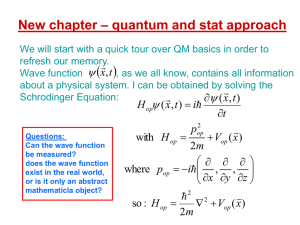
quantum and stat approach
... Therefore, the cn coefficients are often called the “probability amplitudes” *There are some special situations in which it is possible to predict the outcome of a QM measurement – can you think of an example? ...
... Therefore, the cn coefficients are often called the “probability amplitudes” *There are some special situations in which it is possible to predict the outcome of a QM measurement – can you think of an example? ...
Chapter 8 The quantum theory of motion
... Classical mechanics It is impossible for a particle to surmount over a barrier with potential energy high than its kinetic energy. Quantum mechanics If the barrier is thin and the barrier energy is not infinite, particles have the probability to penetrate into the potential region forbidden by class ...
... Classical mechanics It is impossible for a particle to surmount over a barrier with potential energy high than its kinetic energy. Quantum mechanics If the barrier is thin and the barrier energy is not infinite, particles have the probability to penetrate into the potential region forbidden by class ...
The Quantum Numbers
... If two negatively charged particles occupy the same orbital, how do they keep from repelling one another? It is possible the electrons spin in opposite directions and therefore, produce opposite magnetic fields that attract rather than repel one another. Scientist refer to these possible spins as (+ ...
... If two negatively charged particles occupy the same orbital, how do they keep from repelling one another? It is possible the electrons spin in opposite directions and therefore, produce opposite magnetic fields that attract rather than repel one another. Scientist refer to these possible spins as (+ ...
Learning station X: Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) - Quantum Spin-off
... Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes. ...
... Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes. ...
1 Classical mechanics vs. quantum mechanics - Assets
... relationship between C(x, t) and C(px, t), much as that between "(t) and "(!). Either representation will eventually lead to the same results for experimentally measurable properties, or the ‘‘observables,’’ of the system. Thus, as far as interpreting experimental results goes, it makes no differenc ...
... relationship between C(x, t) and C(px, t), much as that between "(t) and "(!). Either representation will eventually lead to the same results for experimentally measurable properties, or the ‘‘observables,’’ of the system. Thus, as far as interpreting experimental results goes, it makes no differenc ...
Employing of quantum chemical methods for calculations of
... calculated data (e.g. enthalpy of formation, entropy and Gibbs (free) energies) is one possible way for objective choice of quantum-chemical methods. The comparison of experimental and calculated values of thermodynamic functions is analyzed in this report. The abilities of the various theoretical m ...
... calculated data (e.g. enthalpy of formation, entropy and Gibbs (free) energies) is one possible way for objective choice of quantum-chemical methods. The comparison of experimental and calculated values of thermodynamic functions is analyzed in this report. The abilities of the various theoretical m ...
Document
... Any pure state of a spin-1/2 (or a photon) can be represented as a point on the surface of the sphere – it is parametrized by a single amplitude and a single relative phase. This is the same as the description of a classical spin, or the polarisation (Stokes parameters) of a classical light field. O ...
... Any pure state of a spin-1/2 (or a photon) can be represented as a point on the surface of the sphere – it is parametrized by a single amplitude and a single relative phase. This is the same as the description of a classical spin, or the polarisation (Stokes parameters) of a classical light field. O ...
Quantum Mechanics - UCSD Department of Physics
... Quantum Wavelength • Every particle or system of particles can be defined in quantum mechanical terms – and therefore have wave-like properties ...
... Quantum Wavelength • Every particle or system of particles can be defined in quantum mechanical terms – and therefore have wave-like properties ...
Electron Configurations
... probably didn’t have much trouble with these concepts. Otherwise, you may want some extra information on the subject. Most of this below is “borrowed” from Sparknotes.com. The first and most important rule to remember when attempting to determine how electrons will be arranged in the atom is Hund’s ...
... probably didn’t have much trouble with these concepts. Otherwise, you may want some extra information on the subject. Most of this below is “borrowed” from Sparknotes.com. The first and most important rule to remember when attempting to determine how electrons will be arranged in the atom is Hund’s ...
Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics
... with quantum-enhanced measurements, such as with squeezed states of light, and by controlling interactions. FrPNC experiment: We are part of a collaboration at the TRIUMF accelerator (Canada) to measure parity violation and the nuclear anapole moment in laser cooled francium. ...
... with quantum-enhanced measurements, such as with squeezed states of light, and by controlling interactions. FrPNC experiment: We are part of a collaboration at the TRIUMF accelerator (Canada) to measure parity violation and the nuclear anapole moment in laser cooled francium. ...
Doctoral Programmes in Physics at IMSc
... • Fundamentals of Quantum Theory: The breakdown of classical physics, the polarization of photons, Wave-particle duality: Particle properties of photons and wave properties of electrons, Schrodinger evolution, Hamiltonian, examples: free particle, one-dimensional potential well, potential barrier, h ...
... • Fundamentals of Quantum Theory: The breakdown of classical physics, the polarization of photons, Wave-particle duality: Particle properties of photons and wave properties of electrons, Schrodinger evolution, Hamiltonian, examples: free particle, one-dimensional potential well, potential barrier, h ...
Quantum Game Theory
... Even with an EOM eg. SE or DE and the initial conditions, it’s possible to end up with a probabilistic outcome. ...
... Even with an EOM eg. SE or DE and the initial conditions, it’s possible to end up with a probabilistic outcome. ...
SEQUENTIALLY INDEPENDENT EFFECTS 1. Introduction
... This last equation practically never holds and is rarely considered. Notice also that stochastic independence is a symmetric relation in classical probability while it is not in quantum probability. The main goal of this paper is the study of sequentially independent quantum effects. An effect corre ...
... This last equation practically never holds and is rarely considered. Notice also that stochastic independence is a symmetric relation in classical probability while it is not in quantum probability. The main goal of this paper is the study of sequentially independent quantum effects. An effect corre ...
quantum mechanical model
... Orbital Energy: The amount of energy associated with an electron in a particular orbital. Quantum Number: A number describing a property of an electron. Principal (n): Describes the principal energy level of the electron. Aizmuthal (l): Describes the shape of the electron orbital (s: l=0, p: l=1, d: ...
... Orbital Energy: The amount of energy associated with an electron in a particular orbital. Quantum Number: A number describing a property of an electron. Principal (n): Describes the principal energy level of the electron. Aizmuthal (l): Describes the shape of the electron orbital (s: l=0, p: l=1, d: ...
How the Quantum Universe Became Classical
... systems are affected as a result of being measured. Suppose, for example, the quantum state of the system is a superposition state in which a single particle is localized about two different positions, as in Figure 1. If we perform a measurement which asks whether the particle is in a certain region ...
... systems are affected as a result of being measured. Suppose, for example, the quantum state of the system is a superposition state in which a single particle is localized about two different positions, as in Figure 1. If we perform a measurement which asks whether the particle is in a certain region ...
HW 12 - stKFUPM
... A Nobel Laureate (Chemistry & Peace) who used the shell model greatly in his teaching and research is ...
... A Nobel Laureate (Chemistry & Peace) who used the shell model greatly in his teaching and research is ...























