A Noncommutative Sigma Model by Mauritz van den Worm
... and study some of its more interesting properties, such as the fact that it can be written as a crossed product which will greatly aid us in determining its K-theory and the unique trace on the quantum torus. The final section of Chapter 1 deals with a finite dimensional representation of the quantu ...
... and study some of its more interesting properties, such as the fact that it can be written as a crossed product which will greatly aid us in determining its K-theory and the unique trace on the quantum torus. The final section of Chapter 1 deals with a finite dimensional representation of the quantu ...
mixing in quantum field theory
... 4. Neutrino oscillations In the standard QM treatment [15], the Pontecorvo states (35)–(36) are usually assumed to be produced in a charged current weak interaction process, together with the respective charged (anti-) leptons. However, as we have shown above, such states are not eigenstates of the ...
... 4. Neutrino oscillations In the standard QM treatment [15], the Pontecorvo states (35)–(36) are usually assumed to be produced in a charged current weak interaction process, together with the respective charged (anti-) leptons. However, as we have shown above, such states are not eigenstates of the ...
Decoherence of a Quantum Bit Circuit
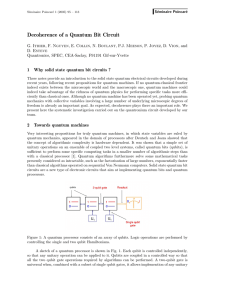
... provided by the hyperfine interaction with a bound electron around each impurity. Each qubit is controlled by applying a voltage to an A gate electrode that displaces slightly the wavefunction of the bound electron, and thus modifies the hyperfine interaction. The two qubit operations are performed ...
... provided by the hyperfine interaction with a bound electron around each impurity. Each qubit is controlled by applying a voltage to an A gate electrode that displaces slightly the wavefunction of the bound electron, and thus modifies the hyperfine interaction. The two qubit operations are performed ...
A new approach for the two-electron cumulant in natural orbital
... conditions that have to be imposed on variations of ⌫ are well known [12]. Finally, the natural orbital functional (NOF) incorporates fractional occupation numbers in a natural way, which provides a correct description of both dynamical and nondynamical correlation. An NOF requires an expression of ...
... conditions that have to be imposed on variations of ⌫ are well known [12]. Finally, the natural orbital functional (NOF) incorporates fractional occupation numbers in a natural way, which provides a correct description of both dynamical and nondynamical correlation. An NOF requires an expression of ...
Dealing with ignorance: universal discrimination, learning and quantum correlations Gael Sentís Herrera
... further, this is the technique that the statisticians used to come up with the number 246. It is, though, a particular way of handling available information and uncertainty, and certainly not the only possible approach. There is an alternative solution to this problem that, involving different assum ...
... further, this is the technique that the statisticians used to come up with the number 246. It is, though, a particular way of handling available information and uncertainty, and certainly not the only possible approach. There is an alternative solution to this problem that, involving different assum ...
letter
... turns out that this is a vector quantity which points in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rotation. The x-, y- and z-components of this vector can be specified, and these are the angular momenta in the x-, y- and z-directions. In quantum mechanics, there are operators which represent th ...
... turns out that this is a vector quantity which points in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rotation. The x-, y- and z-components of this vector can be specified, and these are the angular momenta in the x-, y- and z-directions. In quantum mechanics, there are operators which represent th ...
Quantum Mechanics of Many-Electrons Systems and the Theories of
... The first general treatment for many-electron atoms was proposed by Hartree22, who suggested that electrons in atoms would move independently of each other, the motion of each one of the electrons being influenced by the electrostatic potential of the nucleus and an average field due to all the othe ...
... The first general treatment for many-electron atoms was proposed by Hartree22, who suggested that electrons in atoms would move independently of each other, the motion of each one of the electrons being influenced by the electrostatic potential of the nucleus and an average field due to all the othe ...
Spontaneous Formation of Magnetic Moments and Dephasing in Two-Dimensional Disordered Systems
... anomaly, which is in agreement with theory. Both the 0.7 anomaly and the Kondo signatures show a periodic modulation as a function of QPC length, which can be explained by a varying number of spontaneously localized states. We show using spin-density-functional theory calculations that the number of ...
... anomaly, which is in agreement with theory. Both the 0.7 anomaly and the Kondo signatures show a periodic modulation as a function of QPC length, which can be explained by a varying number of spontaneously localized states. We show using spin-density-functional theory calculations that the number of ...
$doc.title
... phases also enter into quantization conditions (recall the Bohr-Sommerfeld rules), and theoretical predictions of energy levels would not agree with experiment if all phases were not accounted for correctly. ...
... phases also enter into quantization conditions (recall the Bohr-Sommerfeld rules), and theoretical predictions of energy levels would not agree with experiment if all phases were not accounted for correctly. ...
Single-Electron Capacitance Spectroscopy R. Ashoori Optics and Devices
... electrons. Not only do the electrons repel one another, they are indistinguishable. This fact, along with the principle that only one electron can exist in any quantum mechanical orbit, produces unusual and sometimes counterintuitive correlations in the motions of electrons. We use extremely sensiti ...
... electrons. Not only do the electrons repel one another, they are indistinguishable. This fact, along with the principle that only one electron can exist in any quantum mechanical orbit, produces unusual and sometimes counterintuitive correlations in the motions of electrons. We use extremely sensiti ...
THE TRIANGLE INEQUALITY AND THE DUAL GROMOV
... Lipschitz seminorm LZ associated with dZ for ιX is given by the Lipschitz seminorm LX associated with dX . Conversely, if ιX : X ,→ Z is an injection and if LX is the quotient of LZ for ιX then ιX is an isometry. This observation justifies our restriction to seminorms defined on the self-adjoint par ...
... Lipschitz seminorm LZ associated with dZ for ιX is given by the Lipschitz seminorm LX associated with dX . Conversely, if ιX : X ,→ Z is an injection and if LX is the quotient of LZ for ιX then ιX is an isometry. This observation justifies our restriction to seminorms defined on the self-adjoint par ...
Electron phase coherence
... Usually it is assumed that in a magnetic field the sample properties change significantly. Thus one can think that at each magnetic field a sample represents a realization of an ensemble (so-called ergodic hypothesis) . Consequently, one can average over magnetic fields rather then over different sa ...
... Usually it is assumed that in a magnetic field the sample properties change significantly. Thus one can think that at each magnetic field a sample represents a realization of an ensemble (so-called ergodic hypothesis) . Consequently, one can average over magnetic fields rather then over different sa ...