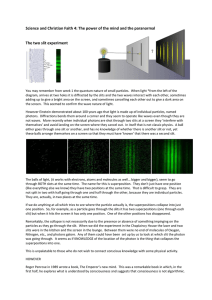
Axioms of Quantum Mechanics
... A physical experiment can be divided into two steps: preparation and measurement. The first step determines the possible outcomes of the experiment, while the measurement retrieves the value of the outcome. In QM the situation is slightly different: the first step determines the probabilities of the va ...
... A physical experiment can be divided into two steps: preparation and measurement. The first step determines the possible outcomes of the experiment, while the measurement retrieves the value of the outcome. In QM the situation is slightly different: the first step determines the probabilities of the va ...
Molecular Electronic Devices
... Needed for present day and future devices where phasebreaking vibrations take longer than electron’s transit time ...
... Needed for present day and future devices where phasebreaking vibrations take longer than electron’s transit time ...
PowerPoint
... For a quantum computer, instead of testing one integer at a time, we could test many at once via superposition of states (or computation in many universes)! Thus, assuming one second per computation, we could get our answer 69 times faster with a quantum computer! ...
... For a quantum computer, instead of testing one integer at a time, we could test many at once via superposition of states (or computation in many universes)! Thus, assuming one second per computation, we could get our answer 69 times faster with a quantum computer! ...
Field extension of real values of physical observables in classical
... complex values. In general, given a non-hermitian operator, its average value in a quantum state is a complex number. In quantum theory, the concept of weak measurement was introduced by Aharonov et al. [4–6] to study the properties of a quantum system in pre- and postselected ensembles. In that for ...
... complex values. In general, given a non-hermitian operator, its average value in a quantum state is a complex number. In quantum theory, the concept of weak measurement was introduced by Aharonov et al. [4–6] to study the properties of a quantum system in pre- and postselected ensembles. In that for ...
PHY 104: Modern Physics - Physlab
... Website: http://physlab.lums.edu.pk/ Lecture format: Two 75 minutes lectures and one 50 minutes lecture. One 75 minute recitation. ____________________________________________________________________________ Course Description: The course is a continuation of the Physics narrative from PHY 101 and i ...
... Website: http://physlab.lums.edu.pk/ Lecture format: Two 75 minutes lectures and one 50 minutes lecture. One 75 minute recitation. ____________________________________________________________________________ Course Description: The course is a continuation of the Physics narrative from PHY 101 and i ...
Chapter 9 review
... If molecules, atoms, or subatomic particles are in the liquid or solid state, the Pauli exclusion principle prevents two particles with identical wave functions from sharing the same space. ...
... If molecules, atoms, or subatomic particles are in the liquid or solid state, the Pauli exclusion principle prevents two particles with identical wave functions from sharing the same space. ...
Midterm Solution
... 1b. Does the improbability she/he mentions mean that there is still a finite probability that a quantum mechanical object could be in a place where its total energy is less than its potential energy? Yes P in principle No (no is acceptable if well argued due to the measurement problem, it’s no in pr ...
... 1b. Does the improbability she/he mentions mean that there is still a finite probability that a quantum mechanical object could be in a place where its total energy is less than its potential energy? Yes P in principle No (no is acceptable if well argued due to the measurement problem, it’s no in pr ...
PPT - LSU Physics - Louisiana State University
... William N Plick, Petr M Anisimov, JPD, Hwang Lee, and Girish S Agarwal Abstract. We present a method for directly obtaining the parity of a Gaussian state of light without recourse to photonnumber counting. The scheme uses only a simple balanced homodyne technique and intensity correlation. Thus int ...
... William N Plick, Petr M Anisimov, JPD, Hwang Lee, and Girish S Agarwal Abstract. We present a method for directly obtaining the parity of a Gaussian state of light without recourse to photonnumber counting. The scheme uses only a simple balanced homodyne technique and intensity correlation. Thus int ...
Unit 2 – Electrons and Periodic Behavior Cartoon courtesy of
... 4-1 Properties of Light • Electromagnetic radiation-is a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travel through space. • Examples x-rays, UV, infrared light, ...
... 4-1 Properties of Light • Electromagnetic radiation-is a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travel through space. • Examples x-rays, UV, infrared light, ...
1 Two qubits - EECS: www
... paper, John Bell showed that properties of Bell (EPR) states were not merely fodder for a philosophical discussion, but had verifiable consequences: local hidden variables are not the answer. How does one rule out every possible hidden variable theory? Here’s how: we will consider an extravagant fra ...
... paper, John Bell showed that properties of Bell (EPR) states were not merely fodder for a philosophical discussion, but had verifiable consequences: local hidden variables are not the answer. How does one rule out every possible hidden variable theory? Here’s how: we will consider an extravagant fra ...
Bell`s Inequality - weylmann.com
... is needed to enforce conservation of angular momentum, which you should already be familiar with. Anyway, after the particles are created let them separate and move in opposite directions at high velocity, while we follow each one with a spin measuring device. When the particles have gotten to a nic ...
... is needed to enforce conservation of angular momentum, which you should already be familiar with. Anyway, after the particles are created let them separate and move in opposite directions at high velocity, while we follow each one with a spin measuring device. When the particles have gotten to a nic ...
Document
... 2.the statistic explanation of wave function wave view particle view Bright fringe: (x,y,z,t)2 big, possibility big; Dark fringe: (x,y,z,t)2 small , possibility small 。 (x,y,z,t)2 is proportion to possibility density in this point. ...
... 2.the statistic explanation of wave function wave view particle view Bright fringe: (x,y,z,t)2 big, possibility big; Dark fringe: (x,y,z,t)2 small , possibility small 。 (x,y,z,t)2 is proportion to possibility density in this point. ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... (i) 1,…,k are uniformly random, or (ii) there’s a partition [n]=AB, |A|=|B| such that the i’s map A to A and B to B but are otherwise random. ...
... (i) 1,…,k are uniformly random, or (ii) there’s a partition [n]=AB, |A|=|B| such that the i’s map A to A and B to B but are otherwise random. ...
Classical World because of Quantum Physics
... I.e. the statistical mixture has a classical time evolution, if measurement and time evolution commute “on the coarse-grained level”. Given fuzzy measurements (or pre-measurement decoherence), it depends on the Hamiltonian whether macrorealism is satisfied. ...
... I.e. the statistical mixture has a classical time evolution, if measurement and time evolution commute “on the coarse-grained level”. Given fuzzy measurements (or pre-measurement decoherence), it depends on the Hamiltonian whether macrorealism is satisfied. ...