Newton`s Second Law
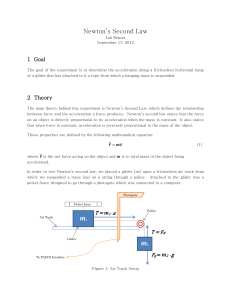
... In this experiment we determined the acceleration along a frictionless horizontal ramp of a sliding object that has attached to it a rope from which ˷4g, ˷6g and ˷8g of mass suspended from it in two independent ways. The uncertainty in the theoretical value of acceleration for the ˷4g, ˷6g, and ˷8g ...
... In this experiment we determined the acceleration along a frictionless horizontal ramp of a sliding object that has attached to it a rope from which ˷4g, ˷6g and ˷8g of mass suspended from it in two independent ways. The uncertainty in the theoretical value of acceleration for the ˷4g, ˷6g, and ˷8g ...
Chapter 3
... per hour to 35 to 30 each second. What is the acceleration? What is this type of acceleration often called? a. -5 mph/sec b. deceleration ...
... per hour to 35 to 30 each second. What is the acceleration? What is this type of acceleration often called? a. -5 mph/sec b. deceleration ...
Momentum and Impulse notes
... The world’s most massive train ran in South Africa in 1989. Over 7 km long, the train traveled 861.0 km in 22.67 h. Imagine that the distance was traveled in a straight line north. If the train’s average momentum was 7.32 x 108 kg•m/s to the north, what was its mass? ...
... The world’s most massive train ran in South Africa in 1989. Over 7 km long, the train traveled 861.0 km in 22.67 h. Imagine that the distance was traveled in a straight line north. If the train’s average momentum was 7.32 x 108 kg•m/s to the north, what was its mass? ...
17AP_Physics_C_-_Rotational_Motion_II
... Maybe but it isn't easy. That extra distance AWAY from the point of rotation gives you the extra leverage you need. THUS we call this distance the LEVER (EFFORT) ARM (r) . ...
... Maybe but it isn't easy. That extra distance AWAY from the point of rotation gives you the extra leverage you need. THUS we call this distance the LEVER (EFFORT) ARM (r) . ...
force and motion unit
... Have you ever wondered why and how objects begin to move and why objects stop all of a sudden? An object starts to move, stops moving, or changes directions ONLY when a force acts on it. Some forces act on objects directly and some forces act on objects indirectly. For example, when you push on a do ...
... Have you ever wondered why and how objects begin to move and why objects stop all of a sudden? An object starts to move, stops moving, or changes directions ONLY when a force acts on it. Some forces act on objects directly and some forces act on objects indirectly. For example, when you push on a do ...
Work and energy
... called the WORK-ENERGY THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! " The net WORK done on an object is equal to the change ...
... called the WORK-ENERGY THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! " The net WORK done on an object is equal to the change ...
AP Test Review – energy
... Hooke’s Law Force exerted by a compressed spring Potential Energy of a spring: ...
... Hooke’s Law Force exerted by a compressed spring Potential Energy of a spring: ...