only external part of the respiratory system? UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT _______ Commonly referred to as the roof of the mouth Separates the nasal cavity from the _____ cavity Anterior part is supported by bone Called the “____ palate” Posterior plate is composed of soft muscle and tissue Called the “____ palate” UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Palate (contd) ____ Hangs from the end of the soft palate Prevents food from entering _____ cavity Small role in speech Small conical mass of connective tissue and ______ fibers UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Palate (contd) When parts of the palate do not completely fuse together during fetal development, a _____ palate is the result A cleft palate leaves an opening in the roof of the mouth, or a gap between the lip and the nose Occurs in 1 out of every ___ babies CLEFT PALATE CLEFT PALATE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Sinuses ___ filled cavities that surround the nose Lined with mucous membranes Connect to nasal cavities by ducts that drain into the nose __ sinuses Frontal sinus Ethmoidal sinus Sphenoidal sinus Maxillary sinus UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT Sinuses _____ the weight of the head Warm and moisten air Amplify the tone of voice “nasaly” sound during a sinus infection (stuffed up) CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING How many types of sinuses do you have and what are they? Where are they located? What is another name for your palate? What is the function of the cilia in your nose? Imagine you are a doctor and one of your patients recently gave birth to a baby with a cleft palate. How would