Guidance On Electrical Installation Practices To Reduce EMF From
... contractors of low voltage systems of measures that may be adopted to reduce the production and effects of electric and magnetic fields associated with electrical installations. The electricity supply industry in Australia, as an appropriate response to scientific uncertainty and community concern r ...
... contractors of low voltage systems of measures that may be adopted to reduce the production and effects of electric and magnetic fields associated with electrical installations. The electricity supply industry in Australia, as an appropriate response to scientific uncertainty and community concern r ...
Experiment FT2: Measurement of Inductance and Mutual Inductance
... Imagine a coil of wire, similar to the one shown in Figure 1, connected to an ac supply. It is found that whenever an effort is made to increase current through it, it is always opposed by the instantaneous production of counter e.m.f of self-induction. Energy required to overcome this opposition is ...
... Imagine a coil of wire, similar to the one shown in Figure 1, connected to an ac supply. It is found that whenever an effort is made to increase current through it, it is always opposed by the instantaneous production of counter e.m.f of self-induction. Energy required to overcome this opposition is ...
HF Mobile Vertical Design
... Fundamental Freq. of a ¼ wave vert. is the lowest freq. for which the reactance (j) is zero at the feedpoint. This is the resonant freq. ¼ = 3 x 108 m x ¼ -- > Free Space Freq. Physical length = Free Space x K This makes the physical length shorter than free space. Approximately 5% shorter due to c ...
... Fundamental Freq. of a ¼ wave vert. is the lowest freq. for which the reactance (j) is zero at the feedpoint. This is the resonant freq. ¼ = 3 x 108 m x ¼ -- > Free Space Freq. Physical length = Free Space x K This makes the physical length shorter than free space. Approximately 5% shorter due to c ...
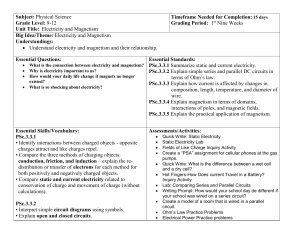
Subject: Physical Science - Currituck County Schools
... • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and resistance. PSc.3.3.3 • Explain how the wire in a circuit can affect the current present – for a set voltage, the current in a wire is inversely proportional to its resistance (more current exists w ...
... • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and resistance. PSc.3.3.3 • Explain how the wire in a circuit can affect the current present – for a set voltage, the current in a wire is inversely proportional to its resistance (more current exists w ...
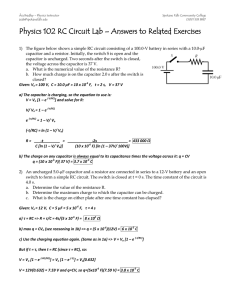
Physics 102 RC Circuit Lab – Answers to Related Exercises
... q = (10 x 10-6 F)( 37 V) = 3.7 x 10-4 C 2) An uncharged 5.0-µF capacitor and a resistor are connected in series to a 12-V battery and an open switch to form a simple RC circuit. The switch is closed at t = 0 s. The time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s. a. Determine the value of the resistance R. b. ...
... q = (10 x 10-6 F)( 37 V) = 3.7 x 10-4 C 2) An uncharged 5.0-µF capacitor and a resistor are connected in series to a 12-V battery and an open switch to form a simple RC circuit. The switch is closed at t = 0 s. The time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s. a. Determine the value of the resistance R. b. ...
WEEK 3-4: DIRECT CURRENT GENERATOR
... • In DC series generators field winding is connected in series with armature and load. Hence, here load current is similar to field current. Thus, the loading characteristic curve is close to the machine magnetization curve. At no load, there is no field current, so VT is reduced to a small level gi ...
... • In DC series generators field winding is connected in series with armature and load. Hence, here load current is similar to field current. Thus, the loading characteristic curve is close to the machine magnetization curve. At no load, there is no field current, so VT is reduced to a small level gi ...
How Motors Operate Presented by John Freeland
... hear the switch open as the motor starts up and close as the motor turns off • Is offset from the running winding ninety degrees for a two pole motor and fortyfive degrees for a four pole motor. • Has fewer turns of smaller gauge wire. • Occupies the outer portion of the stator slots. ...
... hear the switch open as the motor starts up and close as the motor turns off • Is offset from the running winding ninety degrees for a two pole motor and fortyfive degrees for a four pole motor. • Has fewer turns of smaller gauge wire. • Occupies the outer portion of the stator slots. ...
Series DC Motors
... • Generator action: An emf (voltage) is induced in a conductor if it moves through a magnetic field. • Motor action: A force is induced in a conductor that has a current going through it and placed in a magnetic field • Any DC machine can act either as a generator or as a motor. ...
... • Generator action: An emf (voltage) is induced in a conductor if it moves through a magnetic field. • Motor action: A force is induced in a conductor that has a current going through it and placed in a magnetic field • Any DC machine can act either as a generator or as a motor. ...
Investigation of Electric Reactor Magnetic Field using Finite Element
... Therefore, when magnetic field around the power equipment is computing the sizes of current carrying leads can be neglected. We can suppose that current is concentrates on lead axis. These currents are evaluated in a right side of the equation (1). The currents induced in current carrying parts by e ...
... Therefore, when magnetic field around the power equipment is computing the sizes of current carrying leads can be neglected. We can suppose that current is concentrates on lead axis. These currents are evaluated in a right side of the equation (1). The currents induced in current carrying parts by e ...
EPR Spectroscopy
... The microwave cavity is used to amplify weak signals from the sample. The microwave cavity is a metal box or cylinder that resonates with the microwaves. This is connected to the microwave bridge via a waveguide. When at the resonance frequency, the cavity stores the microwave energy inside r ...
... The microwave cavity is used to amplify weak signals from the sample. The microwave cavity is a metal box or cylinder that resonates with the microwaves. This is connected to the microwave bridge via a waveguide. When at the resonance frequency, the cavity stores the microwave energy inside r ...
39. A Simple Motor
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Remind students that they were again acting as engineers in this activity. Ask, What do engineers do? (They solve problems by designing and building devices.) Remind students that they were given a chance to try out new engineering ideas in ...
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Remind students that they were again acting as engineers in this activity. Ask, What do engineers do? (They solve problems by designing and building devices.) Remind students that they were given a chance to try out new engineering ideas in ...
DC Machines
... • The rotor is supplied by dc current through the brushes, commutator and coils. • The interaction of the magnetic field and rotor current generates a force that drives the motor ...
... • The rotor is supplied by dc current through the brushes, commutator and coils. • The interaction of the magnetic field and rotor current generates a force that drives the motor ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.