Physics Review
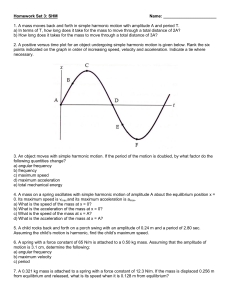
... 1. What is the formula you use to find the speed of an object? speed=distance/time 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving and velocity is the same except it takes in to consideration a certain direction the object is moving. 3. An obj ...
... 1. What is the formula you use to find the speed of an object? speed=distance/time 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving and velocity is the same except it takes in to consideration a certain direction the object is moving. 3. An obj ...
The more momentum an object has, the more difficult it is to stop
... be the same number regardless of the time involved. However, the force can change drastically depending upon the amount of time in which the object is brought to a halt. As the length of time is increased, the force decreases. In stopping an object, force and time are inversely proportional. Damage ...
... be the same number regardless of the time involved. However, the force can change drastically depending upon the amount of time in which the object is brought to a halt. As the length of time is increased, the force decreases. In stopping an object, force and time are inversely proportional. Damage ...
Physics Questions
... 3. A sailboat is tied to a mooring with a line. The wind is from the southwest. Identify all the forces acting on the sailboat. a. 1) the force of gravity; 2) the force of the tide; 3) the force of the wind; 4) the force of the line tied to the mooring b. 1) the force of gravity; 2) the force of wat ...
... 3. A sailboat is tied to a mooring with a line. The wind is from the southwest. Identify all the forces acting on the sailboat. a. 1) the force of gravity; 2) the force of the tide; 3) the force of the wind; 4) the force of the line tied to the mooring b. 1) the force of gravity; 2) the force of wat ...
8th Grade Science
... A hot plate on a stove transforms electrical energy to __________ energy. The energy in fossil fuels originally came from the ________. The amount of work you do depends on both the amount of ____________ you exert and the _____________ the object moves. What are 6 kinds of simple machines? The long ...
... A hot plate on a stove transforms electrical energy to __________ energy. The energy in fossil fuels originally came from the ________. The amount of work you do depends on both the amount of ____________ you exert and the _____________ the object moves. What are 6 kinds of simple machines? The long ...
89mc
... 16. Two vessels of equal volume both contain an ideal gas and are connected by a tube of negligible volume. Initially both vessels are at temperature T0 and pressure P0. One vessel is maintained at T0, while the temperature of the ...
... 16. Two vessels of equal volume both contain an ideal gas and are connected by a tube of negligible volume. Initially both vessels are at temperature T0 and pressure P0. One vessel is maintained at T0, while the temperature of the ...
Study Guide for Ch 6 Test Newtons Laws
... You probably guessed that it takes more force to stop a large truck than a small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has greater momentum. We can find momentum using this equation: momentum = mass of object velocity of object Velocity is a term that refers to both speed and direction. For ...
... You probably guessed that it takes more force to stop a large truck than a small car. In physics terms, we say that the truck has greater momentum. We can find momentum using this equation: momentum = mass of object velocity of object Velocity is a term that refers to both speed and direction. For ...
10_HSPE Review Physical B
... 3. A hammer strikes a nail and drives the nail into a block of wood. If the action force is the hammer striking the nail, the reaction force is A. the nail striking the wood with an equal and opposite force. B. the nail striking the hammer with an equal and opposite force. ...
... 3. A hammer strikes a nail and drives the nail into a block of wood. If the action force is the hammer striking the nail, the reaction force is A. the nail striking the wood with an equal and opposite force. B. the nail striking the hammer with an equal and opposite force. ...
Energy - WordPress.com
... • where: m = mass, g = acceleration due to gravity, and h = height above the Earth’s surface ...
... • where: m = mass, g = acceleration due to gravity, and h = height above the Earth’s surface ...