Student : MengZi Guo
... 13. Magnetic fields are created by ___________ A. magnetic field lines B. potential energy of molecules C. spinning neutrons D. moving electric charges ...
... 13. Magnetic fields are created by ___________ A. magnetic field lines B. potential energy of molecules C. spinning neutrons D. moving electric charges ...
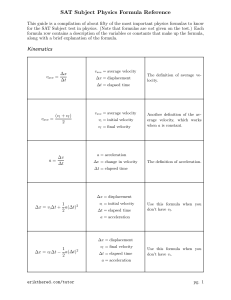
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference
... This formula gives the electric potential energy for two charges a distance r apart. For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit ch ...
... This formula gives the electric potential energy for two charges a distance r apart. For more than one pair of charges, use this formula for each pair, then add all the UE ’s. The potential difference ∆V between two points is defined as the negative of the work done by the electric field per unit ch ...
the field
... 6) Watch Electric field inside a conductor. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WqvImbn9GG4 Tesla Cage of Death http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=Zi4kXgDBFhw&feature=endscreen What is a Faraday cage and how does it protect you? Where are they used? A Faraday cage is made of a conductor. The charges on ...
... 6) Watch Electric field inside a conductor. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WqvImbn9GG4 Tesla Cage of Death http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=Zi4kXgDBFhw&feature=endscreen What is a Faraday cage and how does it protect you? Where are they used? A Faraday cage is made of a conductor. The charges on ...
About the Nature of Gravitational Constant and a Rational Metric
... two quantities. [f however under some experimental conditions one property can be activeiy changed and it is followed by a correlated response of another, there is a strong yet they evidence of existing dependency. If the two measurable quantities are dependent ...
... two quantities. [f however under some experimental conditions one property can be activeiy changed and it is followed by a correlated response of another, there is a strong yet they evidence of existing dependency. If the two measurable quantities are dependent ...
physics cos 2011-2012
... Evaluate the motion of an object in a circle and relate it to the topics of linear motion and Newton’s 2nd law to derive the concept of centripetal force Design and develop an event from which data can be collected, leading to an application of the equations of circular motion Relate the concepts of ...
... Evaluate the motion of an object in a circle and relate it to the topics of linear motion and Newton’s 2nd law to derive the concept of centripetal force Design and develop an event from which data can be collected, leading to an application of the equations of circular motion Relate the concepts of ...
Lecture 7: Electric fields
... One can calculate E from a point-like charge Q at distance r from Q ...
... One can calculate E from a point-like charge Q at distance r from Q ...
Contest
... 33. In which Region(s) is there a place on the x-axis (aside from infinity) at which the electric potential is equal to zero? (A) Only in Region II (B) Only in Region III (C) In both Regions I and II ...
... 33. In which Region(s) is there a place on the x-axis (aside from infinity) at which the electric potential is equal to zero? (A) Only in Region II (B) Only in Region III (C) In both Regions I and II ...
List of Required Definitions
... spacecraft and all objects in it being in constant free-fall together as they circle Earth 37. Weightlessness in deep space – a sensation of weightlessness due to the minimal pull of gravity very far from any massive object Thermal Physics 38. *Temperature (T) – a. The property that determines the d ...
... spacecraft and all objects in it being in constant free-fall together as they circle Earth 37. Weightlessness in deep space – a sensation of weightlessness due to the minimal pull of gravity very far from any massive object Thermal Physics 38. *Temperature (T) – a. The property that determines the d ...
Forces On Moving Objects
... objects are: • Errors of relative distance are used in the calculations based on force laws using the inverse square of the distance. • The four so-called “intrinsic” properties of the stable elementary particles (the electron, proton, positron and antiproton)—charge, spin, magnetic moment, and iner ...
... objects are: • Errors of relative distance are used in the calculations based on force laws using the inverse square of the distance. • The four so-called “intrinsic” properties of the stable elementary particles (the electron, proton, positron and antiproton)—charge, spin, magnetic moment, and iner ...
KE q V 1.6 10 50 100 8 10 = Δ = − × − = × KE 8 10 J = ×
... ΔUA→B = qVB - qVA = 2.0 × 10−6 -61.9 × 103 − 59.9 × 103 = -0.244 J It’s negative because A is at higher potential so q loses potential energy in the move e) The work done by the field in moving q from A to B is positive since the particle loses potential energy (it moves the way the field would move ...
... ΔUA→B = qVB - qVA = 2.0 × 10−6 -61.9 × 103 − 59.9 × 103 = -0.244 J It’s negative because A is at higher potential so q loses potential energy in the move e) The work done by the field in moving q from A to B is positive since the particle loses potential energy (it moves the way the field would move ...
Chapter 18 Test Review Chapter Summary 18.1. Static Electricity
... 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge • Define electric charge, and describe how the two types of charge interact. • Describe three common situations that generate static electricity. • State the law of conservation of charge. 18.2. Conductors and Insulators • Define conductor ...
... 18.1. Static Electricity and Charge: Conservation of Charge • Define electric charge, and describe how the two types of charge interact. • Describe three common situations that generate static electricity. • State the law of conservation of charge. 18.2. Conductors and Insulators • Define conductor ...
II. Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... record the stopwatch readings, the polarity of the E-field, and the voltage reading. A third one will operate the atomizer and control the voltage. For good results it is essential that readings for E = 0, + , and − be made on the same bead, which means that the observer must keep the bead continuou ...
... record the stopwatch readings, the polarity of the E-field, and the voltage reading. A third one will operate the atomizer and control the voltage. For good results it is essential that readings for E = 0, + , and − be made on the same bead, which means that the observer must keep the bead continuou ...
magnetic force solutions
... will attract each other. To prove this consider one wire first and determine the magnetic field created at the position of the second wire and then use the right hand rule to determine the direction of the force on the second wire. Problem 3: The particle shown in the figure enters a region of magne ...
... will attract each other. To prove this consider one wire first and determine the magnetic field created at the position of the second wire and then use the right hand rule to determine the direction of the force on the second wire. Problem 3: The particle shown in the figure enters a region of magne ...
PHB - Indian Statistical Institute
... given λ = λ (1 + V /c) (1 − V /c) where λ is the emitted wavelength as seen in a reference frame at rest with respect to the source, and λ0 is the wavelength measured in a frame moving with velocity V away from the source along the line of sight. Show that the Doppler shift in wavelength is z ≈ V /c ...
... given λ = λ (1 + V /c) (1 − V /c) where λ is the emitted wavelength as seen in a reference frame at rest with respect to the source, and λ0 is the wavelength measured in a frame moving with velocity V away from the source along the line of sight. Show that the Doppler shift in wavelength is z ≈ V /c ...