Ideal Transformers - Help-A-Bull
... Increasing the current increases B, but in a non-linear way. The curve passes to the right of the origin, but intersects itself at the positive saturation point. This closed path is known as a hysteresis loop. ...
... Increasing the current increases B, but in a non-linear way. The curve passes to the right of the origin, but intersects itself at the positive saturation point. This closed path is known as a hysteresis loop. ...
Code - SVNIT
... ELECTROMAGNETICS (04 Hours) Ampere’s law, magnetic flux and flux density, magnetic field strength due to straight conductors and circular coil, field strength due to solenoid, magnetomotive force, magnetic circuit calculations, magnetic leakage, magnetic hysterisis, hysterisis and eddy current losse ...
... ELECTROMAGNETICS (04 Hours) Ampere’s law, magnetic flux and flux density, magnetic field strength due to straight conductors and circular coil, field strength due to solenoid, magnetomotive force, magnetic circuit calculations, magnetic leakage, magnetic hysterisis, hysterisis and eddy current losse ...
Game
... A generator uses magnets and wires to turn mechanical energy to _____________. A- static electricity ...
... A generator uses magnets and wires to turn mechanical energy to _____________. A- static electricity ...
... must be kept to a minimum. To meet these requirements, the computer-aided design a very important step to good order and avoid all the difficulties that may be encountered in the actual design. The system comprises two reels, whose excitation of the one cause the displacement of the core assembled w ...
Inductor commutating circuits
... (c) Switch open, Current still flows in coil due to collapsing magnetic field. Note polarity change on coil. (d) Coil voltage vs time. When the pushbutton switch is actuated, current goes through the inductor, producing a magnetic field around it. When the switch is de-actuated, its contacts open, i ...
... (c) Switch open, Current still flows in coil due to collapsing magnetic field. Note polarity change on coil. (d) Coil voltage vs time. When the pushbutton switch is actuated, current goes through the inductor, producing a magnetic field around it. When the switch is de-actuated, its contacts open, i ...
Chapter 6 Part1: Multiple choices
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
... 7. What energy conversion is achieved by the electric generator? A. Mechanical energy to electrical energy B. Electrical energy to mechanical energy C. Electrical energy to solar energy D. Mechanical energy to nuclear energy 8. If you constantly push the bar magnet through the loop as shown below, t ...
Course Title
... field: Charge moving in static magnetic field, Rotary motor Hall-Effect generator, Moving conductor in static magnetic field, Generator ...
... field: Charge moving in static magnetic field, Rotary motor Hall-Effect generator, Moving conductor in static magnetic field, Generator ...
Physics Form 5 Syllabus
... emissions so that each emission is suited to a particular purpose Describe the different abilities of these emissions to produce ionisation and describe their deflections in electric and magnetic fields ...
... emissions so that each emission is suited to a particular purpose Describe the different abilities of these emissions to produce ionisation and describe their deflections in electric and magnetic fields ...
Instrumentation and Measurement Techniques
... demands of medium capacity motors up to 200 kW • When large loads are connected to the LV system the magnitude of current flow becomes too large resulting in overheating due to high iron and copper losses • P = VI Cos • Copper loss = I2 R [kW] ...
... demands of medium capacity motors up to 200 kW • When large loads are connected to the LV system the magnitude of current flow becomes too large resulting in overheating due to high iron and copper losses • P = VI Cos • Copper loss = I2 R [kW] ...
21.2 Electromagnetism
... If a ferromagnetic material, such as an iron rod is placed inside the coil of a solenoid, the strength of the magnetic field increases. • The magnetic field produced by the current causes the iron rod to become a magnet. • An electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic core. • The current can b ...
... If a ferromagnetic material, such as an iron rod is placed inside the coil of a solenoid, the strength of the magnetic field increases. • The magnetic field produced by the current causes the iron rod to become a magnet. • An electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic core. • The current can b ...
Magnetic effect of a current.pps
... (a) Current in wire will produce Magnetic field to affect the compass (b) To stop the light from the bulb by a black box X : iron, Y : Magnet, Z : Al ...
... (a) Current in wire will produce Magnetic field to affect the compass (b) To stop the light from the bulb by a black box X : iron, Y : Magnet, Z : Al ...
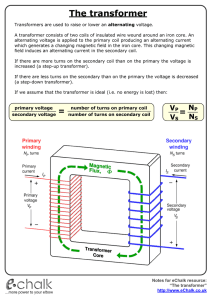
The transformer
... The national grid is the system of pylons and cables that supply electricity to houses and factories around the country. Since: power = current x voltage , the same amount of electrical power can be transported using either of the following: (A) a high voltage and a low current (B) a low voltage and ...
... The national grid is the system of pylons and cables that supply electricity to houses and factories around the country. Since: power = current x voltage , the same amount of electrical power can be transported using either of the following: (A) a high voltage and a low current (B) a low voltage and ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... distance of 0.2m from the centre when a current of 0.1 A flows in it. 6. Calculate the self inductance of 1m long solenoid of 400 turns and 5 cm diameter. 7. Explain time constant in L-R circuit. 8. Obtain the expression for the mean value of a.c. in terms of the peak value. 9. Define magnetic susce ...
... distance of 0.2m from the centre when a current of 0.1 A flows in it. 6. Calculate the self inductance of 1m long solenoid of 400 turns and 5 cm diameter. 7. Explain time constant in L-R circuit. 8. Obtain the expression for the mean value of a.c. in terms of the peak value. 9. Define magnetic susce ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.