Essentials of Biology Sylvia S. Mader
... • Most bony fishes are ray-finned fishes, using fins for balance and movement. • The ray-finned fishes use a swim bladder to adjust their buoyancy in the water. • The bony fishes also have scales that protect the body. • The circulatory system of bony fishes is a single ...
... • Most bony fishes are ray-finned fishes, using fins for balance and movement. • The ray-finned fishes use a swim bladder to adjust their buoyancy in the water. • The bony fishes also have scales that protect the body. • The circulatory system of bony fishes is a single ...
Diversity and Life History of Caecilians (Gymnophiona)
... Reproduction cont’d • Terrestrial or aquatic larvae which hatch from eggs • Females guard eggs. • Others are viviparous. Give birth to young alive. • Embryos in oviduct use up their yolk and females secrete “uterine milk” to nourish the babies. • Embryos shed specialized teeth after birth. • Enormo ...
... Reproduction cont’d • Terrestrial or aquatic larvae which hatch from eggs • Females guard eggs. • Others are viviparous. Give birth to young alive. • Embryos in oviduct use up their yolk and females secrete “uterine milk” to nourish the babies. • Embryos shed specialized teeth after birth. • Enormo ...
WILLIAM F. BRANDON W. KYLE D.
... In the second loop, blood travels from heart to the tissues of the body Reptiles rely on gathering and losing heat from their environment and surroundings ...
... In the second loop, blood travels from heart to the tissues of the body Reptiles rely on gathering and losing heat from their environment and surroundings ...
Amphibians and Reptiles - Vernon Hills High School
... Sound waves hit tympanic membrane (eardrum) Columella moves and takes sound to the inner ear Recognized in inner ear by receptors ...
... Sound waves hit tympanic membrane (eardrum) Columella moves and takes sound to the inner ear Recognized in inner ear by receptors ...
Chordates - Staff Web Pages
... Origin of Mammals • The mass extinction of the dinosaurs at the end of the Mesozoic Era, along with the breaking apart of Pangaea and changes in climate, opened up new niches for early mammals to fill. • The Cenozoic Era (65 million years to present) is sometimes called the golden age of mammals be ...
... Origin of Mammals • The mass extinction of the dinosaurs at the end of the Mesozoic Era, along with the breaking apart of Pangaea and changes in climate, opened up new niches for early mammals to fill. • The Cenozoic Era (65 million years to present) is sometimes called the golden age of mammals be ...
amphibians
... Poison-dart frogs are so named because South American Indians used their poison to tip blowpipe darts. One species, the golden poison-dart frog, carries enough poison to kill almost 1,000 people. ...
... Poison-dart frogs are so named because South American Indians used their poison to tip blowpipe darts. One species, the golden poison-dart frog, carries enough poison to kill almost 1,000 people. ...
Reptiles and Amphibians
... inside or outside the body). Most do not show parental care (alligators and crocodiles are the exceptions).Some snakes do incubate their eggs. Young reptiles resemble adults (mini-adults) and do not go through a metamorphosis to reach adulthood. There are four orders of ReptilesCrocodilians (alligat ...
... inside or outside the body). Most do not show parental care (alligators and crocodiles are the exceptions).Some snakes do incubate their eggs. Young reptiles resemble adults (mini-adults) and do not go through a metamorphosis to reach adulthood. There are four orders of ReptilesCrocodilians (alligat ...
Animal Evolution –The Invertebrates
... Transition from Water to Land Vertebrates evolved in the seas, where cartilaginous and bony fishes still live Of all vertebrates, modern bony fishes are most diverse One group gave rise to aquatic tetrapods (fourlegged walkers), the descendants of which moved onto dry land ...
... Transition from Water to Land Vertebrates evolved in the seas, where cartilaginous and bony fishes still live Of all vertebrates, modern bony fishes are most diverse One group gave rise to aquatic tetrapods (fourlegged walkers), the descendants of which moved onto dry land ...
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 5: The vertebrate skeleton Axial
... Openings for jaw muscles: The temporal region of the skull, behind the orbit, is the attachment zone for numerous jaw muscles. Primitively, the braincase lies deep below the outer bones and jaw muscles of the temporal region. As a muscle contracts, it gets shorter, but the volume remains constant. ...
... Openings for jaw muscles: The temporal region of the skull, behind the orbit, is the attachment zone for numerous jaw muscles. Primitively, the braincase lies deep below the outer bones and jaw muscles of the temporal region. As a muscle contracts, it gets shorter, but the volume remains constant. ...
Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians
... Eggs hatch into tadpoles Tadpoles gradually grow limbs, lose tails/gills, and become carnivorous Young adults move onto land ...
... Eggs hatch into tadpoles Tadpoles gradually grow limbs, lose tails/gills, and become carnivorous Young adults move onto land ...
Chapter 31: Animals: Part II
... Amphibians Amphibians evolved from the lobefinned fishes and are tetrapods with two pairs of limbs. They are represented today by frogs, newts, toads, and salamanders. Amphibians usually return to the water to reproduce and require moist habitats. Frog tadpoles metamorphose into terrestrial adults ...
... Amphibians Amphibians evolved from the lobefinned fishes and are tetrapods with two pairs of limbs. They are represented today by frogs, newts, toads, and salamanders. Amphibians usually return to the water to reproduce and require moist habitats. Frog tadpoles metamorphose into terrestrial adults ...
