PDF
... taking into account other linear combinations? A: This is obvious. There are modifications of Wigner’s quasi-distribution that still give the correct marginal distributions for position and momentum. For an easy example, choose a rectangle R centered at the origin in the (x, p) phase plane and modif ...
... taking into account other linear combinations? A: This is obvious. There are modifications of Wigner’s quasi-distribution that still give the correct marginal distributions for position and momentum. For an easy example, choose a rectangle R centered at the origin in the (x, p) phase plane and modif ...
physics and narrative - Rutgers Philosophy Department
... theory aren’t going to be narratable. Suppose (for example) that the momentum of a free particle is measured along the hypersurface marked t=0 in figure 5, and that later on a collapse leaves the particle localized at P. Then the projection-postulate that Aharonov and I proposed is going to stipulat ...
... theory aren’t going to be narratable. Suppose (for example) that the momentum of a free particle is measured along the hypersurface marked t=0 in figure 5, and that later on a collapse leaves the particle localized at P. Then the projection-postulate that Aharonov and I proposed is going to stipulat ...
Beating the Standard Quantum Limit
... when simultaneously measuring incompatible observables such as position x and momentum p the product of the spreads is lower bounded: ∆x ∆p ≥ ~/2, where ~ is the Planck constant. The same is true when measuring one of the observables (say x) on a set of particles prepared with a spread ∆p on the oth ...
... when simultaneously measuring incompatible observables such as position x and momentum p the product of the spreads is lower bounded: ∆x ∆p ≥ ~/2, where ~ is the Planck constant. The same is true when measuring one of the observables (say x) on a set of particles prepared with a spread ∆p on the oth ...
Quantum interference in the classically forbidden region: A parametric oscillator
... reaching the quantum regime 关9,10兴. In this regime tunneling between coexisting classically stable periodic states should become important, for weak dissipation. It was first studied for a resonantly driven oscillator, where a semiclassical analysis 关11兴 made it possible to find the tunneling expone ...
... reaching the quantum regime 关9,10兴. In this regime tunneling between coexisting classically stable periodic states should become important, for weak dissipation. It was first studied for a resonantly driven oscillator, where a semiclassical analysis 关11兴 made it possible to find the tunneling expone ...
hdwsmp2011 - FSU High Energy Physics
... Colliding bunches of protons and anti-protons; bunches meet each other every 396 ns in the center of two detectors (DØ and CDF) (steered apart at other places) Each particle has ~ 980 GeV of energy, so the total energy in the center of mass ...
... Colliding bunches of protons and anti-protons; bunches meet each other every 396 ns in the center of two detectors (DØ and CDF) (steered apart at other places) Each particle has ~ 980 GeV of energy, so the total energy in the center of mass ...
Hidden symmetries in the energy levels of excitonic `artificial atoms`
... The two lowest traces show the emission spectra when only the s shell is occupied; the other traces give the emission for different pshell occupations (from one up to four excitons) with the s shell fully occupied. Owing to the hidden symmetries the p-shell emission indeed varies only slightly with ...
... The two lowest traces show the emission spectra when only the s shell is occupied; the other traces give the emission for different pshell occupations (from one up to four excitons) with the s shell fully occupied. Owing to the hidden symmetries the p-shell emission indeed varies only slightly with ...
Reflections on Friction in Quantum Mechanics
... An ensemble will have some average energy E = pi Ei (where pi = p(Ei ) is the probability to find the system in a certain energy eigenstate). A rapid change in external constraints corresponds to a change in some external semi-classical field in the system’s Hamiltonian. For the paradigmatic case of ...
... An ensemble will have some average energy E = pi Ei (where pi = p(Ei ) is the probability to find the system in a certain energy eigenstate). A rapid change in external constraints corresponds to a change in some external semi-classical field in the system’s Hamiltonian. For the paradigmatic case of ...
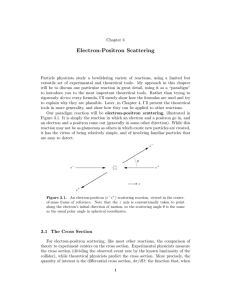
Electron-Positron Scattering
... diagram I’ve labeled each vertex with a four-vector position in spacetime, x or y. I’ve also labeled each external line with a four-vector momentum. (Later we’ll express these momenta in terms of their components in our coordinate system, for instance, p1 = (E, 0, 0, E) for the massless ingoing elec ...
