File
... In 1936, Hitler took control of the Rhineland with no international opposition. In 1938, he took control of Austria, again with no opposition. In 1938, Hitler declared he wanted the Sudetanland, a part of Czechoslavakia with a large German population. The Czech government refused to give it to them. ...
... In 1936, Hitler took control of the Rhineland with no international opposition. In 1938, he took control of Austria, again with no opposition. In 1938, Hitler declared he wanted the Sudetanland, a part of Czechoslavakia with a large German population. The Czech government refused to give it to them. ...
Mein Kampf - PHS-Test-Bank
... ____ 45. In the Battle of Stalingrad, all of the following contributed to the Soviet victory except A. a brutal winter. B. a massive Allied invasion. C. a massive Soviet counterattack. D. Hitler's refusal to order a German retreat. ____ 46. The general who led Allied troops in battles on the islands ...
... ____ 45. In the Battle of Stalingrad, all of the following contributed to the Soviet victory except A. a brutal winter. B. a massive Allied invasion. C. a massive Soviet counterattack. D. Hitler's refusal to order a German retreat. ____ 46. The general who led Allied troops in battles on the islands ...
goals of the wartime conferences
... bomb had successfully been detonated and was ready to be dropped on Japan. • An air of mistrust between Stalin and the western powers had developed. • Stalin was already exerting his power and influence in eastern Europe and there seemed to be nothing that the west could do about it. • The Potsdam c ...
... bomb had successfully been detonated and was ready to be dropped on Japan. • An air of mistrust between Stalin and the western powers had developed. • Stalin was already exerting his power and influence in eastern Europe and there seemed to be nothing that the west could do about it. • The Potsdam c ...
Effects of World War II
... Defeat of Nazi Germany was imminent Churchill saw a democratic Europe headed by Britain Stalin wanted an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks Roosevelt saw a world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
... Defeat of Nazi Germany was imminent Churchill saw a democratic Europe headed by Britain Stalin wanted an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks Roosevelt saw a world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
World History II SOL Review
... • What event marks the beginning of WWII? • Germany’s invasion of Poland ...
... • What event marks the beginning of WWII? • Germany’s invasion of Poland ...
WWII Notes - Binghamton City School District
... Agreement: Czechoslovakia forced to give away Sudetenland German invasion of Czechoslovakia, 1939 Hitler double-crosses Chamberlain Hitler makes demands on port city of Danzig in the Polish Corridor Britain says if Germany attacks Poland there will be war Hitler does not want a two-front ...
... Agreement: Czechoslovakia forced to give away Sudetenland German invasion of Czechoslovakia, 1939 Hitler double-crosses Chamberlain Hitler makes demands on port city of Danzig in the Polish Corridor Britain says if Germany attacks Poland there will be war Hitler does not want a two-front ...
The US Enters WWII… - Warren County Schools
... would not continue to annex/take/invade lands • March 1939 – Hitler annexed the rest of Czechoslovakia Map • Britain and France warned him of war if he continued ...
... would not continue to annex/take/invade lands • March 1939 – Hitler annexed the rest of Czechoslovakia Map • Britain and France warned him of war if he continued ...
World War II Test Bank - PHS-Test-Bank
... B. keep food and war supplies from reaching Great Britain and the Soviet Union. C. prevent Allied forces from landing in Normandy and liberating France. D. prevent the invasion of North Africa. The Supreme Commander of U.S. forces in Europe was A. George Patton. B. George Marshall. C. Douglas MacArt ...
... B. keep food and war supplies from reaching Great Britain and the Soviet Union. C. prevent Allied forces from landing in Normandy and liberating France. D. prevent the invasion of North Africa. The Supreme Commander of U.S. forces in Europe was A. George Patton. B. George Marshall. C. Douglas MacArt ...
Chapter 11 Test
... 9. In 1938 Hitler demanded what part of Czechoslovakia: A. The Rhineland B. Austria C. The Sudetenland D. Danzig 10. European leaders met and gave in to Hitler’s demands at which conference: A. Yalta B. Potsdam C. Tehran D. Munich ...
