* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nth Roots
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
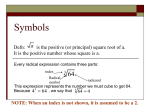
Objective: Students will be able to simplify radicals Key Concept – for any real numbers a and b, and any positive integer n, if a n=b then a is the n th root of b. For example: 62=36, so 6 is the square root of 36 25=32, so 2 is the fifth root of 32 43=64. so 4 is the cube root of 64 The symbol n indicates an n th root. 5 radicand 243 index Another way of interpreting this is to ask yourself, “What number to the 5 th power is equal to 243?” So____________ is the 5th root of 243. Here is a helpful chart to help us determine how many and what type of roots we are solving for. n n b if b>0 n b if b<0 EVEN One positive root, one negative root No real roots ODD One positive root One negative root n b if b=0 One real root, 0 When there is more than one real root, the non-negative root is called the principal root. Let’s stop and check for understanding. Complete the following examples. 1. 16 2. 3 125 3. 4 16 4. 7 1 For your reference: 12 13 14 15 22 23 24 25 32 33 34 35 42 43 44 45 52 53 54 55 This idea can be expanded to perfect powers of a variable in the radicand. The radicand xn is a perfect power when n is a multiple of the index. A quick way to do this is to figure out if the exponent is divisible by the index. 5. 8 6. 25x 4 7. 5 32 x15 y 20 8. 4 ( x 4) 8 9. 10. x8 x 2 8x 16 3 27 x 3 y 9