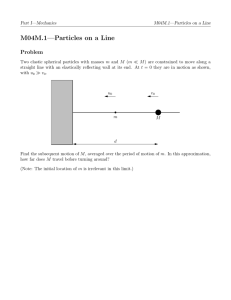
PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable
... PROBLEM 3 [25 PTS] For a gas of distinguishable particles, we’ve seen that the relative probability of any particle having the energy E is given by the Boltzmann factor fB = e−E/kT . Consider a two-dimensional ideal gas of temperature T composed of N distinguishable objects of mass m whose degrees ...
... PROBLEM 3 [25 PTS] For a gas of distinguishable particles, we’ve seen that the relative probability of any particle having the energy E is given by the Boltzmann factor fB = e−E/kT . Consider a two-dimensional ideal gas of temperature T composed of N distinguishable objects of mass m whose degrees ...
The Emergence of a Macro-World: A Study of Intertheory Relations in Classical and Quantum Mechanics
... We look at how Newtonian mechanics addresses the problem of discontinuous jumps in Section 3. Then, in Section 4, we sketch the QM treatment of a particle in an infinite potential well. Our purpose is not merely to prove the incompleteness of Ehrenfest’s equations, but to compare the definitions of pr ...
... We look at how Newtonian mechanics addresses the problem of discontinuous jumps in Section 3. Then, in Section 4, we sketch the QM treatment of a particle in an infinite potential well. Our purpose is not merely to prove the incompleteness of Ehrenfest’s equations, but to compare the definitions of pr ...
Gravitational Waves and Gravitons
... Experimental confirmation of G waves was first provided by Russell Hulse and John Taylor for which they were awarded the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physics. They examined the rotation rate of the system PSR B1913 + 16 which consists of a gravitationally bound star and pulsar (rotating neutron star with hug ...
... Experimental confirmation of G waves was first provided by Russell Hulse and John Taylor for which they were awarded the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physics. They examined the rotation rate of the system PSR B1913 + 16 which consists of a gravitationally bound star and pulsar (rotating neutron star with hug ...
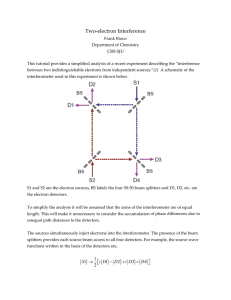
The quantum mechanics of photon addition and subtraction
... By adding only one photon, any input state is converted into a nonclassical state that cannot be described by classical theory. As seen in Figure 2, we added a photon to a thermal field (the most classical field) which makes the state have negative values in its Wigner function. This is a typical si ...
... By adding only one photon, any input state is converted into a nonclassical state that cannot be described by classical theory. As seen in Figure 2, we added a photon to a thermal field (the most classical field) which makes the state have negative values in its Wigner function. This is a typical si ...
Lecture 8 Relevant sections in text: §1.6 Momentum
... to construct a state with a very small dispersion in X (or P ) then the dispersion in P (or X) must become large. Note also that the uncertainty relation shows the dispersion in position or and/or momentum can never vanish! However, either of them can be made arbitrarily small provided the other obs ...
... to construct a state with a very small dispersion in X (or P ) then the dispersion in P (or X) must become large. Note also that the uncertainty relation shows the dispersion in position or and/or momentum can never vanish! However, either of them can be made arbitrarily small provided the other obs ...
May 2004
... What is the degeneracy of the ground state? Give all quantum numbers and symmetries of the ground state(s), including the electron and proton degrees of freedom. ...
... What is the degeneracy of the ground state? Give all quantum numbers and symmetries of the ground state(s), including the electron and proton degrees of freedom. ...
Quantum mechanics of a free particle from properties of the Dirac
... the space of “good” functions.16 Even though this definition might not be very appealing at first sight, it leads to consistent and fruitful mathematics.16 The theory of distributions allows us to perform linear operations on distributions as if they were ordinary functions. One result is the rule f ...
... the space of “good” functions.16 Even though this definition might not be very appealing at first sight, it leads to consistent and fruitful mathematics.16 The theory of distributions allows us to perform linear operations on distributions as if they were ordinary functions. One result is the rule f ...
Multi-Particle States 31.1 Multi
... isolation. Indeed, we can establish the relative correctness of an electron in isolation only by considering its relation to other electrons and particles. This is the task we now undertake: A description of wavefunctions of systems. Particles in isolation is itself a classical concept – fundamental ...
... isolation. Indeed, we can establish the relative correctness of an electron in isolation only by considering its relation to other electrons and particles. This is the task we now undertake: A description of wavefunctions of systems. Particles in isolation is itself a classical concept – fundamental ...
lect4 - Personal Webpages (The University of Manchester)
... These slides at: www.man.ac.uk/dalton/phys30101 ...
... These slides at: www.man.ac.uk/dalton/phys30101 ...
E3570: A particle on a disc with a homogeneous magnetic... levels
... A particle is bound to move on the XY plane in the presence of a homogeneous magnetic field perpendicular to the plane. (1) Write the Hamiltonian in Cartesian coordinates. (2) Show that the Hamiltonian is of a two dimensional harmonic oscillator + a Zeeman term. (3) Write down the Hamiltonian in pol ...
... A particle is bound to move on the XY plane in the presence of a homogeneous magnetic field perpendicular to the plane. (1) Write the Hamiltonian in Cartesian coordinates. (2) Show that the Hamiltonian is of a two dimensional harmonic oscillator + a Zeeman term. (3) Write down the Hamiltonian in pol ...
Presentation - Oxford Physics
... The other thing I learn from all this is how subtle and wonderful the world is. ...
... The other thing I learn from all this is how subtle and wonderful the world is. ...
1 The Time-Dependent and Time-Independent Schrödinger Equations
... ψn for the unperturbed problem form a complete set, i.e., any arbitrary function, in particular the wave functions for the perturbed problem, can be written as a linear sum of these. Our assumption can be formulated thus: X ...
... ψn for the unperturbed problem form a complete set, i.e., any arbitrary function, in particular the wave functions for the perturbed problem, can be written as a linear sum of these. Our assumption can be formulated thus: X ...
Quantum theory
... function is a function of r 1 , r 2 , and r 12 , the distance of the two electrons from each other. He assumed a ‘‘trial function’’ depending on these variables and on some parameters, and then minimized the total energy as a function of these parameters. The resulting energy was very accurate. Othe ...
... function is a function of r 1 , r 2 , and r 12 , the distance of the two electrons from each other. He assumed a ‘‘trial function’’ depending on these variables and on some parameters, and then minimized the total energy as a function of these parameters. The resulting energy was very accurate. Othe ...
ppt - vlsicad server (Prof. Markov`s group)
... • Classical bit – Two possible states: 0 or 1 – Measurement is straightforward ...
... • Classical bit – Two possible states: 0 or 1 – Measurement is straightforward ...
Area Courses Electromagnetics, Optics, Photonics
... Please check the University Catalogue for specific course details including any recommended prepatory courses and Degree Requirements ...
... Please check the University Catalogue for specific course details including any recommended prepatory courses and Degree Requirements ...
![PROBLEM 1 [25 PTS] A system consists of N distinquishable](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006063913_1-e1778e5c6114fd66466f556bb5f30c03-300x300.png)