Introduction to Vertebrates _Notes - Extra Notes
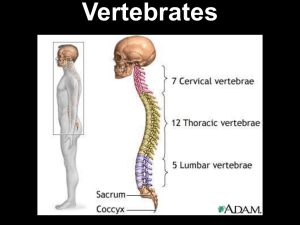
... The subphylum Vertebrata consists of about 43,700 species of animals with backbones. Vertebrates exhibit all three of the chordate characteristics at some point during their lives. The embryonic notochord is replaced by a vertebral column in the adult. The vertebral column is made of individual hard ...
... The subphylum Vertebrata consists of about 43,700 species of animals with backbones. Vertebrates exhibit all three of the chordate characteristics at some point during their lives. The embryonic notochord is replaced by a vertebral column in the adult. The vertebral column is made of individual hard ...
The Chordate Animals - Blue Valley Schools
... • Evolutionary process in which adolescent characteristics are selected for (adults against) such that species become young looking while maintaining the adult ability to reproduce ...
... • Evolutionary process in which adolescent characteristics are selected for (adults against) such that species become young looking while maintaining the adult ability to reproduce ...
Appendicular Skeleton
... interesting story begins with the terrestrial vertebrates. When we look at a primitive tetrapod, each half of the pelvis is a large plate-like structure made of three bones. The two ventral bones (pubis and ischium) of each half join along the midventral side of the body. The dorsal bone (ilium) is ...
... interesting story begins with the terrestrial vertebrates. When we look at a primitive tetrapod, each half of the pelvis is a large plate-like structure made of three bones. The two ventral bones (pubis and ischium) of each half join along the midventral side of the body. The dorsal bone (ilium) is ...
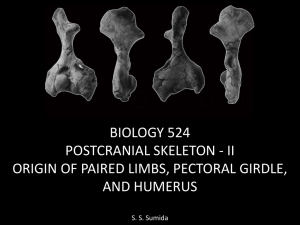
Week 6 Powerpoint - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... There are numerous things to notice about the amphiban / amniote humerus: • Proximally the deltoid, supinator, and pectoral processes are very powerfully developed. • There is little or no distinct shaft in more basal taxa. • As in basal tetrapods, the entepicondyle is very highly developed, highli ...
... There are numerous things to notice about the amphiban / amniote humerus: • Proximally the deltoid, supinator, and pectoral processes are very powerfully developed. • There is little or no distinct shaft in more basal taxa. • As in basal tetrapods, the entepicondyle is very highly developed, highli ...
Post-Midterm Notes
... Flexible Hearts - lungfish can direct blood to gills or lungs - conus is divided; ventricle is partly divided - when lungs are not in use, resistance prevents circulation and redirects blood - frog uses skin primarily to breathe, but can direct a variable fraction of blood to lungs if they are in - ...
... Flexible Hearts - lungfish can direct blood to gills or lungs - conus is divided; ventricle is partly divided - when lungs are not in use, resistance prevents circulation and redirects blood - frog uses skin primarily to breathe, but can direct a variable fraction of blood to lungs if they are in - ...
Reptiles
... Mate: lay eggs or give birth to their young on land The main groups of reptiles are: ...
... Mate: lay eggs or give birth to their young on land The main groups of reptiles are: ...
The Vertebrates The Vertebrates Chordates Notochord Hollow
... descended from a lineage of dinosaurs with a unique trait: feathers Molecular data beginning to support this idea as well – An adolescent female T. rex died 68 million years ago, but its bones still contain intact soft tissue, including the oldest preserved proteins ever found – A comparison of the ...
... descended from a lineage of dinosaurs with a unique trait: feathers Molecular data beginning to support this idea as well – An adolescent female T. rex died 68 million years ago, but its bones still contain intact soft tissue, including the oldest preserved proteins ever found – A comparison of the ...
Tetrapod

The superclass Tetrapoda (Ancient Greek τετραπόδηs tetrapodēs, ""four-footed""), or the tetrapods /ˈtɛtrəpɒd/, comprises the first four-limbed vertebrates and their descendants, including the living and extinct amphibians, reptiles, mammals, birds, and some extinct fish. Tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes around 390 million years ago in the middle Devonian Period, with modern tetrapod groups having appeared by the late Devonian, 367.5 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors of the tetrapods, and the process by which land colonization occurred, remain unclear, and are areas of active research and debate among palaeontologists at present.While most species today are terrestrial, the first tetrapods were fully aquatic. Amphibians today generally remain semiaquatic, living the first stage of their lives as fish-like tadpoles. Amniotes evolved about 340 million years ago (crown amniotes 318 mya), and their descendants drove most amphibians to extinction. One population of amniotes diverged into lizards, dinosaurs, birds and their relatives, while another diverged into mammals and their extinct relatives. Several groups of tetrapods, such as the caecilians, snakes, cetaceans, sirenians, and moas have lost some or all of their limbs. In addition, many tetrapods have returned to partially aquatic or fully aquatic lives throughout the history of the group (modern examples of fully aquatic tetrapods include cetaceans and sirenians). The first returns to an aquatic lifestyle may have occurred as early as the Carboniferous Period, whereas other returns occurred as recently as the Cenozoic, as in cetaceans, pinnipeds, and several modern amphibians.The change from a body plan for breathing and navigating in water to a body plan enabling the animal to move on land is one of the most profound evolutionary changes known. It is also becoming increasingly well-understood as a result of more transitional fossil finds and improved phylogenetic analysis.