PDF of story and photos
... is so vast that many of its details cannot be captured in a single picture. Astronomers, therefore, used multiple images from Hubble and ground-based telescopes to see Orion’s dramatic landscape of glowing gas and dark dust. The images provide clues to the nebula’s formation and history. A perfect s ...
... is so vast that many of its details cannot be captured in a single picture. Astronomers, therefore, used multiple images from Hubble and ground-based telescopes to see Orion’s dramatic landscape of glowing gas and dark dust. The images provide clues to the nebula’s formation and history. A perfect s ...
Uranometria 2000.0`s Dark Nebulae Database
... Dark nebulae are composed of clouds of dust and gas sufficiently dense as to become opaque. They are detectable if positioned between the observer and a bright nebula or a very dense star field, against which they can be seen silhouetted. Observationally, dark nebulae are among the most difficult de ...
... Dark nebulae are composed of clouds of dust and gas sufficiently dense as to become opaque. They are detectable if positioned between the observer and a bright nebula or a very dense star field, against which they can be seen silhouetted. Observationally, dark nebulae are among the most difficult de ...
Slide 1
... The hot stars in the Nebula emit high energy photons that are absorbed by the gas. The heated gases produce an emission spectrum and the particular wavelength of the red light of the nebula is 656nm. The exact wavelength of Hydrogen. ...
... The hot stars in the Nebula emit high energy photons that are absorbed by the gas. The heated gases produce an emission spectrum and the particular wavelength of the red light of the nebula is 656nm. The exact wavelength of Hydrogen. ...
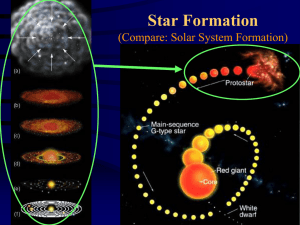
The Life of a Star
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
... a red super giant. After this stage things become more violent. Instead of gentle billowing gas shells being ejected into space (a planetary nebula) the red super giant tears itself apart in an unbelievably violent explosion called a supernova. As the radiation and debris clear, a neutron star emerg ...
Here - Thanet Astronomy Group
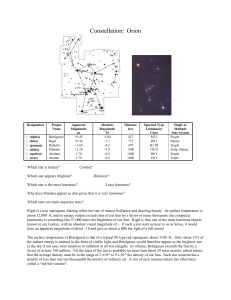
... Between and above Betelgeuse and Bellatrix you will see the star Meissa. This forms a triangle with the stars Betelgeuse and Bellatrix and marks Orion's jaw. This star is over 1055 light years away. Star Saiph At the bottom left corner of Orion, to the left of the bright star Rigal you will see the ...
... Between and above Betelgeuse and Bellatrix you will see the star Meissa. This forms a triangle with the stars Betelgeuse and Bellatrix and marks Orion's jaw. This star is over 1055 light years away. Star Saiph At the bottom left corner of Orion, to the left of the bright star Rigal you will see the ...
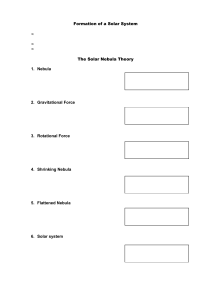
Formation of a Solar System • • • The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
... • The theory of how stars and planets form is called the solar nebula theory. • The Sun is calculated to be 5 billion years old • The Earth is calculated to be 4.6 billion years old The Solar Nebula Theory 1. Nebula Cloud of dust and gas ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... New star clusters form from the clouds of gas and dust, and these illuminate the cloud to form the visible nebula PLANETARY NEBULAE A planetary nebula is a kind of emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from old red giant stars late in their lives. GLOBULAR S ...
... New star clusters form from the clouds of gas and dust, and these illuminate the cloud to form the visible nebula PLANETARY NEBULAE A planetary nebula is a kind of emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from old red giant stars late in their lives. GLOBULAR S ...
Diapositiva 1
... Halo of the Cat's Eye Machine with which the photo has been taken: Nordic Optical Telescope. Explanation: The Cat’s Eye Nebula (NGC 6543) is one of the best known planetary nebulae in the sky. Its haunting symmetries are seen in the very central region of this stunning false-color picture, processe ...
... Halo of the Cat's Eye Machine with which the photo has been taken: Nordic Optical Telescope. Explanation: The Cat’s Eye Nebula (NGC 6543) is one of the best known planetary nebulae in the sky. Its haunting symmetries are seen in the very central region of this stunning false-color picture, processe ...
Astronomy Tour
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
solar system
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
... The Great Nebula (M42) in the constellation Orion, 1,600 light-years from the earth, consists of bright and dark masses of gas and dust where stars are in the process of being born. e. Ronald Royer/Science Source/Photo Researchers, Inc.[1] [1]"Orion Nebula," Microsoft® Encarta® Encyclopedia 2000. © ...
observingnebulaeclusters-1
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
... above the critical limit required for stars to form within the nebula. Visible to the naked eye as the middle "star" in the "sword" of the constellation Orion, the nebula is located 1500 light years from Earth. A closer image taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 aboard the Hubble Space Teles ...
Eagle Nebula - Amazing Space
... Fast Facts Age The Eagle Nebula is two million years old, the EGGs will live for another 1020,000 years. Location In the constellation Serpens, the Serpent, alongside the southern Milky Way Distance from Earth 7,000 light years ...
... Fast Facts Age The Eagle Nebula is two million years old, the EGGs will live for another 1020,000 years. Location In the constellation Serpens, the Serpent, alongside the southern Milky Way Distance from Earth 7,000 light years ...
PHYSICS 015
... not the products of the nuclear reactions deep within the core! It is almost pure H + He. The escaping material eventually merges into the interstellar medium, and is available to be used in other stars that may form later. ...
... not the products of the nuclear reactions deep within the core! It is almost pure H + He. The escaping material eventually merges into the interstellar medium, and is available to be used in other stars that may form later. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
A Solar System is Born 4/29/11
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
Orion
... greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellation Orion. The linear extend of this giant cloud is well several hundreds of light years. It can be visualized by l ...
... greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellation Orion. The linear extend of this giant cloud is well several hundreds of light years. It can be visualized by l ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
Diapositiva 1
... ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that r ...
... ionizing radiation from the Trapezium stars, mostly from the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that r ...
Orion Nebula

The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of 1,344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light years across. It has a mass of about 2000 times the mass of the Sun. Older texts frequently refer to the Orion Nebula as the Great Nebula in Orion or the Great Orion Nebula.The Orion Nebula is one of the most scrutinized and photographed objects in the night sky, and is among the most intensely studied celestial features. The nebula has revealed much about the process of how stars and planetary systems are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust. Astronomers have directly observed protoplanetary disks, brown dwarfs, intense and turbulent motions of the gas, and the photo-ionizing effects of massive nearby stars in the nebula.