Lecture, Week 1: September 27th - October 3rd, 1999 Outline 1
... reality at the level of atoms, sub-atomic particles and below remained mysterious. These effects are approached through quantum mechanics, a branch of physics developed in the early 1900's by Niels Bohr of Denmark, Erwin Schrodinger of Austria, and Werner Heisenberg of Germany.Quantum mechanics expl ...
... reality at the level of atoms, sub-atomic particles and below remained mysterious. These effects are approached through quantum mechanics, a branch of physics developed in the early 1900's by Niels Bohr of Denmark, Erwin Schrodinger of Austria, and Werner Heisenberg of Germany.Quantum mechanics expl ...
Characterizing Quantum Supremacy in Near
... We find a good convergence for the first ten moments and the entropy at depth 25 with circuits of up to 7 × 6 qubits in a 2D lattice. Using chaos theory, the properties of the Porter-Thomas distribution, and numerical simulations, we argue that the cross entropy is closely related to the circuit fid ...
... We find a good convergence for the first ten moments and the entropy at depth 25 with circuits of up to 7 × 6 qubits in a 2D lattice. Using chaos theory, the properties of the Porter-Thomas distribution, and numerical simulations, we argue that the cross entropy is closely related to the circuit fid ...
Variational approach to the Davydov soliton
... There are two different components of Davydov's theory of soliton transport in one-dimensional coupled exciton phonon systems. The first is the form of the wave function (either ~Di & or ~Dz &); the second is the set of equations describing the time evolution of these wave functions. In the present ...
... There are two different components of Davydov's theory of soliton transport in one-dimensional coupled exciton phonon systems. The first is the form of the wave function (either ~Di & or ~Dz &); the second is the set of equations describing the time evolution of these wave functions. In the present ...
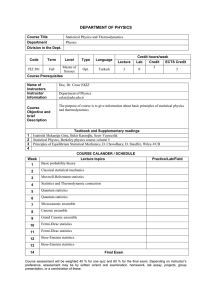
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Course Title Statistical Physics and
... Variational principles and Lagrange’s equations ...
... Variational principles and Lagrange’s equations ...
Quantum Hall Effects and Related Topics International Symposium
... The electron motion in graphene, first fabricated by mechanical exfoliation method and later by various other methods, is governed by Weyl’s equation for a neutrino or the Dirac equation with vanishing rest mass. The pseudo-spin is quantized into the direction of the electron motion and the wave func ...
... The electron motion in graphene, first fabricated by mechanical exfoliation method and later by various other methods, is governed by Weyl’s equation for a neutrino or the Dirac equation with vanishing rest mass. The pseudo-spin is quantized into the direction of the electron motion and the wave func ...
Entanglement spectrum of a random partition: Connection with the
... gram as a function of probability p, finding agreement with the physical phase diagram of a disordered superconductor [16]. We begin by considering a translationally invariant topological state, which can be either a topological insulator or superconductor or a bosonic symmetry-protected topological ...
... gram as a function of probability p, finding agreement with the physical phase diagram of a disordered superconductor [16]. We begin by considering a translationally invariant topological state, which can be either a topological insulator or superconductor or a bosonic symmetry-protected topological ...
Visualizing the Coupling between Red and Blue Stark States
... Stark states was recently validated in experiments on hydrogen [13,20] and lithium [14]. Here, we exploit this capability to directly visualize changes in the Stark wave function when interference narrowing occurs. Photoionization microscopy experiments are best described using parabolic coordinates ...
... Stark states was recently validated in experiments on hydrogen [13,20] and lithium [14]. Here, we exploit this capability to directly visualize changes in the Stark wave function when interference narrowing occurs. Photoionization microscopy experiments are best described using parabolic coordinates ...
Quotient–Comprehension Chains
... where p⊥ is the negation of p. Such a connection between the fundamental concepts of quotient, comprehension and measurement is fascinating! Quotients and comprehension have a clean description in categorical logic as adjoints (see below for details). Does that lead to instruments as a property? Thi ...
... where p⊥ is the negation of p. Such a connection between the fundamental concepts of quotient, comprehension and measurement is fascinating! Quotients and comprehension have a clean description in categorical logic as adjoints (see below for details). Does that lead to instruments as a property? Thi ...
Gnoseology, Ontology, and the Arrow of Time
... what it is supposed to be an ontological property of nature. The strategy is remarkable for a philosopher of science. It shows how the scientist can choose mathematical instruments which allow scientific constructions to (partially) manifest what nature is. Undoubtedly, the measure of time is likewi ...
... what it is supposed to be an ontological property of nature. The strategy is remarkable for a philosopher of science. It shows how the scientist can choose mathematical instruments which allow scientific constructions to (partially) manifest what nature is. Undoubtedly, the measure of time is likewi ...
Lecture notes
... Nikhef is the Dutch institute for subatomic physics. (The name was originally an acronym for ”Nationaal Instituut voor Kern en Hoge Energie Fysica”.) The name Nikhef is used to indicate simultaneously two overlapping organisations: • Nikhef is a national research lab (“institute”) funded by the foun ...
... Nikhef is the Dutch institute for subatomic physics. (The name was originally an acronym for ”Nationaal Instituut voor Kern en Hoge Energie Fysica”.) The name Nikhef is used to indicate simultaneously two overlapping organisations: • Nikhef is a national research lab (“institute”) funded by the foun ...
A parallel repetition theorem for entangled projection
... A game G is specified by a probability distribution µ on pairs of questions (u, v) ∈ U × V to the players, and an acceptance criterion V ⊆ A × B × U × V which states, for every possible pair of questions (u, v), which pairs of answers ( a, b) ∈ A × B are valid. The most basic quantity associated to ...
... A game G is specified by a probability distribution µ on pairs of questions (u, v) ∈ U × V to the players, and an acceptance criterion V ⊆ A × B × U × V which states, for every possible pair of questions (u, v), which pairs of answers ( a, b) ∈ A × B are valid. The most basic quantity associated to ...
Photons and Polarization
... Photons and Polarization Now that we’ve understood the classical picture of polarized light, it will be very enlightening to think about what is going on with the individual photons in some polarization experiments. This simple example will reveal many features common to all quantum mechanical syste ...
... Photons and Polarization Now that we’ve understood the classical picture of polarized light, it will be very enlightening to think about what is going on with the individual photons in some polarization experiments. This simple example will reveal many features common to all quantum mechanical syste ...