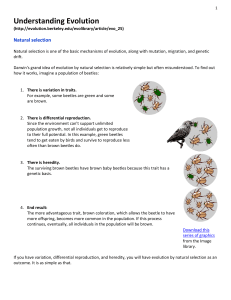
Understanding Evolution Reading Assignment
... Misconceptions about natural selection Because natural selection can produce amazing adaptations, it's tempting to think of it as an all-powerful force, urging organisms on, constantly pushing them in the direction of progress — but this is not what natural selection is like at all. First, natural s ...
... Misconceptions about natural selection Because natural selection can produce amazing adaptations, it's tempting to think of it as an all-powerful force, urging organisms on, constantly pushing them in the direction of progress — but this is not what natural selection is like at all. First, natural s ...
Diversity Notes
... a)3 stages: egg, nymph, and adult b)Insects emerge from the egg as a nymph (small version of adult w/o wings). c)As the nymph matures, reproductive organs appear and wings (adult). d)Ex: cinch bugs ...
... a)3 stages: egg, nymph, and adult b)Insects emerge from the egg as a nymph (small version of adult w/o wings). c)As the nymph matures, reproductive organs appear and wings (adult). d)Ex: cinch bugs ...
darwinism - Science Vision
... when various species split off from related ones. With reference to the establishment of evolutionary relationship, even the conventional genetic analysis is not considered fool-proof. It goes awry when the same mutation occurs independently in two different species. It makes two animal sequences lo ...
... when various species split off from related ones. With reference to the establishment of evolutionary relationship, even the conventional genetic analysis is not considered fool-proof. It goes awry when the same mutation occurs independently in two different species. It makes two animal sequences lo ...
Darwin - rgreenbergscience
... Fill the speech bubbles in with Lamarck’s and Darwin’s arguments in your own words. Which argument do you agree with? Which one do you agree with? Why? ...
... Fill the speech bubbles in with Lamarck’s and Darwin’s arguments in your own words. Which argument do you agree with? Which one do you agree with? Why? ...
Zoology / Lemmons / Guided Notes: Scientific Method, Basics
... Illustrate/Draw how the tortoises differ between Isabela and Hood Galapagos Islands; circle the one with adaptations that would allow it to reach higher vegetation (p. 371 Figure) How did the birds differ among the islands of the Galapagos? (p. 372) Based on what Darwin learned about certain birds o ...
... Illustrate/Draw how the tortoises differ between Isabela and Hood Galapagos Islands; circle the one with adaptations that would allow it to reach higher vegetation (p. 371 Figure) How did the birds differ among the islands of the Galapagos? (p. 372) Based on what Darwin learned about certain birds o ...
Gov 2015 Introduction to Computational Modeling for Social
... a) Select a pair of parent chromosomes from the current population, the probability of selection being an increasing function of fitness b) Crossover the pair, with probability pc (crossover rate), at one or two randomly chosen points, to produce two new offspring c) Mutate the offspring at each loc ...
... a) Select a pair of parent chromosomes from the current population, the probability of selection being an increasing function of fitness b) Crossover the pair, with probability pc (crossover rate), at one or two randomly chosen points, to produce two new offspring c) Mutate the offspring at each loc ...
Lecture2 - Indiana University Bloomington
... gradual. And there is a gradual radiation of species from a common ancestor (the tree of life.) Reaction to The Origin of Species --Evolution as such accepted --Natural selection rejected. As we discussed before, one of the main objections to Evolution by Natural Selection was that there was no know ...
... gradual. And there is a gradual radiation of species from a common ancestor (the tree of life.) Reaction to The Origin of Species --Evolution as such accepted --Natural selection rejected. As we discussed before, one of the main objections to Evolution by Natural Selection was that there was no know ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2014 – BIOLOGY – MICHALEC
... Directions: You will need to answer these questions on a google doc and share it with me at [email protected]. This is due no later than May 30th. Chapter 16 - Evolutionary Theory 1. What is Lamarck’s theory of evolution? Explain it using a giraffe as an example. 2. Explain Darwin’s theory of ...
... Directions: You will need to answer these questions on a google doc and share it with me at [email protected]. This is due no later than May 30th. Chapter 16 - Evolutionary Theory 1. What is Lamarck’s theory of evolution? Explain it using a giraffe as an example. 2. Explain Darwin’s theory of ...
FINAL-without_populations.doc
... 34. Which of the following does NOT belong to the basic premises that Darwin used to support his Theory of Evolution through Natural Selection? a. There is variation among individuals and at least some of that variation is inheritable. b. Individuals with certain characteristics have a better chance ...
... 34. Which of the following does NOT belong to the basic premises that Darwin used to support his Theory of Evolution through Natural Selection? a. There is variation among individuals and at least some of that variation is inheritable. b. Individuals with certain characteristics have a better chance ...
Unit 2 Science 7 - Volusia County Schools
... become the 14 species we see today. The pictures on the next page represent some examples of the types of beaks Darwin encountered and the habitat and food source found on that particular island. ...
... become the 14 species we see today. The pictures on the next page represent some examples of the types of beaks Darwin encountered and the habitat and food source found on that particular island. ...
Building Critical Thinkers
... daily and hourly scrutinising, throughout the world, every variation, even the slightest; rejecting that which is bad, preserving and adding up all that is good; silently and insensibly working, whenever and wherever opportunity offers.” Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural S ...
... daily and hourly scrutinising, throughout the world, every variation, even the slightest; rejecting that which is bad, preserving and adding up all that is good; silently and insensibly working, whenever and wherever opportunity offers.” Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural S ...
ch1lecture.pdf
... • Deductive Reasoning – Generating hypotheses based on a wellsupported generalization (such as a theory) – e.g., based on the cell theory, any newly discovered organism would be expected to be composed of cells ...
