Oleg Teryaev
... Newtonian – “Falling elevator” – well known and checked Post-Newtonian – gravity action on SPIN – known since 1962 (Kobzarev and Okun) – not checked on purpose but in fact checked in atomic spins experiments at % level (Silenko,OT’07) Anomalous gravitomagnetic moment iz ZERO or Classical and QUANTUM ...
... Newtonian – “Falling elevator” – well known and checked Post-Newtonian – gravity action on SPIN – known since 1962 (Kobzarev and Okun) – not checked on purpose but in fact checked in atomic spins experiments at % level (Silenko,OT’07) Anomalous gravitomagnetic moment iz ZERO or Classical and QUANTUM ...
Chemistry in Four Dimensions
... The reluctance to abandon dogmatic theory often results in the introduction of secondary ad hoc explanations to cover up any cracks in the theory, as they occur. A prime example occurs in the quantum theory of elemental periodicity. Based on the wave-mechanical ordering of electronic energy levels i ...
... The reluctance to abandon dogmatic theory often results in the introduction of secondary ad hoc explanations to cover up any cracks in the theory, as they occur. A prime example occurs in the quantum theory of elemental periodicity. Based on the wave-mechanical ordering of electronic energy levels i ...
Nick-Evans
... coupled at the Planck Scale The strings length at 10-34 m would cut off the theory Quantum vacuum energies represent an enormous and unobserved dark energy component ...
... coupled at the Planck Scale The strings length at 10-34 m would cut off the theory Quantum vacuum energies represent an enormous and unobserved dark energy component ...
Atom 2 - UF Physics
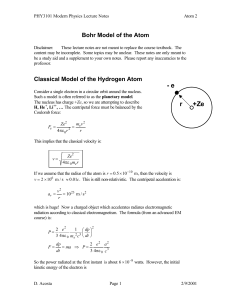
... Bohr’s Postulates In 1913, Bohr proposed several postulates in an attempt to describe the atom. 1. Atoms have stationary states of definite energy. These states do not radiate any energy, as is necessary to explain the stability of atoms. 2. The emission and absorption of electromagnetic energy can ...
... Bohr’s Postulates In 1913, Bohr proposed several postulates in an attempt to describe the atom. 1. Atoms have stationary states of definite energy. These states do not radiate any energy, as is necessary to explain the stability of atoms. 2. The emission and absorption of electromagnetic energy can ...
CHAPTER 7: The Hydrogen Atom
... emitted by atoms in a magnetic field split into multiple energy levels. It is called the Zeeman effect. A spectral line is split into three lines. Consider the atom to behave like a small magnet. Think of an electron as an orbiting circular current loop of I = dq / dt around the nucleus. The current ...
... emitted by atoms in a magnetic field split into multiple energy levels. It is called the Zeeman effect. A spectral line is split into three lines. Consider the atom to behave like a small magnet. Think of an electron as an orbiting circular current loop of I = dq / dt around the nucleus. The current ...
Peter Heuer - Quantum Cryptography Using Single and Entangled
... defects, but the small size of nanodiamonds limits the effects of refraction due the high index of refraction of diamond. When illuminated, color centers fluoresce much like a quantum dot. Unlike quantum dots, color centers do not bleach or blink, making them more much more stable. However, since c ...
... defects, but the small size of nanodiamonds limits the effects of refraction due the high index of refraction of diamond. When illuminated, color centers fluoresce much like a quantum dot. Unlike quantum dots, color centers do not bleach or blink, making them more much more stable. However, since c ...
How are quantum numbers used to describe electrons
... How many orbitals in the 4th energy level? How many electrons can be in the 4th energy level? For the known elements, ________ orbitals and ______ electrons is the maximum number in energy levels 5-7. What rules are used to explain how electrons fill orbitals? Pauli exclusion principle—no two electr ...
... How many orbitals in the 4th energy level? How many electrons can be in the 4th energy level? For the known elements, ________ orbitals and ______ electrons is the maximum number in energy levels 5-7. What rules are used to explain how electrons fill orbitals? Pauli exclusion principle—no two electr ...
5 Path Integrals in Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Field Theory
... where, in the last equality we have rescaled τ → τ /!. Eq. (5.63) is known as the Feynman-Kac Formula. Since the Partition Function is a trace over states, we must use boundary conditions such that the initial and final states are the same state, and to sum over all such states. In other terms, we m ...
