Distributed Databases - Computer Information Systems
... communications across any network, supporting both distributed processing and distributed DBMS capability. Even if a process is running on same machine as database instance, Net8 still required to establish its database connection. Net8 also responsible for translating any differences in character s ...
... communications across any network, supporting both distributed processing and distributed DBMS capability. Even if a process is running on same machine as database instance, Net8 still required to establish its database connection. Net8 also responsible for translating any differences in character s ...
Syllabus
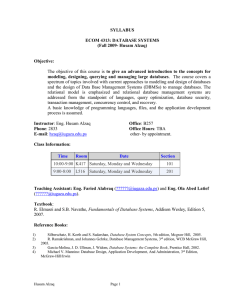
... prohibited. If you arrive at least 5 minutes late, you will be considered absent even if you attend the lecture. Please come to the lecture on time. Respect office hours as listed above. Do not come to the office outside office hours. If the office hours conflict with your schedule, you can arrange ...
... prohibited. If you arrive at least 5 minutes late, you will be considered absent even if you attend the lecture. Please come to the lecture on time. Respect office hours as listed above. Do not come to the office outside office hours. If the office hours conflict with your schedule, you can arrange ...
Advanced DB Tech
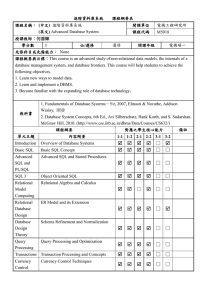
... integration of SQL with programming languages; Explain, discuss and evaluate object-oriented databases; Compare and contrast the relational with object -relational and objectoriented databases; Have understanding of the principles, methods, techniques and tools that underpin query processing/optimiz ...
... integration of SQL with programming languages; Explain, discuss and evaluate object-oriented databases; Compare and contrast the relational with object -relational and objectoriented databases; Have understanding of the principles, methods, techniques and tools that underpin query processing/optimiz ...
Concurrency Control
... transaction to be run out without interference from other transaction – can be achieve by locking or timestamping Durability – property of a transaction requires the value that the transaction commit to the database persistent. ...
... transaction to be run out without interference from other transaction – can be achieve by locking or timestamping Durability – property of a transaction requires the value that the transaction commit to the database persistent. ...
The Low-Cal Database Environment
... – Better multi-instance management – Scale the number of instances without scaling the management difficulty ...
... – Better multi-instance management – Scale the number of instances without scaling the management difficulty ...
Slide 1
... escalation over those that will require an increase in fees paid to their DBMS providers. Worry- free, Zero administration application. ...
... escalation over those that will require an increase in fees paid to their DBMS providers. Worry- free, Zero administration application. ...
Module Descriptor 2014/15 School of Computer Science and Statistics.
... Analyse and assess various database concurrency protocols and algorithms to assess their performance and relative appropriateness in differing operating environments. ...
... Analyse and assess various database concurrency protocols and algorithms to assess their performance and relative appropriateness in differing operating environments. ...
Scaling HTM-Supported Database Transactions to Many Cores
... absence of an efficient hardware implementation. Intel's Haswell microarchitecture introduced hardware transactional memory (HTM) in mainstream CPUs. HTM allows for efficient concurrent, atomic operations, which is also highly desirable in the context of databases. On the other hand, HTM has several ...
... absence of an efficient hardware implementation. Intel's Haswell microarchitecture introduced hardware transactional memory (HTM) in mainstream CPUs. HTM allows for efficient concurrent, atomic operations, which is also highly desirable in the context of databases. On the other hand, HTM has several ...
Database Systems I 91.309
... Possible Topics, cont. • on-line analytic processing systems and multidimensional databases ...
... Possible Topics, cont. • on-line analytic processing systems and multidimensional databases ...
EI010 606 L02 Database Managemnet System
... (Common to EC010 606 L02) Teaching scheme 3 hours lecture and 1 hour tutorial per week ...
... (Common to EC010 606 L02) Teaching scheme 3 hours lecture and 1 hour tutorial per week ...
Lecture Note 9
... – Two transactions cannot have conflicting locks – No unlock operation can precede a lock operation in the same transaction – No data are affected until all locks are obtained—that is, until the transaction is in its locked point ...
