Stars - HMXEarthScience
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
View the sky`s greatest nebula
... lies roughly 10' north of M42. This section features a hot, bright star (center) that is ionizing the gas near it. This creates a sphere of glowing hydrogen, which appears pink. This image was shot through a 20-inch RC Optical Systems RitcheyChrétien telescope at f/8.4 with an SBIG ST10XME CCD camer ...
... lies roughly 10' north of M42. This section features a hot, bright star (center) that is ionizing the gas near it. This creates a sphere of glowing hydrogen, which appears pink. This image was shot through a 20-inch RC Optical Systems RitcheyChrétien telescope at f/8.4 with an SBIG ST10XME CCD camer ...
March
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
Investigation 1 Solar Nebula Theory Student Guide 3_16_13_draft
... above in order to make stars and planets. But scientists are not satisfied with speculation that this simply seems to make sense. Astronomers want to see more direct visual evidence that the ideas outlined above are actually occurring. Shown in the following sequence of images are examples various s ...
... above in order to make stars and planets. But scientists are not satisfied with speculation that this simply seems to make sense. Astronomers want to see more direct visual evidence that the ideas outlined above are actually occurring. Shown in the following sequence of images are examples various s ...
CAPSTONE-poster
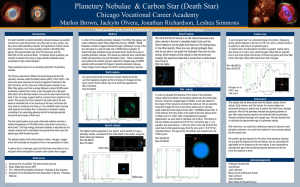
... Our team decided to explore planetary nebulae because we wanted to know how were they formed, why they had so many colors, why they were called planetary nebulae, the significance of their names, their composition, how many possibly existed in the Milky Way galaxy, their approximate age, their first ...
... Our team decided to explore planetary nebulae because we wanted to know how were they formed, why they had so many colors, why they were called planetary nebulae, the significance of their names, their composition, how many possibly existed in the Milky Way galaxy, their approximate age, their first ...
Powerpoint for today
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
Star Cycle2013
... is an explosion _____________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
... is an explosion _____________ that marks the end of a very massive star’s life. When it occurs, the exploding star can outshine all of the other stars in the galaxy in total for several days and may leave behind only a crushed core. ...
Guess The Spectra!!
... emitted from the central star. The Ring Nebula has spectral lines from Hydrogen, Helium, and Oxygen! ...
... emitted from the central star. The Ring Nebula has spectral lines from Hydrogen, Helium, and Oxygen! ...
Lecture 13 - Star Formation
... • Gas is mainly hydrogen, but also contains other elements and molecules. • Density is typically around 1 atom per cubic centimeter. ...
... • Gas is mainly hydrogen, but also contains other elements and molecules. • Density is typically around 1 atom per cubic centimeter. ...
mass of star
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
Outline - March 16, 2010 Interstellar Medium (ISM) Why should you
... formation. Most likely link of rotation and outflowing gas are magnetic field lines. We’ll see this again when we talk about “active galaxies”. ...
... formation. Most likely link of rotation and outflowing gas are magnetic field lines. We’ll see this again when we talk about “active galaxies”. ...
33-3 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... This object is a very faint planetary nebula but it’s BIG. The outer circumference is about 25 arc minutes, so it fills up a large portion of my field of view. Compared to other planetary nebulae, it’s only 700 light-years from Earth! There are no really bright stars close to the Helix. When I first ...
... This object is a very faint planetary nebula but it’s BIG. The outer circumference is about 25 arc minutes, so it fills up a large portion of my field of view. Compared to other planetary nebulae, it’s only 700 light-years from Earth! There are no really bright stars close to the Helix. When I first ...
INTERSTELLAR MedLab
... Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study the interstellar medium – where stars are formed and into which the ste ...
... Dark – high densities of dust and gas that redden or extinct the light from the stars located behind the cloud. These are also where molecules are likely to be found. During the course of this laboratory exercise, you will study the interstellar medium – where stars are formed and into which the ste ...
Study Guide for Stars and Galaxies Quiz ANSWER KEY
... 3. What is a lightyear? The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. 4. Define and describe parallax. Why is it useful for only nearby stars? The apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places. Astronomers can use parallax to mea ...
... 3. What is a lightyear? The distance that light travels in one year, about 9.5 million million kilometers. 4. Define and describe parallax. Why is it useful for only nearby stars? The apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places. Astronomers can use parallax to mea ...
hubble amazing universe worksheet
... green is ___________________. 8. This region is _____________ light years across! 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in _____ ...