... 9. In 1938 Hitler demanded what part of Czechoslovakia: A. The Rhineland B. Austria C. The Sudetenland D. Danzig 10. European leaders met and gave in to Hitler’s demands at which conference: A. Yalta B. Potsdam C. Tehran D. Munich ...
The USSR in World War II
... Hitler was determined to prevent Western democracies and USSR from joining forces: beat them one by one Stalin was determined to avoid war with Germany as long as possible – but convinced that such a war was inevitable 1939: A divergence of interests between USSR and Western democracies – and a conv ...
... Hitler was determined to prevent Western democracies and USSR from joining forces: beat them one by one Stalin was determined to avoid war with Germany as long as possible – but convinced that such a war was inevitable 1939: A divergence of interests between USSR and Western democracies – and a conv ...
1. World War II
... to test weapons and tactics. The war in Spain was also a rehearsal for World War II in that it split the world into forces that either supported or opposed Nazism and Fascism. ...
... to test weapons and tactics. The war in Spain was also a rehearsal for World War II in that it split the world into forces that either supported or opposed Nazism and Fascism. ...
Nationalism - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... Hitler violated the Treaty of Versailles in all of the following ways except by A. invading the Soviet Union for Lebensraum B. annexing Austria as a German province C. reclaiming the Sudetenland for the 3rd Reich D. militarizing the Rhineland A ...
... Hitler violated the Treaty of Versailles in all of the following ways except by A. invading the Soviet Union for Lebensraum B. annexing Austria as a German province C. reclaiming the Sudetenland for the 3rd Reich D. militarizing the Rhineland A ...
World War II
... • One of the most powerful countries at the time, the US, practiced the policy of isolationism. They tried to stay out of the affairs of Europe and therefore did nothing to stop the aggression of Germany, Italy, or Japan. ...
... • One of the most powerful countries at the time, the US, practiced the policy of isolationism. They tried to stay out of the affairs of Europe and therefore did nothing to stop the aggression of Germany, Italy, or Japan. ...
THE COLD WAR - Rankin County School District
... d. The Korean War e. The Eisenhower Doctrine (occurred later during the presidency of Dwight D. ...
... d. The Korean War e. The Eisenhower Doctrine (occurred later during the presidency of Dwight D. ...
European History Lecture 11
... An agreement signed between the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop. Officially titled as the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union. It was signed in Moscow in 23 August 1939. It was a non-aggression pact under whi ...
... An agreement signed between the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop. Officially titled as the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union. It was signed in Moscow in 23 August 1939. It was a non-aggression pact under whi ...
World War II Name
... ____ 7. Which group of people suffered 6 million deaths during the Holocaust? A. Nationalists B. Aryans C. Facists D. Jews ...
... ____ 7. Which group of people suffered 6 million deaths during the Holocaust? A. Nationalists B. Aryans C. Facists D. Jews ...
24-2: War in Europe
... Britain and France appease Hitler by allowing Germany to take the Sudetenland • In return Hitler agrees that this would be his last territorial demand ...
... Britain and France appease Hitler by allowing Germany to take the Sudetenland • In return Hitler agrees that this would be his last territorial demand ...
A Wartime Alliance Begins to Erode
... distrust of the United States. Truman also felt wary of Stalin. The Soviet army still occupied much of Eastern Europe, and Truman was suspicious of Soviet intentions. The Soviet leader had promised to allow free elections in Eastern Europe but had not yet fulfilled that promise. In fact, in Poland t ...
... distrust of the United States. Truman also felt wary of Stalin. The Soviet army still occupied much of Eastern Europe, and Truman was suspicious of Soviet intentions. The Soviet leader had promised to allow free elections in Eastern Europe but had not yet fulfilled that promise. In fact, in Poland t ...
Effects
... Hitler rebuilds German army 1933, Italy invaded Albania 1939 (Britain and France sign non-aggression pact with Greece, Turkey, Romania and Poland) Defeat of Democracy in Spain: Hitler and Mussolini supported General Francisco Franco’s “nationalists” in Spanish Civil War ...
