Removal of hydrogen fluoride from gas streams
... I would like to thank my supervisors, Professor N. J. Coville, University of Witwatersrand and Dr. P. A. B. Carstens, South African Nuclear Energy Corporation Limited (Necsa) for their support, suggestions and guidance. ...
... I would like to thank my supervisors, Professor N. J. Coville, University of Witwatersrand and Dr. P. A. B. Carstens, South African Nuclear Energy Corporation Limited (Necsa) for their support, suggestions and guidance. ...
Document
... isotope abundances (especially differences in natural abundance) e.g. Carbon 0 ‰ = 1.1057 atom% 13C 5 ‰ = 1.1111 atom% 13C ...
... isotope abundances (especially differences in natural abundance) e.g. Carbon 0 ‰ = 1.1057 atom% 13C 5 ‰ = 1.1111 atom% 13C ...
Lactose/D-Galactose
... time to time. For clarification, add 5 ml of Carrez-I-solution (3.60 g potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), K4[Fe(CN)6] × 3 H2O/100 ml), 5 ml of Carrez-II-solution (7.20 g of zinc sulfate, ZnSO4 × 7 H2O/100 ml) and 10 ml of NaOH (0.1 M); mix after each addition, adjust to 20-25°C and fill up to the mark ...
... time to time. For clarification, add 5 ml of Carrez-I-solution (3.60 g potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), K4[Fe(CN)6] × 3 H2O/100 ml), 5 ml of Carrez-II-solution (7.20 g of zinc sulfate, ZnSO4 × 7 H2O/100 ml) and 10 ml of NaOH (0.1 M); mix after each addition, adjust to 20-25°C and fill up to the mark ...
Lactose/D-Galactose
... time to time. For clarification, add 5 ml of Carrez-I-solution (3.60 g potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), K4[Fe(CN)6] × 3 H2O/100 ml), 5 ml of Carrez-II-solution (7.20 g of zinc sulfate, ZnSO4 × 7 H2O/100 ml) and 10 ml of NaOH (0.1 M); mix after each addition, adjust to 20-25°C and fill up to the mark ...
... time to time. For clarification, add 5 ml of Carrez-I-solution (3.60 g potassium hexacyanoferrate(II), K4[Fe(CN)6] × 3 H2O/100 ml), 5 ml of Carrez-II-solution (7.20 g of zinc sulfate, ZnSO4 × 7 H2O/100 ml) and 10 ml of NaOH (0.1 M); mix after each addition, adjust to 20-25°C and fill up to the mark ...
Isotopes of Volatile Organic Compounds: An Emerging Approach for
... processes have distinctly different isotopic signatures.4,5 So far, 13C/12C is the only stable isotope system which has been used in published studies of VOCs in the ambient atmosphere.1,3,5-14 However, source or sink characterizations have been done for a wider set of isotope pairs, including 2H/1H ...
... processes have distinctly different isotopic signatures.4,5 So far, 13C/12C is the only stable isotope system which has been used in published studies of VOCs in the ambient atmosphere.1,3,5-14 However, source or sink characterizations have been done for a wider set of isotope pairs, including 2H/1H ...
ХИМИЯ НА АНГЛИЙСКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ
... 1.38. A standard solution of Mn2+ was prepared by dissolving 0.250 g of Mn in 10 mL of concentrated HNO3 (measured with a graduated cylinder). The resulting solution was quantitatively transferred to a 100-mL volumetric flask and diluted to volume with distilled water. A 10-mL aliquot of the soluti ...
... 1.38. A standard solution of Mn2+ was prepared by dissolving 0.250 g of Mn in 10 mL of concentrated HNO3 (measured with a graduated cylinder). The resulting solution was quantitatively transferred to a 100-mL volumetric flask and diluted to volume with distilled water. A 10-mL aliquot of the soluti ...
radiometric dating - Tulane University
... Prior to 1905 the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the Earth to cool to its present temperature from a completely liquid state. Although we now recognize lots of problems with that calculation, the age of 25 my was acc ...
... Prior to 1905 the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the Earth to cool to its present temperature from a completely liquid state. Although we now recognize lots of problems with that calculation, the age of 25 my was acc ...
Unit 2 Lesson 3
... • The type of isotope used depends on the type of material being dated. • The half-life of the isotope used is also very important. It can’t be too short or too long compared to the age of the sample. ...
... • The type of isotope used depends on the type of material being dated. • The half-life of the isotope used is also very important. It can’t be too short or too long compared to the age of the sample. ...
Lab 77 Nuclear Radiation Detection
... of mass equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an isotope called carbon-12. An atomic mass unit is equal to 1.6605 x 10-27 kilograms, and is specified by the letter u. Isotopes of certain elements are unstable and therefore are in a process of decay. As they decay they emit unseen radiations. This phen ...
... of mass equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an isotope called carbon-12. An atomic mass unit is equal to 1.6605 x 10-27 kilograms, and is specified by the letter u. Isotopes of certain elements are unstable and therefore are in a process of decay. As they decay they emit unseen radiations. This phen ...
