AST4930 Star and Planet Formation
... the actual fraction of stars in multiple systems, its variation with stellar mass (e.g., massive stars more likely to be in multiple systems than low-mass stars), and the companion mass distribution. “stellar IMF” – corrected for multiplicity ...
... the actual fraction of stars in multiple systems, its variation with stellar mass (e.g., massive stars more likely to be in multiple systems than low-mass stars), and the companion mass distribution. “stellar IMF” – corrected for multiplicity ...
Discovering Planetary Nebula Geometries: Explorations with a
... Astronomical objects known as planetary nebulae (PNe) consist of a shell of gas expelled by an aging star. In cases where the gas shell can be assumed to be ellipsoidal, the PN can be easily modeled in three spatial dimensions. We utilize a model that joins the physics of PNe to this geometry and ge ...
... Astronomical objects known as planetary nebulae (PNe) consist of a shell of gas expelled by an aging star. In cases where the gas shell can be assumed to be ellipsoidal, the PN can be easily modeled in three spatial dimensions. We utilize a model that joins the physics of PNe to this geometry and ge ...
ref evlution of stars
... formation of this type, with a mass 100 to 1,000,000 times that of the Sun, a diameter of 15 to 60 parsec and a temperature of up to 10 K. Molecular clouds can contain more than 60 kinds of molecules. ...
... formation of this type, with a mass 100 to 1,000,000 times that of the Sun, a diameter of 15 to 60 parsec and a temperature of up to 10 K. Molecular clouds can contain more than 60 kinds of molecules. ...
Major Stars of the Orion Constellation
... We start our comparison of major Orion stars by describing Alpha Orionis, Betelgeuse, which forms Orion’s right shoulder. It’s actually fainter than Beta Orionis (Rigel) due to a misclassification error as Betelgeuse was found to be a variable star. [Wiscweb] “Astronomers now know that these regula ...
... We start our comparison of major Orion stars by describing Alpha Orionis, Betelgeuse, which forms Orion’s right shoulder. It’s actually fainter than Beta Orionis (Rigel) due to a misclassification error as Betelgeuse was found to be a variable star. [Wiscweb] “Astronomers now know that these regula ...
... The temperature range over which the growth occurred is about 100 oC, so Meibom was able to calculate a cooling rate for the portion of the nebula in which the metal grains grew. By dividing the temperature interval (100 oC) by the growth time (19 days, or 456 hours), he found a cooling rate of 0.2 ...
M - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... mass distribution of molecular cloud core masses. Measurements of the absolute magnitude of the stars in the solar neighborhood revealed a preponderance of large magnitudes, I.e., faint low-mass stars. This is due to the long main-sequence lifetimes of low-mass stars and to the seeming preference fo ...
... mass distribution of molecular cloud core masses. Measurements of the absolute magnitude of the stars in the solar neighborhood revealed a preponderance of large magnitudes, I.e., faint low-mass stars. This is due to the long main-sequence lifetimes of low-mass stars and to the seeming preference fo ...
Diapositiva 1
... The spectra of two nebulous objects near NGC 1999 (ApJ 113, 697). On a series of direct photographs taken with the Crosslyer reflector in 1946 and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1 ...
... The spectra of two nebulous objects near NGC 1999 (ApJ 113, 697). On a series of direct photographs taken with the Crosslyer reflector in 1946 and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1 ...
East Valley Astronomy Club
... New models of the “minimum mass solar nebula” show the nebula really was very dense, but this structure is only understood if the disk was photoevaporating because of a nearby massive star. Meteorites show the Solar System contained live 60Fe, almost certainly ejected by a nearby massive star that w ...
... New models of the “minimum mass solar nebula” show the nebula really was very dense, but this structure is only understood if the disk was photoevaporating because of a nearby massive star. Meteorites show the Solar System contained live 60Fe, almost certainly ejected by a nearby massive star that w ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... progressed to the element, Iron, all fusion stopped, gravity took over, and in seconds, the star collapsed into a sphere approximately 10 km across. The blast destroyed the star and spewed its remains outward into deep space at a velocity of several thousand kilometers per second. The long streamers ...
... progressed to the element, Iron, all fusion stopped, gravity took over, and in seconds, the star collapsed into a sphere approximately 10 km across. The blast destroyed the star and spewed its remains outward into deep space at a velocity of several thousand kilometers per second. The long streamers ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... 7293), a well studied and nearby example of a Planetary Nebula, typical of this final phase of stellar evolution for a solar mass star. ...
... 7293), a well studied and nearby example of a Planetary Nebula, typical of this final phase of stellar evolution for a solar mass star. ...
Helium Fusion What Will Happen When There Is No More Helium in
... Electron degeneracy pressure balances inward crush of its own gravity Very high density and hence gravity Maximum mass=1.4 Msun (Chandrasekar limit) ...
... Electron degeneracy pressure balances inward crush of its own gravity Very high density and hence gravity Maximum mass=1.4 Msun (Chandrasekar limit) ...
What do “yellowballs” have to do with the birth of new stars?
... wind moves at velocities of several hundred kilometers/second. ...
... wind moves at velocities of several hundred kilometers/second. ...
Lecture 10: Interstellar gas
... connected to H II regions; (e.g. Orion nebula). The number densities in such clouds are estimated as 109 to 1012 H2 molecules/m3, other molecules are, far less abundant although more readily observed. The cloud temperature are low, usually 10 to 30 K and sometimes as high as 100 K. We can not observ ...
