Compounds Power point
... That atoms are made up of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... That atoms are made up of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons The identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus ...
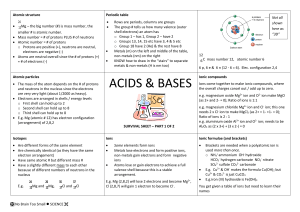
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... The group # tells us how many valence (outer shell electrons) an atom has o Group 1 – has 1, Group 2 – have 2 o Groups 13, 14, 15 etc have 3, 4 & 5 etc o Group 18 have 2 (He) & the rest have 8 Metals (m) on the left and middle of the table, non-metals (nm) on the right KNOW how to draw in the “stair ...
... The group # tells us how many valence (outer shell electrons) an atom has o Group 1 – has 1, Group 2 – have 2 o Groups 13, 14, 15 etc have 3, 4 & 5 etc o Group 18 have 2 (He) & the rest have 8 Metals (m) on the left and middle of the table, non-metals (nm) on the right KNOW how to draw in the “stair ...
Primary electrons make random elastic and inelastic collision either
... Characteristic X-ray emission is that generated by the relaxation of an excited atomic state arising from an inner shell vacancy. The transition of an electron from one of the outer shells produces an X-ray phonon with an energy (or wavelength) that represents the difference between the two states…. ...
... Characteristic X-ray emission is that generated by the relaxation of an excited atomic state arising from an inner shell vacancy. The transition of an electron from one of the outer shells produces an X-ray phonon with an energy (or wavelength) that represents the difference between the two states…. ...
Intro Biochemistry/Ecology
... Because they have the same number of protons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. The main types of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Section 2-2: Properties of Water A water molecule is polar, because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between th ...
... Because they have the same number of protons, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties. The main types of chemical bonds are covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Section 2-2: Properties of Water A water molecule is polar, because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between th ...