Radiometric Dating - Tulane University
... breathing, feeding, and photosynthesis. Thus, so long as the organism is alive, it will have the same ratio of 14C to 14N as the atmosphere. ...
... breathing, feeding, and photosynthesis. Thus, so long as the organism is alive, it will have the same ratio of 14C to 14N as the atmosphere. ...
Practice Exam I solutions
... of nitrate in drinking water samples. Both labs were given a National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standard to analyze and results of 5 measurements by each lab are shown below. Shaky Hands Testing: 3.50, 3.57, 3.38, 3.47, 3.41 ppm High Accuracy, Inc.: 3.23, 3.21, 3.29, 3.30, 3.24 pp ...
... of nitrate in drinking water samples. Both labs were given a National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standard to analyze and results of 5 measurements by each lab are shown below. Shaky Hands Testing: 3.50, 3.57, 3.38, 3.47, 3.41 ppm High Accuracy, Inc.: 3.23, 3.21, 3.29, 3.30, 3.24 pp ...
TANNIC ACID
... sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate only to hydrolysable gallotannins, i.e., those which yield gallic acid on hyd ...
... sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate only to hydrolysable gallotannins, i.e., those which yield gallic acid on hyd ...
Effects of antioxidants for the degradation of flame
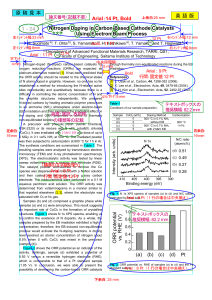
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
... 6 MGy in 0.1 vol% NH3 at 500 °C. The irradiated powder was then subjected to carbonization at 800 °C for 1 h in Ar. The synthesis conditions are summarized in Table 1. The resulting samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The electr ...
2013 Q9 - Loreto Balbriggan
... Iodine–131 decays with the emission of a beta-particle and has a half-life of 8 days. Write an equation for the beta-decay of iodine–131. Estimate the fraction of the iodine–131 that remained after 40 days. (15) Caesium–137 has a half-life of 30 years and it remains a significant contaminant in the ...
... Iodine–131 decays with the emission of a beta-particle and has a half-life of 8 days. Write an equation for the beta-decay of iodine–131. Estimate the fraction of the iodine–131 that remained after 40 days. (15) Caesium–137 has a half-life of 30 years and it remains a significant contaminant in the ...
4550-15Lecture29 - Cornell Geological Sciences
... Cosmogenic Nuclides • Cosmic rays are high energy nuclei (mainly of H and He) from space. When they collide with nuclei in the atmosphere or the surface of the Earth, they induce nuclear reactions. The resulting particles also have high energies and can induce further reactions. The one of greatest ...
... Cosmogenic Nuclides • Cosmic rays are high energy nuclei (mainly of H and He) from space. When they collide with nuclei in the atmosphere or the surface of the Earth, they induce nuclear reactions. The resulting particles also have high energies and can induce further reactions. The one of greatest ...
Lecture 33 - Cornell Geological Sciences
... Cosmogenic Nuclides • Cosmic rays are high energy nuclei (mainly of H and He) from space. When they collide with nuclei in the atmosphere or the surface of the Earth, they induce nuclear reactions. The resulting particles also have high energies and can induce further reactions. The one of greatest ...
... Cosmogenic Nuclides • Cosmic rays are high energy nuclei (mainly of H and He) from space. When they collide with nuclei in the atmosphere or the surface of the Earth, they induce nuclear reactions. The resulting particles also have high energies and can induce further reactions. The one of greatest ...
lect6_geomorphology
... 5730 year ½ life Useful between 100 and about 50,000 years old Can date things that contain organic carbon (Used to be living): bones, shells, wood, charcoal, plants, paper, cloth, pollen, seeds) ...
... 5730 year ½ life Useful between 100 and about 50,000 years old Can date things that contain organic carbon (Used to be living): bones, shells, wood, charcoal, plants, paper, cloth, pollen, seeds) ...
Geologic Dating! - rgreenbergscience
... lowest layer is the oldest, the top most layer, the most recent (youngest). These are called “strata”. • Stratification: enables a scientist to establish the “relative age” of something based on where it is found compared to other layers. • Relative Dating – estimating the age of a fossil by compari ...
... lowest layer is the oldest, the top most layer, the most recent (youngest). These are called “strata”. • Stratification: enables a scientist to establish the “relative age” of something based on where it is found compared to other layers. • Relative Dating – estimating the age of a fossil by compari ...
Radiocarbon dating
... radiocarbon dating is to estimate the age of organic remains from archaeological sites. • When plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic material during photosynthesis they incorporate a quantity of 14C that approximately matches the level of this isotope in the atmosphere. After plan ...
... radiocarbon dating is to estimate the age of organic remains from archaeological sites. • When plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into organic material during photosynthesis they incorporate a quantity of 14C that approximately matches the level of this isotope in the atmosphere. After plan ...