... – Two transactions cannot have conflicting locks – No unlock operation can precede a lock operation in the same transaction – No data are affected until all locks are obtained—that is, until the transaction is in its locked point ...
Transactions Transactions Transaction Concept Example of Fund
... must equal value of cash-in-hand " A transaction must see a consistent database. " During transaction execution the database may be temporarily inconsistent. " When the transaction completes successfully the database must be ...
... must equal value of cash-in-hand " A transaction must see a consistent database. " During transaction execution the database may be temporarily inconsistent. " When the transaction completes successfully the database must be ...
Sullbus
... database management system or tool. This is to give opportunity to the students who want to try some hands on database experience that this course does not otherwise offer. The instructor is completely open about this and would like students to think of applications in their own areas of interest an ...
... database management system or tool. This is to give opportunity to the students who want to try some hands on database experience that this course does not otherwise offer. The instructor is completely open about this and would like students to think of applications in their own areas of interest an ...
Introduction to Software Engineering
... Objectives First course in databases Fundamental concepts of database management Aspects of Database design Aspects of Database languages Some aspects of Database-system implementation Concepts and algorithms in a general setting that is not tied to one particular database system ...
... Objectives First course in databases Fundamental concepts of database management Aspects of Database design Aspects of Database languages Some aspects of Database-system implementation Concepts and algorithms in a general setting that is not tied to one particular database system ...
4D2a – Data Engineering
... Information systems management course runs over the entire 1st Semester. In each week, there are three one-hour lectures. However, tutorials are scheduled in place of a lecture every two weeks. Alongside the lectures, a full online course on the application of database language SQL is delivered. Thi ...
... Information systems management course runs over the entire 1st Semester. In each week, there are three one-hour lectures. However, tutorials are scheduled in place of a lecture every two weeks. Alongside the lectures, a full online course on the application of database language SQL is delivered. Thi ...
CSc-340 10a
... Extension to test for view serializability has cost exponential in the size of the precedence graph. ...
... Extension to test for view serializability has cost exponential in the size of the precedence graph. ...
HAT, not CAP: Towards Highly Available Transactions
... is not achievable with high availability [36]. However, most ACID and “NewSQL” databases provide weaker forms of isolation—usually by default, and often as the only options offered (§2). Databases have provided these weak guarantees for decades [43], suggesting that they are useful to application pr ...
... is not achievable with high availability [36]. However, most ACID and “NewSQL” databases provide weaker forms of isolation—usually by default, and often as the only options offered (§2). Databases have provided these weak guarantees for decades [43], suggesting that they are useful to application pr ...
G08 - Spatial Database Group
... – Relational Cloud periodically determines which databases should be placed on which machines using a novel non-linear optimization formulation. – a cost model that estimates the combined resource utilization of multiple databases running on a machine. ...
... – Relational Cloud periodically determines which databases should be placed on which machines using a novel non-linear optimization formulation. – a cost model that estimates the combined resource utilization of multiple databases running on a machine. ...
Data Warehousing – CG124
... Assess different ways of extending the relational model and SQL (e.g object-relational extensions, PL/SQL); Explain, discuss, and evaluate Object-Oriented databases; Compare and contrast the relational data model with objectrelational and object-oriented data models; Critically evaluate query optimi ...
... Assess different ways of extending the relational model and SQL (e.g object-relational extensions, PL/SQL); Explain, discuss, and evaluate Object-Oriented databases; Compare and contrast the relational data model with objectrelational and object-oriented data models; Critically evaluate query optimi ...
Realisation of Active Multidatabases by Extending Standard
... of another component system of the MDBS directly. This may be useful when monitoring global business rules or checking global constraints (i.e. referential integrity of global data). • Few limitations to local autonomy: Many DBMSs already provide active behaviour in the form of trigger and stored pr ...
... of another component system of the MDBS directly. This may be useful when monitoring global business rules or checking global constraints (i.e. referential integrity of global data). • Few limitations to local autonomy: Many DBMSs already provide active behaviour in the form of trigger and stored pr ...