Physiology د. نصير جواد المختار Lecture X: Acid – Base Balance The
... The H ion concentration has always to be kept with normal range, otherwise enzymatic activities might be affected as increasing or decreasing the level and this might either stimulate or depress the activity. In general the H+ concentration of extracellular fluid represented by blood is usually cons ...
... The H ion concentration has always to be kept with normal range, otherwise enzymatic activities might be affected as increasing or decreasing the level and this might either stimulate or depress the activity. In general the H+ concentration of extracellular fluid represented by blood is usually cons ...
Document
... contracts - Systolic pressure Lowest BP is when the heart rests - Diastolic pressure Pulse pressure is the difference between the Systolic and Diastolic pressures BP 140/90 PP (pulse pressure) = 50 ...
... contracts - Systolic pressure Lowest BP is when the heart rests - Diastolic pressure Pulse pressure is the difference between the Systolic and Diastolic pressures BP 140/90 PP (pulse pressure) = 50 ...
Chapter 21: Blood Vessels and Circulation
... In clinical settings, blood pressure usually refers to blood pressure in the main arteries, which varies during the cardiac cycle, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 21-9 (Pressures within the Systemic Circuit). The systolic blood pressure is the peak of arterial pressure generated during ventricular c ...
... In clinical settings, blood pressure usually refers to blood pressure in the main arteries, which varies during the cardiac cycle, as shown in 10th Martini Figure 21-9 (Pressures within the Systemic Circuit). The systolic blood pressure is the peak of arterial pressure generated during ventricular c ...
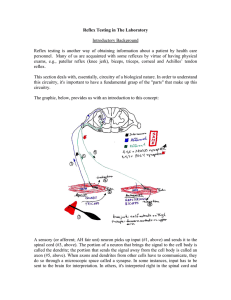
Reflex Testing in The Laboratory
... examiner strikes his or her OWN thumb (nail is best) with the pointed end of the reflex hammer. As it may be difficult to observe forearm flexion, the observer feels for and looks for a twitching in the area struck under and around the examiner’s thumb. ...
... examiner strikes his or her OWN thumb (nail is best) with the pointed end of the reflex hammer. As it may be difficult to observe forearm flexion, the observer feels for and looks for a twitching in the area struck under and around the examiner’s thumb. ...
PAC01 Pulmonary Physiology
... the aortic arch and communicate with the medulla via CN-X (vagus). There are other peripheral chemoreceptors located in the carotid bodies (where the CCA biforcates into ECA and ICA). The carotid bodies communicate with the medulla via CN-IX (glossopharyngeal) The chemoreceptors input to the brainst ...
... the aortic arch and communicate with the medulla via CN-X (vagus). There are other peripheral chemoreceptors located in the carotid bodies (where the CCA biforcates into ECA and ICA). The carotid bodies communicate with the medulla via CN-IX (glossopharyngeal) The chemoreceptors input to the brainst ...
Haemodynamics
... Inhibits cardioacceleratory centers-CO↓ Stimulates cardioinhibitory center-CO↓ decreased blood pressure ...
... Inhibits cardioacceleratory centers-CO↓ Stimulates cardioinhibitory center-CO↓ decreased blood pressure ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign kj - Region 11 Math And Science Teacher
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
D - VCOMcc
... C. Agent B increased preload while Agent A did not. D. Agent B increased the internal work of the LV more than agent A. E. Cardiac efficiency is greater with agent B than agent A. 32. Which of the following statements about cerebral circulation is true? A. Excessive pressure in the brain case is rem ...
... C. Agent B increased preload while Agent A did not. D. Agent B increased the internal work of the LV more than agent A. E. Cardiac efficiency is greater with agent B than agent A. 32. Which of the following statements about cerebral circulation is true? A. Excessive pressure in the brain case is rem ...
Does an increase in filtration always cause edema? NO NO NO
... There is less pressure to act as a retaining force in the capillary, so fluid leaves the vessels for the interstitial spaces This increases the tissue pressure significantly above its normal level of about zero mm/Hg Lymphatics try to remove the excessive filtration out of the circulation alon ...
... There is less pressure to act as a retaining force in the capillary, so fluid leaves the vessels for the interstitial spaces This increases the tissue pressure significantly above its normal level of about zero mm/Hg Lymphatics try to remove the excessive filtration out of the circulation alon ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign LQ
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
07 Blood Press Vital Sign
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
... Blood pressure is a measure of the changing fluid pressure within the circulatory system. It varies from a peak pressure produced by contraction of the left ventricle, to a low pressure, which is maintained by closure of the aortic valve and elastic recoil of the arterial system. The peak pressure i ...
Regulation of Blood
... cardiac output) and the decreased 02 -carrying capacity of the blood (decreased hematocrit). 7. Mrs. Byrne's pale, cold skin is typical of the response to hemorrhage, reflecting vasoconstriction of cutaneous arterioles. As the baroreceptor reflex was initiated in response to decreased arterial press ...
... cardiac output) and the decreased 02 -carrying capacity of the blood (decreased hematocrit). 7. Mrs. Byrne's pale, cold skin is typical of the response to hemorrhage, reflecting vasoconstriction of cutaneous arterioles. As the baroreceptor reflex was initiated in response to decreased arterial press ...
13/mhso2/015 course code: phs212 physiology of
... are somewhat different from those of the corpora cavernosa. During erection , the arterial flow increases in a similar manner; however, the pressure in the corpora cavernosa because the tunical covering (thin over the corpus spongiosum and virtually absent over the glans) ensures minimal venous occl ...