... where, in the last equality we have rescaled τ → τ /!. Eq. (5.63) is known as the Feynman-Kac Formula. Since the Partition Function is a trace over states, we must use boundary conditions such that the initial and final states are the same state, and to sum over all such states. In other terms, we m ...
Calculation of the energies of hard X
... This property is published in IEEE J. Quantum Electronics, 43, 1183, 2007 This property is proved without using the semiclassical (WKB) approximation or the approximation of the geometrical optics CONCLUSION There is a direct connection between the quantum and classical functions, Ψ0 and S0 which co ...
... This property is published in IEEE J. Quantum Electronics, 43, 1183, 2007 This property is proved without using the semiclassical (WKB) approximation or the approximation of the geometrical optics CONCLUSION There is a direct connection between the quantum and classical functions, Ψ0 and S0 which co ...
quantum numbers - Cloudfront.net
... PRINCIPAL QUANTUM NUMBER Electron Cloud Size (n) Indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron Can take on integer values n = 1, 2, 3,…. Largely determine the energy of the orbital (bigger n value = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of n belong to the same she ...
... PRINCIPAL QUANTUM NUMBER Electron Cloud Size (n) Indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron Can take on integer values n = 1, 2, 3,…. Largely determine the energy of the orbital (bigger n value = higher energy) All electrons in an atom with the same value of n belong to the same she ...
institute of chemical technology
... Physics is a fundamental science close to nature and involves study of matter and its motion in space- time, energy and force. Physics is both important and influential because advances in its understanding have often translated into newer technologies, which are of interdisciplinary consequences. A ...
... Physics is a fundamental science close to nature and involves study of matter and its motion in space- time, energy and force. Physics is both important and influential because advances in its understanding have often translated into newer technologies, which are of interdisciplinary consequences. A ...
QUANTUM MATTERS What is the matter? Einstein`s
... into something that we are more familiar with—sets. The object x is completely characterized by the sets Hom(x,y). 1.2.2. Unitarity and Locality. In the sense above, all physical systems are quantum systems. Their theoretical models are ultimately established by a trial-and-error process from experi ...
... into something that we are more familiar with—sets. The object x is completely characterized by the sets Hom(x,y). 1.2.2. Unitarity and Locality. In the sense above, all physical systems are quantum systems. Their theoretical models are ultimately established by a trial-and-error process from experi ...
Document
... This splitting is called fine structure Another quantum number, ms, called the spin magnetic quantum number, was introduced to explain the fine structure ...
... This splitting is called fine structure Another quantum number, ms, called the spin magnetic quantum number, was introduced to explain the fine structure ...
powerpoint
... your superpower?". Everyone has superpowers, even if their individual beliefs may hinder their development. This talk is for you, whether you disbelieve in superpowers because "science says it impossible" or you already know one of your superpowers. We will discuss the science behind how the mind ca ...
... your superpower?". Everyone has superpowers, even if their individual beliefs may hinder their development. This talk is for you, whether you disbelieve in superpowers because "science says it impossible" or you already know one of your superpowers. We will discuss the science behind how the mind ca ...
22.101 Applied Nuclear Physics (Fall 2004) Lecture 4 (9/20/04)
... from the origin. This effect is of course absent in the case of l = 0, a state of zero orbital angular momentum, as one would expect. The first few l states usually are the only ones of interest in our discussion (because they tend to have the lowest energies); they are given special spectroscopic d ...
... from the origin. This effect is of course absent in the case of l = 0, a state of zero orbital angular momentum, as one would expect. The first few l states usually are the only ones of interest in our discussion (because they tend to have the lowest energies); they are given special spectroscopic d ...
Asymptotic Freedom and Quantum
... they showed that a systematic perturbation expansion could be defined. This means that the amplitude for scattering between electrically charged particles can be written as an expansion in powers of the fine structure constant, αem, which is a measure of the strength of the electric force. When comp ...
... they showed that a systematic perturbation expansion could be defined. This means that the amplitude for scattering between electrically charged particles can be written as an expansion in powers of the fine structure constant, αem, which is a measure of the strength of the electric force. When comp ...