* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OBJECTIVES: To recognise and make quadrilaterals with increasing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
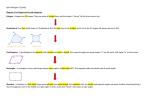
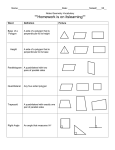
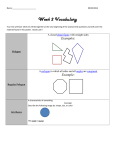
OBJECTIVES: To recognise and make quadrilaterals with increasing accuracy. UNIT: 2 To explain definitions and some properties about quadrilaterals. FOCUS: QUADRILATERALS LESSON: 4 COMMUNICATION LANGUAGE OF LEARNING Vocabulary of the topic Vocabulary U2 L1, U2 L3(start) Pentagon Equal sides Isosceles Equilateral Scalene Right-angle Acute Obtuse Quadrilateral’s classification(main teaching) parallelograms squares rectangles rhombus kites inverted kites trapezium trapezoid. Measuring triangles U2 L3 Protactor Degrees Sum LANGUAGE FOR LEARNING Language instruction Ask children to answer the following questions on their whiteboard (mental problems U2 L4). Tell them, in pairs, to make quadrilaterals on the geoboard. Children draw them on the dot paper. Encourage them to think about possible classifications. Establish the classification according to sides and angles. Children cut out their quadrilaterals and stick them in the right places (worksheet 2.7). Pupils draw some quadrilaterals on the worksheet and measure the angles. They fill the table (worksheet 2.8). Cut the vertices of a quadrilateral to show the sum of the four angles. Ask to look carefully at the quadrilaterals picture (worksheet 2.9). Questions for learning What’s a quadrilateral? How many quadrilaterals do you know? What do you know about them? How can you be sure if two quadrilaterals, you have drawn in a different position, are equal? How can we classify them? Where’s the place for this quadrilateral? Why? Possible answers It’s a … with … sides and …. angles. I know squares, rectangles, rhombus,… A square has……..and……… May be we can overlap them. We can classify them depending on the….. or the …….. Here it is, because it has……… LANGUAGE THROUGH LEARNING Language that comes through the lesson Definitions and properties Adjacent Parallel Width Length Angle What do you notice about the sum of the angles of a quadrilateral? What quadrilaterals can you see on the picture? I think the…… is………..degrees. I can see………….. Language to express conclusions “A quadrilateral is a four-sided shape. They can be classified as parallelograms, squares, rectangles, rhombus, kites, inverted kites, trapezium, trapezoid.” “Quadrilateral: A four-sided polygon. The angles of a quadrilateral total 360º. Rectangle: A three-sided polygon having all right angles but different length and width. Square: A four-sided polygon having equal-length sides and all right angles. Rhombus: A four-sided polygon having all four sides of equal length and opposite angles equal. It has not right angles. Parallelogram: A four-sided polygon with two pairs of parallel sides and opposite angles equal. It has not right angles. Trapezium: A four-sided polygon having exactly one pair of parallel sides. Trapezoid: A four-sided polygon having no sides parallel” RESOURCES: whiteboard, pen, mental problem U2 L4 sheet, worksheets 2.7, 2.8, 2.9,protactor, ruler, geoboard, elastic bands, dot paper, http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/revisewise/maths/shape/, http://www.primarygames.co.uk/PG5/Shape/year6.html, http://www.eyepleezers.com/aaamath/geo612x3.htm