Chapter 22 Distributed DBMSs - Concepts and Design Transparencies
... u Ensures that all distributed transactions maintain distributed database’s integrity and consistency. u Distributed transaction accesses data stored at more than one location. u Each transaction is divided into number of subtransactions, one for each site that has to be accessed. u DDBMS must ensur ...
... u Ensures that all distributed transactions maintain distributed database’s integrity and consistency. u Distributed transaction accesses data stored at more than one location. u Each transaction is divided into number of subtransactions, one for each site that has to be accessed. u DDBMS must ensur ...
Query Processing - Department of Computer Science
... entirety or do not occur at all, and if they occur, nothing else apparently went on during the time of their occurrence. The normal approach to ensuring atomicity of transactions is ‘serialization’, which forces transactions to run concurrently in a way that makes it appear that they ran one-at-atim ...
... entirety or do not occur at all, and if they occur, nothing else apparently went on during the time of their occurrence. The normal approach to ensuring atomicity of transactions is ‘serialization’, which forces transactions to run concurrently in a way that makes it appear that they ran one-at-atim ...
Introduction
... Shared resource, used by many departments and applications of an enterprise Contains several different record types Contains metadata -“knows” about structure and relationships in data Managed by database administrator - DBA ...
... Shared resource, used by many departments and applications of an enterprise Contains several different record types Contains metadata -“knows” about structure and relationships in data Managed by database administrator - DBA ...
Database Systems
... Shared resource, used by many departments and applications of an enterprise Contains several different record types Contains metadata -“knows” about structure and relationships in data Managed by database administrator - DBA ...
... Shared resource, used by many departments and applications of an enterprise Contains several different record types Contains metadata -“knows” about structure and relationships in data Managed by database administrator - DBA ...
DBdesignstages
... write it down in words ( and clearly) • If you find that additional assumptions are necessary, make them explicitly and include in your document. ...
... write it down in words ( and clearly) • If you find that additional assumptions are necessary, make them explicitly and include in your document. ...
Basic Marketing, 16e - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... according to the logical structure of the information Relational database – series of logically related two-dimensional tables or files for storing information ...
... according to the logical structure of the information Relational database – series of logically related two-dimensional tables or files for storing information ...
ConcurrencyControl
... In the first two cases, the transaction can continue immediately. In the last case the transaction is blocked until the lock is granted ...
... In the first two cases, the transaction can continue immediately. In the last case the transaction is blocked until the lock is granted ...
CH9
... A shared lock is issued when a transaction wants to read data from the database and no exclusive lock is held on that data item. ...
... A shared lock is issued when a transaction wants to read data from the database and no exclusive lock is held on that data item. ...
Database Intrusion Detection with Automated Recovery
... In addition to the medium level of security, even the recovery can be automated. Recovery Phase In automated recovery rollback the database to the state just before the intrusion. Create a transaction dependency graph beginning from the malicious transaction. Use this graph to redo all the ben ...
... In addition to the medium level of security, even the recovery can be automated. Recovery Phase In automated recovery rollback the database to the state just before the intrusion. Create a transaction dependency graph beginning from the malicious transaction. Use this graph to redo all the ben ...
WISC & AS3AP
... • If lock table size is a problem can release locks, but at the cost of serializability * In case of failure during a mini-batch, must complete its remaining portion on recovery, to ensure atomicity. ...
... • If lock table size is a problem can release locks, but at the cost of serializability * In case of failure during a mini-batch, must complete its remaining portion on recovery, to ensure atomicity. ...
Advanced Database Management Systems
... To develop an understanding of the manner in which relational systems are implemented and the implications of the techniques of implementation for database performance To assess the impact of emerging database standards on the facilities which future database management systems will provide. ...
... To develop an understanding of the manner in which relational systems are implemented and the implications of the techniques of implementation for database performance To assess the impact of emerging database standards on the facilities which future database management systems will provide. ...
MS-Access(Basics)
... • A collection of related tables is called a database, or a relational database • You connect the records in the separate tables through a common field • A primary key is a field, or a collection of fields, whose values uniquely identify each record in a table • When you include the primary key from ...
... • A collection of related tables is called a database, or a relational database • You connect the records in the separate tables through a common field • A primary key is a field, or a collection of fields, whose values uniquely identify each record in a table • When you include the primary key from ...
RPPA12_poster - MKS 2
... database is used as a common repository, Each application (corresponding to different configuration files) has a different set of tables defined in the database. ...
... database is used as a common repository, Each application (corresponding to different configuration files) has a different set of tables defined in the database. ...
transaction
... Schedules – sequences that indicate the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed ...
... Schedules – sequences that indicate the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed ...
Document
... 1. For each data item Q, if transaction Ti reads the initial value of Q in schedule S, then transaction Ti must, in schedule S´, also read the initial value of Q. 2. For each data item Q if transaction Ti executes read(Q) in schedule S, and that value was produced by transaction Tj (if any), then tr ...
... 1. For each data item Q, if transaction Ti reads the initial value of Q in schedule S, then transaction Ti must, in schedule S´, also read the initial value of Q. 2. For each data item Q if transaction Ti executes read(Q) in schedule S, and that value was produced by transaction Tj (if any), then tr ...
CSCI 526 Database Systems
... COURSE REQUIREMENT DEADLINES: Credit will be given for ONLY those exams, programs, and/or projects turned in no later than the deadline as announced by the instructor of this class, unless prior arrangement has been made with the instructor. Late programs / projects / assignments can or cannot gain ...
... COURSE REQUIREMENT DEADLINES: Credit will be given for ONLY those exams, programs, and/or projects turned in no later than the deadline as announced by the instructor of this class, unless prior arrangement has been made with the instructor. Late programs / projects / assignments can or cannot gain ...
Introduction to Database Systems
... Search/query/update Change the structure Concurrent access to many user Recover from crashes Security ...
... Search/query/update Change the structure Concurrent access to many user Recover from crashes Security ...
Building Deterministic Transaction Processing Systems without
... Deployed in a main-memory-only setting and under typical OLTP workloads, our deterministic transaction execution model comes with three significant benefits in addition to the debugging and repeatability perks that typically accompany deterministic behavior: • Unsynchronized active replication. Give ...
... Deployed in a main-memory-only setting and under typical OLTP workloads, our deterministic transaction execution model comes with three significant benefits in addition to the debugging and repeatability perks that typically accompany deterministic behavior: • Unsynchronized active replication. Give ...
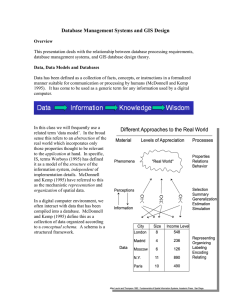
Database Management Systems and GIS Design
... all information systems and extends it at the beginning to understand the area of use or application domain at hand. The analysis phase has been broken down into an application domain model. This model is, in turn, transformed into a conceptual computational model. This is said to be computationally ...
... all information systems and extends it at the beginning to understand the area of use or application domain at hand. The analysis phase has been broken down into an application domain model. This model is, in turn, transformed into a conceptual computational model. This is said to be computationally ...