Answer the following questions
... 5- Two blocks are placed one on the top of the other as shown in the figure. A force F is applied to the lower block. If the coefficients of friction between the lower block and the surface are μ s = 0.50 and μ k = 0.25, a) What value of F is needed to put the block into motion? ...
... 5- Two blocks are placed one on the top of the other as shown in the figure. A force F is applied to the lower block. If the coefficients of friction between the lower block and the surface are μ s = 0.50 and μ k = 0.25, a) What value of F is needed to put the block into motion? ...
Newtons Second Law
... Would you weigh more on Earth or Jupiter? Jupiter because... greater mass greater gravity ...
... Would you weigh more on Earth or Jupiter? Jupiter because... greater mass greater gravity ...
answer
... For example: The plates create a vertical electric field that exerts a vertical force on the particle. The cross-product of the velocity and the magnetic field also results in a vertical force. No matter what the charge of the particle, these forces are in opposite directions. Since the charge moves ...
... For example: The plates create a vertical electric field that exerts a vertical force on the particle. The cross-product of the velocity and the magnetic field also results in a vertical force. No matter what the charge of the particle, these forces are in opposite directions. Since the charge moves ...
Introduction and Kinematics
... How to solve problems involving Newton’s second law (step 4) Extract the equations • Calculate the net force along every component for every part of the system. Be sure to pay attention to signs. • Do this by calculating the components of all the forces against the coordinate system. • Set this tot ...
... How to solve problems involving Newton’s second law (step 4) Extract the equations • Calculate the net force along every component for every part of the system. Be sure to pay attention to signs. • Do this by calculating the components of all the forces against the coordinate system. • Set this tot ...
Gravity Simulation Introduction: Every object around you is attracted
... confirmed that all objects with mass are attracted to all other objects with mass by a force that is proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects' centers. This relationship became Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation. In this simulation, ...
... confirmed that all objects with mass are attracted to all other objects with mass by a force that is proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects' centers. This relationship became Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation. In this simulation, ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
... • A force is what we call a push or a pull, or any action that has the ability to change motion of an object. • The metric unit used to describe force is called the Newton (N). One Newton is equal to: 1 Kg x 1 m/s/s Thus, one Newton of force causes a one kilogram object to accelerate at a rate of on ...
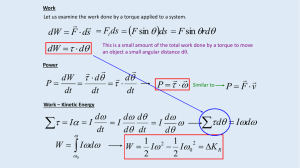
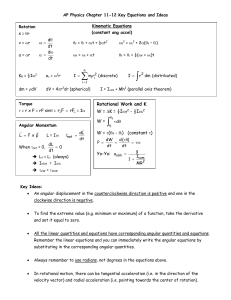
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
PHYS1111
... You and your lab partner pull a slinky across the hallway floor so that it is stretched out to 10.0meters. Your partner shakes one end through five full cycles in two seconds. The first wave peak reaches you 0.50s after starting to shake. a) What is the wave speed? b) What is the frequency and wavel ...
... You and your lab partner pull a slinky across the hallway floor so that it is stretched out to 10.0meters. Your partner shakes one end through five full cycles in two seconds. The first wave peak reaches you 0.50s after starting to shake. a) What is the wave speed? b) What is the frequency and wavel ...
MASS, WEIGHT AND GRAVITY. 1. THE FORCE OF GRAVITY: THE
... As we have seen, all planets attract anything that is on or above its surface. This property is called gravity. Gravity causes acceleration in all objects that fall freely from a height. Gravitational acceleration is represented by letter g, and it increases as gravity increases. The weight of an ob ...
... As we have seen, all planets attract anything that is on or above its surface. This property is called gravity. Gravity causes acceleration in all objects that fall freely from a height. Gravitational acceleration is represented by letter g, and it increases as gravity increases. The weight of an ob ...
Physics: Practice Problems for Final
... to the ground. How long is it in the air? What is its maximum height and range, neglecting air resistance and assuming it lands on ground the same height as that from which it was launched? (2.3 s, 6.5 m, 71 m) 20. The mass of a bicycle and rider is 53.0 kg. How much work has been done if the bicycl ...
... to the ground. How long is it in the air? What is its maximum height and range, neglecting air resistance and assuming it lands on ground the same height as that from which it was launched? (2.3 s, 6.5 m, 71 m) 20. The mass of a bicycle and rider is 53.0 kg. How much work has been done if the bicycl ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... 2. What is Newton’s first law of motion? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Which of Newton’s laws of motion describes the motion of an object that has a net force of 0? __________________________________ ...
... 2. What is Newton’s first law of motion? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Which of Newton’s laws of motion describes the motion of an object that has a net force of 0? __________________________________ ...
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
... 16.If a softball and a bowling ball are dropped from the same height at the same time, and there is no air resistance, which ball will hit the ground first? Why? (pg. 542) They would both hit the ground at the same time b/c the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects when there is no ...
... 16.If a softball and a bowling ball are dropped from the same height at the same time, and there is no air resistance, which ball will hit the ground first? Why? (pg. 542) They would both hit the ground at the same time b/c the acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects when there is no ...
Newton`s Laws Gravity & Falling Objects Energy, Work
... Which of the following does not need a net force? A.Positive acceleration B.Negative acceleration C.Maintaining constant ...
... Which of the following does not need a net force? A.Positive acceleration B.Negative acceleration C.Maintaining constant ...