... green is ___________________. 8. This region is _____________ light years across! 9. Hubble even showed a star about to die! As a star runs out of ______________, it expands, and it is released into space. 10. Someday, our own star will expand and engulf the earth. Luckily, this will happen in _____ ...
Slide 1
... core dies, gravity crushes down, but it crushes even harder than electron degeneracy pressure. As the electrons overlap, they merge with the protons to turn into neutrons. The neutrons all crush together, at which point their neutron pressure is enough to stop the collapse from gravity. ...
... core dies, gravity crushes down, but it crushes even harder than electron degeneracy pressure. As the electrons overlap, they merge with the protons to turn into neutrons. The neutrons all crush together, at which point their neutron pressure is enough to stop the collapse from gravity. ...
Winter Stargazing - Trimble County Schools
... • The most famous and beautiful star cluster is just north of Taurus. • The brightest of these bluish stars are perfectly visible to the unaided eye. • All the stars in Pleiades were born about the same time, about 70 Million years ago. ...
... • The most famous and beautiful star cluster is just north of Taurus. • The brightest of these bluish stars are perfectly visible to the unaided eye. • All the stars in Pleiades were born about the same time, about 70 Million years ago. ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... young star cluster near its center. The dust lanes appear dark because they obscure visible light, and are thus seen in silhouette against the brighter, glowing, hydrogen gas. Surrounding the red nebula is a blue reflection nebula, especially bright at northern end. The reflection nebula glows by re ...
... young star cluster near its center. The dust lanes appear dark because they obscure visible light, and are thus seen in silhouette against the brighter, glowing, hydrogen gas. Surrounding the red nebula is a blue reflection nebula, especially bright at northern end. The reflection nebula glows by re ...
11/17/2011 1 Ch. 27 Notes: Nebular Hypothesis The Nebular
... • A rotating cloud of gas and dust condensed to form the sun and surrounding planets. ...
... • A rotating cloud of gas and dust condensed to form the sun and surrounding planets. ...
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) - Sunshine Coast Centre RASC
... Other astronomers had looked at the data and missed the signal. Joceyln Bell, the grad student who found it, had found a pulsar, the first observational evidence for neutron stars. Fortuitously, the signals of quasars and pulsars could both be detected by the same antennae Her supervisor, Anthony He ...
... Other astronomers had looked at the data and missed the signal. Joceyln Bell, the grad student who found it, had found a pulsar, the first observational evidence for neutron stars. Fortuitously, the signals of quasars and pulsars could both be detected by the same antennae Her supervisor, Anthony He ...
bYTEBoss lesson 3 life of star
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
... The end of the life cycle of really massive stars is different to that of massive stars. After a really massive red giant collapses in a supernova explosion, it leaves a star so dense that not even light can escape its gravitational pull. This is called a black hole! Some scientists believe that the ...
Powerpoint
... when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force (remember, stars are ~1020 x denser than a molecular cloud). As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense ...
... when part of a dust cloud begins to contract under its own gravitational force (remember, stars are ~1020 x denser than a molecular cloud). As it collapses, the center becomes hotter and hotter until nuclear fusion begins in the core. Probably new molecular clouds form continually out of less dense ...
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
... photons, a process called damping. In the case of NGC 40 the central star is a high temperature object with a spectral type of WC 8, so it is likely that this is a high density object. My main interest here though is not in the planetary nebula itself but in the strange loop of gas seen in the image ...
... photons, a process called damping. In the case of NGC 40 the central star is a high temperature object with a spectral type of WC 8, so it is likely that this is a high density object. My main interest here though is not in the planetary nebula itself but in the strange loop of gas seen in the image ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
... Gas in which H is atomic. Fills much (most?) of interstellar space. Density ~1 atom / cm3. Too cold (~100 K) to give optical emission lines. Primarily observed through radiation of H at wavelength of 21 cm. H I accounts for almost half the mass in the ISM: ~2 x 109 MSun ! ...
Orion Nebula

The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of 1,344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light years across. It has a mass of about 2000 times the mass of the Sun. Older texts frequently refer to the Orion Nebula as the Great Nebula in Orion or the Great Orion Nebula.The Orion Nebula is one of the most scrutinized and photographed objects in the night sky, and is among the most intensely studied celestial features. The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarfs, intense and turbulent motions of the gas, and the photo-ionizing effects of massive nearby stars in the nebula.