* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Word wall vocabulary doc
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
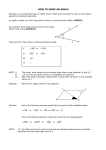
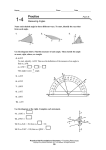
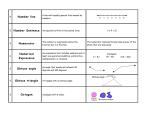
Word Wall Vocabulary Accelerant: something that makes a fire develop faster Acute (angle): less than 90° (what a cute little angle!) Adjacent: next to Adjacent angles: A B angles that are next to each other Aerobatics: rolls, loops, and other stunts performed in an airplane or glider Aerodynamic: fast (with very little drag) Aerodynamics: the study of how objects move through the air Angle: corner; a figure formed by two lines or rays; the measurement of that corner Association: something linked mentally Asymmetric: without symmetry Axis: an imaginary line/mirror (axis of symmetry), a line used an a reference (coordinate axes) “Biological” Fruit: what a biologist would consider fruit (the part of the plant that has seeds). Tomatoes, zucchini, and cucumbers are considered to be fruit to biologists, even though they are considered vegetables to cooks. Categorize: put into groups Centimeter: in one inch) 1/100th of a meter, about the width of your little finger (there are 2.4 cm Clarification: another (more detailed) explanation Collaboration: working together Compare/Contrast: what is similar, what is different between two things Concave (also known as concave up): opens up, like a smile or valley Conical: like an ice-cream cone Convex (also known as concave down): opens down, like a frown Cooperation: working together Cotyledon: the first leaf in the plant embryo (it becomes the first leaf or leaves) Craters: a pit created by a meteor or volcano Cylindrical: like a roll of paper towels, toilet paper Diagonal: a line across a figure Dialogue: conversation, discussion Diameter: Diamond: bottom) the line across the middle of a circle (or the length of that line). (often a rhombus – all equal sides – but drawn with the corners at the top and MST Creating Inquiry-Based classroom projects for Students in Grades K-6 Page 1 of 3 Summer 2007 Dicot (dicotyledon): plants having an embryo with two cotyledon Displacement: the length from the starting point to the ending point Drag: air resistance, something that slows down progress Edge: a line boundary (sometimes used for any line that connects points) Elasticity: how well an object goes back to its original shape if bent Embryo: a plant/person in the earliest stages of development Erosion: the process (or result) of wearing away Face: the flat side of a 3-dimentional figure (e.g. there are six faces on a cube) Flower: the reproductive structure in some plants Force: a push, pull, twist, or acceleration Fractions: portions of an object (like one-half or four-thirds). Fuel: a substance (like food or oil) used to produce energy or power Geometry: the study of shapes and measurement Germinate: start to grow Gravitational Force: the natural force that draws objects together (but is only noticeable if the objects are really large) Gravity: the attraction of objects to the earth (or moon or other large objects) Human vs. Artificial Intelligence: human thought vs. technology that appears to mimic human thought. Hypothesis: an educated guess, a prediction Impact: a forceful collision Invasive Species: a plant or animal that thrives so well in a new environment that it kills off the other plants/animals that live there Kinetic Energy: energy related to motion Launch: to generate enough thrust to propel a device Life Cycle: the stages through which an organism passes between successive recurrences of a specified primary stage Line: a one-dimensional geometric shape Meteor: debris from the early days that the solar system that gets trapped by gravity and collides with a planet or moon Momentum: a property of a moving body that the body has by virtue of its mass and motion and that is equal to the product of the body's mass and velocity Monocot (monocotyledon): plants having an embryo with a single cotyledon, usually parallelveined leaves, and floral organs arranged in cycles of three. Motion: an act, process, or instance of changing place MST Creating Inquiry-Based classroom projects for Students in Grades K-6 Page 2 of 3 Summer 2007 Obtuse (angle): more than 90° [obtuse can also mean not sharp, as in dull or blunt, both for angles and for people] Opposite: being the other of a pair that are corresponding or complementary in position, function, or nature Parallel: two lines that are equidistant apart at all points. Pentagon: a five-sided figure Planes: two-dimensional surface Pollination: the transfer of pollen from an anther to the stigma in angiosperms or from the microsporangium to the micropyle in gymnosperms Polygon: a closed figure bounded by straight lines Pressure: force spread over a given area Reflectivity: that amount of energy that bounces back from a surface Rhombus: a parallelogram with four equal sides Rippled: to impart a wavy motion Scalene (for a triangle): having three unequal signs Scribe: a person assigned to record observations Seed Coat (testa): the outer protective coating on a seed Seedling: young plant grown from a seed Semicircle: one-half of a circle Strategies: careful plan or method Symbols: short-hand item for something else Symmetric: having the property of being identical on two sides. Temperature: measurement of internal heat. Thrust: force causing movement Trapezoid: a four-sided figure with only two sides are parallel Triangles: three sided figures (depending on the relative lengths of the sides, you can have equilateral (all three sides the same), isosceles (two sides the same), etc.) Two-dimensional: having length and width but no depth (flat) Upward Thrust: force which causes motion towards higher altitudes Vertex: a point (as of an angle, polygon, polyhedron, graph, or network) that terminates a line or curve or comprises the intersection of two or more lines or curves Volatile: readily vaporizable at a relatively low temperature Yaw: to turn by angular motion about the vertical axis MST Creating Inquiry-Based classroom projects for Students in Grades K-6 Page 3 of 3 Summer 2007