... Hitler rebuilds German army 1933, Italy invaded Albania 1939 (Britain and France sign non-aggression pact with Greece, Turkey, Romania and Poland) Defeat of Democracy in Spain: Hitler and Mussolini supported General Francisco Franco’s “nationalists” in Spanish Civil War ...
World War II
... British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain, French Prime Minister Édouard Daladier, Hitler, Mussolini, and Italian Foreign Minister Galeazzo Ciano. ...
... British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain, French Prime Minister Édouard Daladier, Hitler, Mussolini, and Italian Foreign Minister Galeazzo Ciano. ...
Origins of World War II
... In Europe in the 1930s, the stage was set for the rise of dictators who would rule in a TOTALITARIAN system Complete rule by a single party and it’s leader All aspects of people’s lives are controlled without ...
... In Europe in the 1930s, the stage was set for the rise of dictators who would rule in a TOTALITARIAN system Complete rule by a single party and it’s leader All aspects of people’s lives are controlled without ...
APWH CH. 36 New Conflagrations: World War II and the Cold War
... A single homeland • Gained Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) ...
... A single homeland • Gained Sudetenland (part of Czechoslovakia) ...
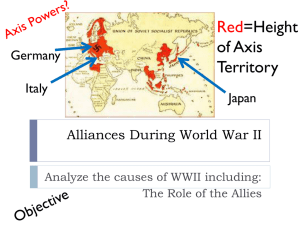
The Role of The Allies-Axis vs. Allies
... 7. Does the U.S. practice neutrality with regards to the lend-lease act? Explain. ...
... 7. Does the U.S. practice neutrality with regards to the lend-lease act? Explain. ...
Causes of the Cold War
... suitors. Molotov, dressed as a woman, is reading a book entitled: 'Western political thriller'. ...
... suitors. Molotov, dressed as a woman, is reading a book entitled: 'Western political thriller'. ...
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact

The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, officially the Treaty of Non-aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, was a non-aggression pact signed between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union in Moscow on 23 August 1939. It is also known as the Ribbentrop–Molotov Pact or Nazi–Soviet Pact.The pact remained in force until the German government broke it by invading the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941.The pact's publicly stated intentions were a guarantee of non-belligerence by each party towards the other and a commitment that neither party would ally itself to or aid an enemy of the other party. In addition to stipulations of non-aggression, the treaty included a secret protocol that divided territories of Romania, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, and Finland into German and Soviet ""spheres of influence"", anticipating potential ""territorial and political rearrangements"" of these countries. Thereafter, Germany invaded Poland on 1 September 1939. After the Soviet–Japanese ceasefire agreement took effect on 16 September, Stalin ordered his own invasion of Poland on 17 September. Part of southeastern (Karelia) and Salla region in Finland were annexed by the Soviet Union after the Winter War. This was followed by Soviet annexations of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and parts of Romania (Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina, and the Hertza region). Concern about ethnic Ukrainians and Belarusians had been proffered as the reason for the Soviet invasion of Poland.Of the territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union between 1939 and 1940, the region around Białystok and a minor part of Galicia east of the San river around Przemyśl were returned to the Polish state at the end of World War II. Of all other territories annexed by the USSR in 1939–40, the ones detached from Finland (Karelia, Petsamo), Estonia (Ingrian area and Petseri County) and Latvia (Abrene) remained part of the Russian Federation, the successor state of the Soviet Union, after 1991. Northern Bukovina, Southern Bessarabia and Hertza remain part of Ukraine.The existence of the secret protocol was denied by Soviet leadership until 1989, when it was acknowledged and denounced. Some time afterwards the Russian historiography has been inclined to describe the pact as a necessary measure. This includes books by Alexander Dyukov, and one edited by N.A. Narochnitskaya that carries an approving foreword by Russian foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov. Vladimir Putin has defended the pact as well.