... connected to H II regions; (e.g. Orion nebula). The number densities in such clouds are estimated as 109 to 1012 H2 molecules/m3, other molecules are, far less abundant although more readily observed. The cloud temperature are low, usually 10 to 30 K and sometimes as high as 100 K. We can not observ ...
theh – rdiagramsofyoungclust ersandtheformati on ofp
... to the present radius of pluto's orbit, and its mass ten times the present mass of the planetary system, hence the density of the solar nebula at that stage was 2.5 X 10-14 gm/cm3. As the dust follows the motion of the gas, its concentration in the solar nebula was increased accordingly in relation ...
... to the present radius of pluto's orbit, and its mass ten times the present mass of the planetary system, hence the density of the solar nebula at that stage was 2.5 X 10-14 gm/cm3. As the dust follows the motion of the gas, its concentration in the solar nebula was increased accordingly in relation ...
Lecture6
... (ii) Star Formation – Protostars and Birth (Main Ref.: Lecture notes; FK Sec. 18-3 to 8; CD photos shown in class) • As already noted in Section (i), the interstellar matter (ISM) is not uniform, but clumpy. New stars are formed in these clumpy, cool, dense clouds called `dark nebulae’ in or near m ...
... (ii) Star Formation – Protostars and Birth (Main Ref.: Lecture notes; FK Sec. 18-3 to 8; CD photos shown in class) • As already noted in Section (i), the interstellar matter (ISM) is not uniform, but clumpy. New stars are formed in these clumpy, cool, dense clouds called `dark nebulae’ in or near m ...
1705 Star Charts
... around 10 billion years old, twice the age of the sun. Omega Centauri is the biggest of the hundred-odd globulars randomly orbiting our galaxy. It may originally have been the core of a small galaxy that collided with the Milky Way and was stripped of its outer stars. 47 Tucanae, by the SMC, is a si ...
... around 10 billion years old, twice the age of the sun. Omega Centauri is the biggest of the hundred-odd globulars randomly orbiting our galaxy. It may originally have been the core of a small galaxy that collided with the Milky Way and was stripped of its outer stars. 47 Tucanae, by the SMC, is a si ...
Winter 2014
... brightest, Betelgeuse, has a reddish cast. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant and glows orange-red because its surface is actually cooler than the surfaces of most other stars we see in the night sky. Having exhausted the hydrogen fuel in its core, someday Betelgeuse will explode in a brilliant supernov ...
... brightest, Betelgeuse, has a reddish cast. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant and glows orange-red because its surface is actually cooler than the surfaces of most other stars we see in the night sky. Having exhausted the hydrogen fuel in its core, someday Betelgeuse will explode in a brilliant supernov ...
MESSIER - EarthLink
... His first own deep sky discovery of globular cluster M3, cataloged on May 3, probably causes him to undertake a systematical search for nebulous objects, leading to the observation and recording of the objects M3-M40, many of which were own discoveries, but several from old catalogs. Messier was mad ...
... His first own deep sky discovery of globular cluster M3, cataloged on May 3, probably causes him to undertake a systematical search for nebulous objects, leading to the observation and recording of the objects M3-M40, many of which were own discoveries, but several from old catalogs. Messier was mad ...
January 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... As well as being one of the most spectacular and A star like our Sun will fuse Hydrogen into Helium and beautiful constellations, Orion is also very interesting towards the end of its life will begin to fuse some of the because we can see evidence of all the stages of the life Helium. A larger star ...
... As well as being one of the most spectacular and A star like our Sun will fuse Hydrogen into Helium and beautiful constellations, Orion is also very interesting towards the end of its life will begin to fuse some of the because we can see evidence of all the stages of the life Helium. A larger star ...
The Interstellar Medium
... reflection nebulae appear blue because blue light is scattered by larger angles than red light; the same phenomenon makes the day sky appear blue (if it’s not cloudy). ...
... reflection nebulae appear blue because blue light is scattered by larger angles than red light; the same phenomenon makes the day sky appear blue (if it’s not cloudy). ...
Star Formation
... • Supernova blast waves near clouds can initiate star formation (happened for our own sun, from SNe produced radioactive daughter products in meteorites) • Collapse raises density, core cannot radiate away heat gravitational collapse heat fast enough, and temp rises, until H fusion begins at 10 mill ...
... • Supernova blast waves near clouds can initiate star formation (happened for our own sun, from SNe produced radioactive daughter products in meteorites) • Collapse raises density, core cannot radiate away heat gravitational collapse heat fast enough, and temp rises, until H fusion begins at 10 mill ...
nebula - Harding University
... Similar features have been recently observe with the Hubble Space Telescope. In the slide that follows, the knobby jets of material appears to be emitted along the polar axes of the star in what is called bi-polar outflow. These small nebula are known as Herbig-Haro objects. Such young, gas-ejecting ...
... Similar features have been recently observe with the Hubble Space Telescope. In the slide that follows, the knobby jets of material appears to be emitted along the polar axes of the star in what is called bi-polar outflow. These small nebula are known as Herbig-Haro objects. Such young, gas-ejecting ...
20 pm - Starmap
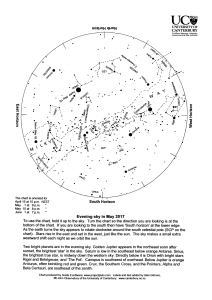
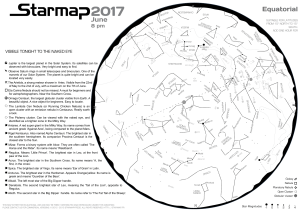
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... ...
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... ...
Orion Nebula

The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of 1,344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light years across. It has a mass of about 2000 times the mass of the Sun. Older texts frequently refer to the Orion Nebula as the Great Nebula in Orion or the Great Orion Nebula.The Orion Nebula is one of the most scrutinized and photographed objects in the night sky, and is among the most intensely studied celestial features. The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarfs, intense and turbulent motions of the gas, and the photo-ionizing effects of massive nearby stars in the nebula.