Magnetic Fields, Hall effect and Electromagnetic - Physlab
... where (VH ) is the Hall voltage and w is the width of the conductor. Combining Equation 8 and Equation 9 we get, VH = υw B. ...
... where (VH ) is the Hall voltage and w is the width of the conductor. Combining Equation 8 and Equation 9 we get, VH = υw B. ...
Lecture 16
... Each electron in an atom has an orbital magnetic dipole moment and a spin magnetic dipole moment. The resultant of these two vectors combines with similar resultants for all other electrons in the atom, and the resultant for each atom combines with those for all the other atoms in a sample of a mate ...
... Each electron in an atom has an orbital magnetic dipole moment and a spin magnetic dipole moment. The resultant of these two vectors combines with similar resultants for all other electrons in the atom, and the resultant for each atom combines with those for all the other atoms in a sample of a mate ...
P30/P40 Series - Richardson RFPD
... Users should thoroughly review the technical data before selecting a product part number. It is recommended that users also seek out the pertinent approvals files of the agencies/laboratories and review them to ensure the product meets the requirements for a given application. ...
... Users should thoroughly review the technical data before selecting a product part number. It is recommended that users also seek out the pertinent approvals files of the agencies/laboratories and review them to ensure the product meets the requirements for a given application. ...
Summary Sheets
... A reed switch has two thin pieces of iron inside it. If a magnet is held near the switch, the pieces of iron are magnetised and touch each other. A reed switch can also be switched on using an electromagnet. Any switch that is worked by electricity is called a relay. Relays are used to make things s ...
... A reed switch has two thin pieces of iron inside it. If a magnet is held near the switch, the pieces of iron are magnetised and touch each other. A reed switch can also be switched on using an electromagnet. Any switch that is worked by electricity is called a relay. Relays are used to make things s ...
3D Finite Element Analysis for Arcing Chamber Optimization
... Computer-aided analysis of field distribution for evaluating electromagnetic device or component performance has become the most advantageous way of design. Analytical methods have limited uses and experimental methods are time requirement and expensive [1]. The particular torque-speed characteristi ...
... Computer-aided analysis of field distribution for evaluating electromagnetic device or component performance has become the most advantageous way of design. Analytical methods have limited uses and experimental methods are time requirement and expensive [1]. The particular torque-speed characteristi ...
lecture13
... The first transformer has a 2:1 ratio of turns, so the voltage doubles. But the second transformer has a 1:2 ratio, so the voltage is halved again. Therefore, the end result is the same as the original voltage. ...
... The first transformer has a 2:1 ratio of turns, so the voltage doubles. But the second transformer has a 1:2 ratio, so the voltage is halved again. Therefore, the end result is the same as the original voltage. ...
of the field.
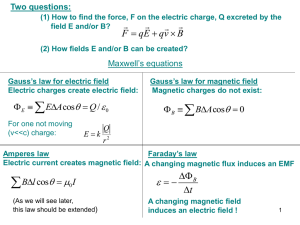
... Stronger magnetic field in a long solenoid: For a solenoid of any given length, the strength of the magnetic field can be increased by: ...
... Stronger magnetic field in a long solenoid: For a solenoid of any given length, the strength of the magnetic field can be increased by: ...
Reed relays - Go ELECTRONICS
... which can be completely separate from the first. For example a low voltage battery circuit can use a relay to switch a 230V AC mains circuit. There is no electrical connection inside the relay between the two circuits, the link is magnetic and mechanical. The coil of a relay passes a relatively larg ...
... which can be completely separate from the first. For example a low voltage battery circuit can use a relay to switch a 230V AC mains circuit. There is no electrical connection inside the relay between the two circuits, the link is magnetic and mechanical. The coil of a relay passes a relatively larg ...
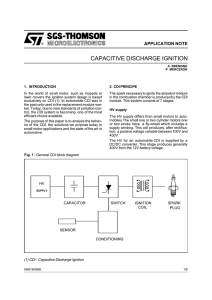
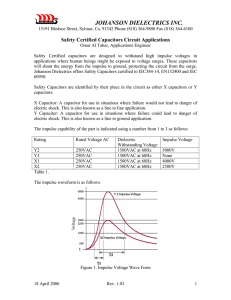
Safety Certified Capacitors Circuit Applications
... Sales Office for the latest specifications. All statements, information and data given herein are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without guarantee, warranty, or responsibility of any kind, expressed or implied. Statements or suggestions concerning possible use of our product ...
... Sales Office for the latest specifications. All statements, information and data given herein are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without guarantee, warranty, or responsibility of any kind, expressed or implied. Statements or suggestions concerning possible use of our product ...
Document
... If the plate is large enough it will intercept the bulk of the electric field lines between source and receptor plates. The circuit equivalent is shown in Figure 1(c). If impedance Z3 is low enough, little voltage will be transmitted from the voltage source to the load Z2. For electric shielding to ...
... If the plate is large enough it will intercept the bulk of the electric field lines between source and receptor plates. The circuit equivalent is shown in Figure 1(c). If impedance Z3 is low enough, little voltage will be transmitted from the voltage source to the load Z2. For electric shielding to ...
433_1.PDF
... structure. The maximum gradient will be constrained below the dark current limit by rf breakdown [1], and further limited in practice by surface fatigue due to pulsed heating that can affect structure lifetime [2]. Further experimental tests to determine the maximum achievable accelerating gradient ...
... structure. The maximum gradient will be constrained below the dark current limit by rf breakdown [1], and further limited in practice by surface fatigue due to pulsed heating that can affect structure lifetime [2]. Further experimental tests to determine the maximum achievable accelerating gradient ...
Coilgun

A coilgun (or Gauss rifle, in reference to Carl Friedrich Gauss, who formulated mathematical descriptions of the magnetic effect used by magnetic accelerators) is a type of projectile accelerator consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis.Coilguns generally consist of one or more coils arranged along a barrel, so the path of the accelerating projectile lies along the central axis of the coils. The coils are switched on and off in a precisely timed sequence, causing the projectile to be accelerated quickly along the barrel via magnetic forces. Coilguns are distinct from railguns, as the direction of acceleration in a railgun is at right angles to the central axis of the current loop formed by the conducting rails. In addition, railguns usually require the use of sliding contacts to pass a large current through the projectile or sabot but coilguns do not necessarily require sliding contacts. Whilst some simple coilgun concepts can use ferromagnetic projectiles or even permanent magnet projectiles, most designs for high velocities actually incorporate a coupled coil as part of the projectile.