... diagram I’ve labeled each vertex with a four-vector position in spacetime, x or y. I’ve also labeled each external line with a four-vector momentum. (Later we’ll express these momenta in terms of their components in our coordinate system, for instance, p1 = (E, 0, 0, E) for the massless ingoing elec ...
Schumacher Compression
... the IID setting (recall the development in Section 13.4). That is, if one compresses at a rate above the Shannon entropy, then it is possible to recover the compressed data perfectly in the asymptotic limit, and otherwise, it is not possible to do so.1 This theorem establishes the prominent role of ...
... the IID setting (recall the development in Section 13.4). That is, if one compresses at a rate above the Shannon entropy, then it is possible to recover the compressed data perfectly in the asymptotic limit, and otherwise, it is not possible to do so.1 This theorem establishes the prominent role of ...
THERMODYNAMICS AND INTRODUCTORY STATISTICAL
... 2) If the particles are quantal, that is, indistinguishable and there are no restrictions as to the number of particles per energy state, we have to use the Bose-Einstein statistical count. 3) If the particles are quantal, that is, indistinguishable and restricted to no more than one particle per st ...
... 2) If the particles are quantal, that is, indistinguishable and there are no restrictions as to the number of particles per energy state, we have to use the Bose-Einstein statistical count. 3) If the particles are quantal, that is, indistinguishable and restricted to no more than one particle per st ...
Superfluidity in Ultracold Fermi Gases
... Cooper suggested that the instability of the normal (metallic) phase, because of electrons binding into pairs, was associated with the occurrence of superconductivity N.B. Cooper pairs form and condensed at the same temperature scale (pairing instability)! ...
... Cooper suggested that the instability of the normal (metallic) phase, because of electrons binding into pairs, was associated with the occurrence of superconductivity N.B. Cooper pairs form and condensed at the same temperature scale (pairing instability)! ...
Science Journals — AAAS
... quantum computers (1–3), which, as they increase in scale, will allow enhanced performance of tasks in secure networking, simulations, distributed computing, and other key tasks where exponential speedups are available. Processing circuits to realize these applications are built up from logic gates ...
... quantum computers (1–3), which, as they increase in scale, will allow enhanced performance of tasks in secure networking, simulations, distributed computing, and other key tasks where exponential speedups are available. Processing circuits to realize these applications are built up from logic gates ...
Quantum computation and cryptography: an overview
... traditional, classical, methods. The processing of the information carried by the wave function of a quantum physical system is the task of the new Quantum Information Theory (Schumacher 1995), a perfect marriage between Information Theory and Quantum Mechanics, comparable to the symbiosis between P ...
... traditional, classical, methods. The processing of the information carried by the wave function of a quantum physical system is the task of the new Quantum Information Theory (Schumacher 1995), a perfect marriage between Information Theory and Quantum Mechanics, comparable to the symbiosis between P ...
“Formal” vs. “Empirical” Approaches to Quantum
... at the level of the real physical behavior that can be accurately (if approximately) modeled in the theories. It is conceivable that one could successfully effect an empirical reduction by means of a formal reduction: if the reduced theory is a special case of the reducing theory, then any physical ...
... at the level of the real physical behavior that can be accurately (if approximately) modeled in the theories. It is conceivable that one could successfully effect an empirical reduction by means of a formal reduction: if the reduced theory is a special case of the reducing theory, then any physical ...
Presentation - Quantum History Project
... About Dirac’s book (with footnotes to 1927 papers by Dirac and Jordan): “Dirac’s method does not meet the demands of mathematical rigor in any way—not even when it is reduced in the natural and cheap way to the level that is common in theoretical physics … the correct formulation is not just a matte ...
... About Dirac’s book (with footnotes to 1927 papers by Dirac and Jordan): “Dirac’s method does not meet the demands of mathematical rigor in any way—not even when it is reduced in the natural and cheap way to the level that is common in theoretical physics … the correct formulation is not just a matte ...
A quantum logical and geometrical approach to the study of
... more information than “the sum” of the information contained in the states of its parts. This feature of quantum systems may be regarded as a strange fact when using classical reasoning, but it not strange at all in a landscape where the superposition principle holds. Given two systems S1 and S2, if ...
... more information than “the sum” of the information contained in the states of its parts. This feature of quantum systems may be regarded as a strange fact when using classical reasoning, but it not strange at all in a landscape where the superposition principle holds. Given two systems S1 and S2, if ...