... are somewhat different from those of the corpora cavernosa. During erection , the arterial flow increases in a similar manner; however, the pressure in the corpora cavernosa because the tunical covering (thin over the corpus spongiosum and virtually absent over the glans) ensures minimal venous occl ...
Lec 8Aviation, High-Altitude by Prof. Saboohi
... expands the capillaries and increases the surface area through which oxygen can diffuse into the blood. • 2-An increase in lung air volume, which expands the surface area of the alveolar-capillary interface still more. • 3-An increase in pulmonary arterial blood pressure; this • forces blood into gr ...
... expands the capillaries and increases the surface area through which oxygen can diffuse into the blood. • 2-An increase in lung air volume, which expands the surface area of the alveolar-capillary interface still more. • 3-An increase in pulmonary arterial blood pressure; this • forces blood into gr ...
Conduction Velocity and Patellar Reflex Blah A. Blah Partner B
... based on the patellar reflex as the subject is put through three different conditions: the Jendrassik’s maneuver, mental distraction, and fatigue. The main function of the stretch reflex is to maintain the muscle at a constant length, which the brain sets via the motor neurons. This experiment will ...
... based on the patellar reflex as the subject is put through three different conditions: the Jendrassik’s maneuver, mental distraction, and fatigue. The main function of the stretch reflex is to maintain the muscle at a constant length, which the brain sets via the motor neurons. This experiment will ...
Conduction Velocity and Patellar Reflex Blah A. Blah Parter 1
... based on the patellar reflex as the subject is put through three different conditions: the Jendrassik’s maneuver, mental distraction, and fatigue. The main function of the stretch reflex is to maintain the muscle at a constant length, which the brain sets via the motor neurons. This experiment will ...
... based on the patellar reflex as the subject is put through three different conditions: the Jendrassik’s maneuver, mental distraction, and fatigue. The main function of the stretch reflex is to maintain the muscle at a constant length, which the brain sets via the motor neurons. This experiment will ...
Glomerular Filtration
... • The cortex receives more than 90% of the blood that perfused into the kidney, which is perfused at a rate of about 500 ml/min per 100 gm tissue. (100 times greater than resting muscle blood flow) The remainder of the renal blood supply goes to the capsule and the renal adipose tissue. Some of the ...
... • The cortex receives more than 90% of the blood that perfused into the kidney, which is perfused at a rate of about 500 ml/min per 100 gm tissue. (100 times greater than resting muscle blood flow) The remainder of the renal blood supply goes to the capsule and the renal adipose tissue. Some of the ...
PP Chapter 19-Blood Vessels
... Even with the two factors above, this is not enough to cause proper flow – Respiratory pump (pressure changes in ventral body cavity) in which breathing squeezes the BV’s and causes blood flow – Muscular pump and the contraction of muscles ...
... Even with the two factors above, this is not enough to cause proper flow – Respiratory pump (pressure changes in ventral body cavity) in which breathing squeezes the BV’s and causes blood flow – Muscular pump and the contraction of muscles ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... Low Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol (LDL-C) is required for normal cell function… transporting cholesterol to the cells for use in synthesis of hormones as well as maintenance of cell membranes Excess LDL-C is taken in by the endothelial cells (especially areas of low endothelial sheer – where blood ...
... Low Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol (LDL-C) is required for normal cell function… transporting cholesterol to the cells for use in synthesis of hormones as well as maintenance of cell membranes Excess LDL-C is taken in by the endothelial cells (especially areas of low endothelial sheer – where blood ...
(Renal haemodynamic and GFR).
... • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, shape and electrical charges and ultra-filtration coefficient. • Describe Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanism that regulate GFR. • Describe autoregul ...
... • Define GFR and quote normal value. • Identify and describe the factors controlling GFR in terms of starling forces, permeability with respect to size, shape and electrical charges and ultra-filtration coefficient. • Describe Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanism that regulate GFR. • Describe autoregul ...
Michael Zundel, MD (MARC Presenter) Handout
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
... Upon standing, impaired vasoconstriction allows blood pooling in dependent extremities Venous pooling causes decreased venous return, leading to intrathoracic hypovolemia and compensatory reflex tachycardia Blood pressure usually normal but can be low Tx: Vasoconstrictors, mineralocorticoid analogs ...
Effects Of Microgravity on the Circulatory System
... of the blood, such as the quantity of blood cells within the plasma ...
... of the blood, such as the quantity of blood cells within the plasma ...
LAB: Nerve Reflexes
... Nerve impulses follow routes through the nervous system called nerve pathways. Some of the simplest nerve pathways consist of little more than two neurons that communicate across a single synapse. A reflex is a relatively simple motor response that does not involve a large number of interneurons (or ...
... Nerve impulses follow routes through the nervous system called nerve pathways. Some of the simplest nerve pathways consist of little more than two neurons that communicate across a single synapse. A reflex is a relatively simple motor response that does not involve a large number of interneurons (or ...
Reflexes Reaction time
... – simple (blink, cough, sneeze) or complex (gulping reflex, defensive reflex). ...
... – simple (blink, cough, sneeze) or complex (gulping reflex, defensive reflex). ...
Cushing reflex

Cushing reflex (also referred to as the vasopressor response, the Cushing effect, the Cushing reaction, the Cushing phenomenon, the Cushing response, or Cushing's Law) is a physiological nervous system response to increased intracranial pressure (ICP) that results in Cushing's triad of increased blood pressure, irregular breathing, and a reduction of the heart rate. It is usually seen in the terminal stages of acute head injury and may indicate imminent brain herniation. It can also be seen after the intravenous administration of epinephrine and similar drugs. It was first described in detail by American neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing in 1901.