... • Deductive Reasoning – Generating hypotheses based on a wellsupported generalization (such as a theory) – e.g., based on the cell theory, any newly discovered organism would be expected to be composed of cells ...
Ch22_Evolution1
... • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on natural selection as the mechanism of descent with modification, but did not introduce his theory publicly • Natural selection is a process in which individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce • In June 1858, Darwin recei ...
... • In 1844, Darwin wrote an essay on natural selection as the mechanism of descent with modification, but did not introduce his theory publicly • Natural selection is a process in which individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce • In June 1858, Darwin recei ...
Theories of evolution - George Pindar School Scarborough
... Scientists investigated how red-bellied black snakes had changed in the 70 years since cane toads were introduced into their area. They found that red-bellied black snakes had become longer by around ...
... Scientists investigated how red-bellied black snakes had changed in the 70 years since cane toads were introduced into their area. They found that red-bellied black snakes had become longer by around ...
Darwinian Evolution_Matcuk
... • Went to Christ’s College at U. of Cambridge for theology – studied to become a clergyman & “explore the wonders of God’s creation” • 1831 – he was an unpaid “gentleman’s companion” to the captain on a “2-year” voyage aboard the HMS Beagle to chart maps in South America • The “2 year” voyage turned ...
... • Went to Christ’s College at U. of Cambridge for theology – studied to become a clergyman & “explore the wonders of God’s creation” • 1831 – he was an unpaid “gentleman’s companion” to the captain on a “2-year” voyage aboard the HMS Beagle to chart maps in South America • The “2 year” voyage turned ...
Darwin notes
... theology – studied to become a clergyman & “explore the wonders of God’s creation” • 1831 – he was an unpaid “gentleman’s companion” to the captain on a “2-year” voyage aboard the HMS Beagle to chart maps in South America • The “2 year” voyage turned into 5 years! – returned October 1836 ...
... theology – studied to become a clergyman & “explore the wonders of God’s creation” • 1831 – he was an unpaid “gentleman’s companion” to the captain on a “2-year” voyage aboard the HMS Beagle to chart maps in South America • The “2 year” voyage turned into 5 years! – returned October 1836 ...
The Return of Hopeful Monsters
... pocket mice) have invaginated their cheeks to form external fur-lined pouches with no connection to the mouth or pharynx. What good is an incipient groove or furrow on the outside? Did such hypothetical ancestors run about three-legged while holding a few scraps of food in an imperfect crease with t ...
... pocket mice) have invaginated their cheeks to form external fur-lined pouches with no connection to the mouth or pharynx. What good is an incipient groove or furrow on the outside? Did such hypothetical ancestors run about three-legged while holding a few scraps of food in an imperfect crease with t ...
The evolution of life according to the law of syntropy
... theory must make use of causality and should avoid resorting to chance. The use of chance puts naturalism in contradiction with its fundamental premise, namely that all natural phenomena can and should be explained using causality. The theory of syntropy extends causality to retrocausality and super ...
... theory must make use of causality and should avoid resorting to chance. The use of chance puts naturalism in contradiction with its fundamental premise, namely that all natural phenomena can and should be explained using causality. The theory of syntropy extends causality to retrocausality and super ...
Evolution Essential Knowledge
... Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. a. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, competition for limited resources results in differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, ...
... Essential knowledge 1.A.1: Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution. a. According to Darwin’s theory of natural selection, competition for limited resources results in differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, ...
HSC – Biology – Maintaining a Balance
... idea that living things arose in a particular sequence or order. Today, Darwin’s prediction of intermediate forms is supported by evidence in the form of thousands of known fossils that appear to have features common to two known groups, suggesting that a transition occurred in the past from one gro ...
... idea that living things arose in a particular sequence or order. Today, Darwin’s prediction of intermediate forms is supported by evidence in the form of thousands of known fossils that appear to have features common to two known groups, suggesting that a transition occurred in the past from one gro ...
Darwin and Natural Selection
... • Thus, over a few generations, birds like the black-necked stilt could evolve longer and longer legs. ...
... • Thus, over a few generations, birds like the black-necked stilt could evolve longer and longer legs. ...
ORGANIC EVOLUTION
... slow down or prevent some changes. 5. Summarize how natural selection works. ...
... slow down or prevent some changes. 5. Summarize how natural selection works. ...
“The Sexual Brain” and Dawkins
... • (2) They ALSO replicate, or reproduce, over generations, as they are passed from parents to offspring (offspring inherit their parents genes) – (a) in single-celled organisms, one mother (or parental ) cell s genes double then divide and are passed on to two daughter (or offspring ) cells (the p ...
... • (2) They ALSO replicate, or reproduce, over generations, as they are passed from parents to offspring (offspring inherit their parents genes) – (a) in single-celled organisms, one mother (or parental ) cell s genes double then divide and are passed on to two daughter (or offspring ) cells (the p ...
Study Questions for Exam 1 Biology 354 Lecture 1: Natural selection
... raised them in the laboratory from birth to death. You monitored their survival patterns and found that they were the same – in other words, they died at the same rate. How would this cause you to reinterpret figure 12.14a in the text? Lecture 4: Sexual Selection Males and females often differ in bo ...
... raised them in the laboratory from birth to death. You monitored their survival patterns and found that they were the same – in other words, they died at the same rate. How would this cause you to reinterpret figure 12.14a in the text? Lecture 4: Sexual Selection Males and females often differ in bo ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.























