21.3 Electric Energy Generation and Transmission
... It does this by having the primary coil have more loops than the secondary coil. By having less loops in the secondary coil, the secondary coil is not able to collect as much of the magnetic field to help push electrons through it. A step-up transformer ...
... It does this by having the primary coil have more loops than the secondary coil. By having less loops in the secondary coil, the secondary coil is not able to collect as much of the magnetic field to help push electrons through it. A step-up transformer ...
electrom - studylib.net
... magnitude of the current, and the magnetic permeability of the core material; a strong field can be produced from a small current if a large number of turns of wire are used. Unlike the materials from which permanent magnets are made, the soft iron in the core of an electromagnet retains little of t ...
... magnitude of the current, and the magnetic permeability of the core material; a strong field can be produced from a small current if a large number of turns of wire are used. Unlike the materials from which permanent magnets are made, the soft iron in the core of an electromagnet retains little of t ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move (electromagnetic induction) ...
... atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move (electromagnetic induction) ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism.pptx
... atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move (electromagnetic induction) ...
... atom produces a magnetic field • currents in wires will produce magnetic fields • The opposite is also true: moving magnetic fields will cause charges to move (electromagnetic induction) ...
Chapter 20 and 21 study guide
... Define Voltage. (do not just define Potential Electrical Difference, or else) Give the name of the device that converts chemical energy to electric energy. Give Ohm’s law. To keep constant current when resistance increases, what must we do? Give the formulas for Electrical Power, Electric Energy, an ...
... Define Voltage. (do not just define Potential Electrical Difference, or else) Give the name of the device that converts chemical energy to electric energy. Give Ohm’s law. To keep constant current when resistance increases, what must we do? Give the formulas for Electrical Power, Electric Energy, an ...
Worksheet 8.7 - Transformers
... 1) Currents of 0.25 A and 0.95 A flow through the primary and secondary coils of a transformer respectively if there are 1.0x103 turns in the primary coil how many turns are in the secondary coil? 2) A step-down transformer has coils of 1.20 x 103 and 1.5- x 102 turns. If the transformer is connecte ...
... 1) Currents of 0.25 A and 0.95 A flow through the primary and secondary coils of a transformer respectively if there are 1.0x103 turns in the primary coil how many turns are in the secondary coil? 2) A step-down transformer has coils of 1.20 x 103 and 1.5- x 102 turns. If the transformer is connecte ...
Real Contents
... (23.10.) Capacitance and Dielectrics. Current and Resistance Definition of capacitance Calculation of capacitance Combinations of capacitors Energy stored in a charged capacitor Electric current Resistance and Ohm's law The resistivity of different conductors Electrical energy and power ...
... (23.10.) Capacitance and Dielectrics. Current and Resistance Definition of capacitance Calculation of capacitance Combinations of capacitors Energy stored in a charged capacitor Electric current Resistance and Ohm's law The resistivity of different conductors Electrical energy and power ...
EE205 - KFUPM Resources v3
... Fig31-3 Magnetically Coupled coils with coil 1 excited and coil 2 open. ...
... Fig31-3 Magnetically Coupled coils with coil 1 excited and coil 2 open. ...
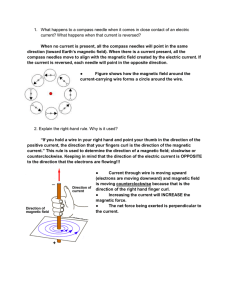
When no current is present, all the compass
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
magnetic field
... Vectors going into the page are represented with a cross (X), vectors going out of a page are represented with a ...
... Vectors going into the page are represented with a cross (X), vectors going out of a page are represented with a ...
HADES at FAIR Measurement of di-lepton pairs (e+e-) A
... focusing only certain bunches are chosen we are able to work with pulsed applications, which can provide a similar magnetic gradient as superconducting magnets. The current needed to reach strong magnetic field gradients for typical energies and sizes of SIS18 (18Tm accelerator at GSI) beams is abou ...
... focusing only certain bunches are chosen we are able to work with pulsed applications, which can provide a similar magnetic gradient as superconducting magnets. The current needed to reach strong magnetic field gradients for typical energies and sizes of SIS18 (18Tm accelerator at GSI) beams is abou ...
Micrometers Vernier caliper
... Inductive displacement sensor. Coil is excited at high frequency (typically 1 MHz) This induces eddy current in the target Eddy current alters the inductance of the probe coil This change can be translated into a voltage proportional to the air gap ...
... Inductive displacement sensor. Coil is excited at high frequency (typically 1 MHz) This induces eddy current in the target Eddy current alters the inductance of the probe coil This change can be translated into a voltage proportional to the air gap ...
Slide 1
... Suppose that in the circuit above the thick rod has a length of 20 cm and a resistance of 500 ohms and is free to move (without friction) along the track of thin wire (with ~0 resistance), completing a loop circuit. If there is a uniform 2 T B field everywhere into the page, and the rod is pulled to ...
... Suppose that in the circuit above the thick rod has a length of 20 cm and a resistance of 500 ohms and is free to move (without friction) along the track of thin wire (with ~0 resistance), completing a loop circuit. If there is a uniform 2 T B field everywhere into the page, and the rod is pulled to ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.