Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
... is the distance between two arbitrary points, one located within the first object, the other one within the second object. Generally, the two integrals are difficult to compute, and explicit formulas are available only for very simple geometries. As an example, let us perform the integration for the ...
... is the distance between two arbitrary points, one located within the first object, the other one within the second object. Generally, the two integrals are difficult to compute, and explicit formulas are available only for very simple geometries. As an example, let us perform the integration for the ...
Electrostatics
... charged particle would feel at any given point if we were to place it in the field. The electric field allows us to do this only knowing the charge generating the field, to know the actual force we need to know both or all charges involved. Often an electric field will exist and we are interested in ...
... charged particle would feel at any given point if we were to place it in the field. The electric field allows us to do this only knowing the charge generating the field, to know the actual force we need to know both or all charges involved. Often an electric field will exist and we are interested in ...
Chapter 5 Using Newton`s Laws: Friction, Circular Motion
... Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Exam 3 review suggestions and sample problems
... rope makes with the vertical is 30°, and released from rest. At the bottom of its path, the swing hits a lip of a level table, such that the swing stops but the block continues to slide forward. The block slides a distance of 2.0 m before coming to rest. Note: you may not use kinematics for any part ...
... rope makes with the vertical is 30°, and released from rest. At the bottom of its path, the swing hits a lip of a level table, such that the swing stops but the block continues to slide forward. The block slides a distance of 2.0 m before coming to rest. Note: you may not use kinematics for any part ...
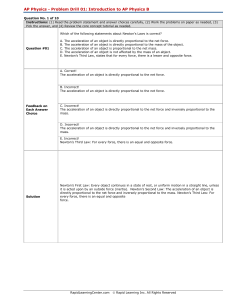
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... E. The score is determined in the following way: You are awarded 1 point for every correct answer. You are deducted 1/4 point for every incorrect answer. You are not awarded or deducted any points for blank ...
... E. The score is determined in the following way: You are awarded 1 point for every correct answer. You are deducted 1/4 point for every incorrect answer. You are not awarded or deducted any points for blank ...
physica - University of Warwick
... case if a force acts only on one or very few reptons in the bulk of the polymer. One would intuitively expect that in such a situation the formation of hernias by these special reptons will dominate the overall motion of the DNA. This is indeed the situation that we propose to study. Attaching a mag ...
... case if a force acts only on one or very few reptons in the bulk of the polymer. One would intuitively expect that in such a situation the formation of hernias by these special reptons will dominate the overall motion of the DNA. This is indeed the situation that we propose to study. Attaching a mag ...
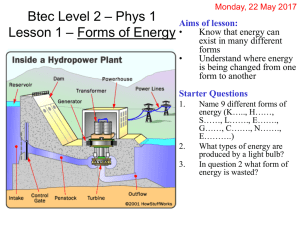
Chapter 6: Energy
... Energy may be converted from one form to another or transferred between bodies. ...
... Energy may be converted from one form to another or transferred between bodies. ...
Lecture 15
... If the spring constant is 16 lb/ft, what is the numerical value of the weight? 10. A 4-lb weight is attached to a spring, whose spring constant is 16 lb/ft . What is period of simple harmonic motion? 11. A 24-lb weight, attached to the spring, stretches it 4 inches. Find the equation of the motion i ...
... If the spring constant is 16 lb/ft, what is the numerical value of the weight? 10. A 4-lb weight is attached to a spring, whose spring constant is 16 lb/ft . What is period of simple harmonic motion? 11. A 24-lb weight, attached to the spring, stretches it 4 inches. Find the equation of the motion i ...
Unit 2 - Angelfire
... When encountering a car collision, the driver and passenger tend to keep moving in accord with Newton's first law. Their motion carries them towards a windshield which results in a large force exerted over a short time in order to stop their momentum. If instead of hitting the windshield, the driver ...
... When encountering a car collision, the driver and passenger tend to keep moving in accord with Newton's first law. Their motion carries them towards a windshield which results in a large force exerted over a short time in order to stop their momentum. If instead of hitting the windshield, the driver ...