* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understand congruence and similarity using physical models
Plane of rotation wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
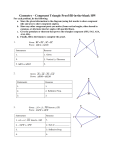
Grade/Course: Grade 8 Instructional Unit 1: Congruence and Similarity Instructional Schedule: First Nine Weeks (suggested for 20 days) ( Bold text is new content ) Adapted from Timothy Kanold Scope-and-Sequence documents Standards: Evidence Of Standard: (student should be able to…) Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, transparencies, or geometry software. (BA 3.3) Verify experimentally the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: a. Lines are taken to lines, and line -Construct: segments to line segments of the 1. An image from pre-image, using same length. geometric tools. 2. A rotation. 3. A reflection. 4. A translation. -Understand image and pre-image are congruent in: 1. Translations. 2. Reflections. 3. Rotations. -Explore and justify figures created from transformations using compasses, protractors, and rulers or technology. b. Angles are taken to angles of the - Defend whether or not two figures same measure. are congruent given the graph of a figure and its transformation using: 1. Translation. 2. Rotation. 3. Reflection. Prerequisite Knowledge: (standards linked to content taught in previous grades) Assessment Tools: (formative assessments, quizzes, mastery tasks/activities) c. Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. (BA 3.4) Use coordinates to describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on twodimensional figures. (PASS 3.1) Construct models, sketch, and classify solid figures such as rectangular solids, prisms, cones, cylinders, pyramids, and combined forms. -Recognize the angles formed by two parallel lines and a transversal. -Justify why angles (formed by parallel lines and a transversal) are congruent using angle relationships. -Determine if two figures are congruent by identifying the transformation used to produce the figures. -Write congruent statements. -Recognize the congruent symbol. -Define congruent. -Write statements that justify the process of transformation as well as the conclusion. -Describe the sequence of transformations from one figure to another. -Identify the new coordinates of: 1. A translation. 2. A reflection. 3. A rotation. 4. A dilation. -Understand image and pre-image are similar in dilations. -Given two similar figures describe the sequence of rotations, reflections, translations, and dilations. -Create a figure congruent to a given figure by: 1. Applying knowledge of translation. 2. Applying knowledge of reflection. 3. Applying knowledge of rotation (90, 180, 270 degrees) both clockwise and counterclockwise. - Construct models, sketch, and classify solid figures such as rectangular solids, prisms, cones, cylinders, pyramids, and combined forms. (PASS 4.3) Identify basic 2dimensional figures from a composite figure. Find the area of composite figures. -Separate composite figures into basic 2-dimensional figures (rectangle, square, triangle, trapezoid). -Calculate the area of each 2dimensional figure and combine to find the area of the complete composite figure. (BA 4.4) Understand that a two-Define congruent. dimensional figure is congruent to -Recognize the congruent symbol. another if the second can be -Write congruent statements. obtained from the first by a sequence -Determine if two figures are of rotations, reflections, and congruent by identifying the translations. Describe a sequence transformation used to produce the that exhibits the congruence figures. between two different figures. - Write statements that justify the process of transformation as well as the conclusion. - Describe the sequence of transformations from one figure to another. (BA 4.5) Understand that a two-Create similar figures using dilations dimensional figure is similar to and transform them. another if the second can be -Comprehend and describe that the obtained from the first by a sequence angles of similar figures are congruent of rotations, reflections, translations, and the sides of similar figures are and dilations; given two similar two- proportional. dimensional figures, describe a -Produce similar figures from dilations sequence that exhibits the similarity using scale factors. between them. -Interpret the meaning of similar figures and describe their similarities. -Describe the list of steps that would produce similar figures when given the scale factors (dilation). -Differentiate between scale factor that would enlarge a figure’s size and one that would reduce it. (PASS 4.2) Set up and solve for - Set up and solve for missing side missing side lengths of similar lengths of similar geometric shapes geometric shapes using ratios and using ratios and proportions. proportions. (BA 4.6) Use informal arguments to establish facts about the angle sum and exterior angle of triangles, about the angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal, and the angle-angle criterion for similarity of triangles. For example, arrange three copies of the same triangle so that the sum of the three angles appears to form a line, and give an argument in terms of transversals why this is so. -Find the measures of missing angles. -Make conjectures about relationships between angles. -Construct parallel lines and a transversal to: 1. Examine and determine the relationships between created angles. 2. Explore and justify relationships that exist between angles created when parallel lines are cut by a transversal. -Apply knowledge of vertical, adjacent, and supplementary angles to identify other pairs of congruent angles. -Find a missing angle and and/or exterior angle of a triangle. -Find the missing angle measure when given two similar triangles. Resources/Exemplar Tasks: ( list possible task/activities students could engage in within this unit) Standards for Mathematical Practice: (highlight practice standards to be emphasized in the instructional unit) 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of instruction. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. ( BA: Broken Arrow rigor standard; PASS: Priority Academic Student Skills standard; BA/PASS: Combination standard )