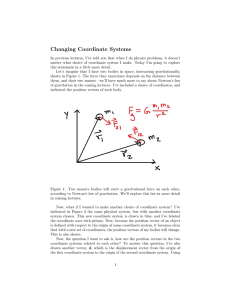
Physics I Lab Packet
... B. Criteria: Conducts the Experiment Student demonstrates knowledge and skills necessary to perform scientific inquiry. Standards and Benchmarks: SCI 1.3.1; 11.3.2; SCI 1.8.4; and SCI 1.1.X ...
... B. Criteria: Conducts the Experiment Student demonstrates knowledge and skills necessary to perform scientific inquiry. Standards and Benchmarks: SCI 1.3.1; 11.3.2; SCI 1.8.4; and SCI 1.1.X ...
AP Physics II.A
... Ex. A proton is released in an electric field with a magnitude of 8.0 EE 4 V/m directed along the positive x-axis. The proton undergoes a displacement of 0.50 m in the direction of the field. a) Find the potential difference. b) Find the change in electrical potential energy c) Find the speed if th ...
... Ex. A proton is released in an electric field with a magnitude of 8.0 EE 4 V/m directed along the positive x-axis. The proton undergoes a displacement of 0.50 m in the direction of the field. a) Find the potential difference. b) Find the change in electrical potential energy c) Find the speed if th ...
Chapter 9 - s3.amazonaws.com
... The momentum of a system changes if a net force from the environment acts on the system. For momentum considerations, a system is non-isolated if a net force acts on the system for a time interval. From Newton’s Second Law, F Solving for dp gives ...
... The momentum of a system changes if a net force from the environment acts on the system. For momentum considerations, a system is non-isolated if a net force acts on the system for a time interval. From Newton’s Second Law, F Solving for dp gives ...
In the previous chapter we discussed energy, and
... laws of motion and pathways into deeper understandings of Newtonian mechanics. The basic understanding of Newton's second law that we have discussed so far is that the acceleration of an object is caused by the net force acting on it. However, there are situations where it is difficult to measure th ...
... laws of motion and pathways into deeper understandings of Newtonian mechanics. The basic understanding of Newton's second law that we have discussed so far is that the acceleration of an object is caused by the net force acting on it. However, there are situations where it is difficult to measure th ...
Scheme of work, chapter 11
... Sketch how the force versus time graph changes when, say, the impact time is increased. Lesson 11: Analyse data from one of the collisions (the disintegration is possibly the most instructive) to illustrate the principle that the change in momentum is the same for each body. Use this result to dis ...
... Sketch how the force versus time graph changes when, say, the impact time is increased. Lesson 11: Analyse data from one of the collisions (the disintegration is possibly the most instructive) to illustrate the principle that the change in momentum is the same for each body. Use this result to dis ...
Chapter 4 SINGLE PARTICLE MOTIONS
... The spiralling particles are themselves current loops and generate their own magnetic induction. Consider that generated by the ions. With reference to Fig. 4.1 it is clear that inside the orbit, the induction is into the page, i.e. opposite the direction of B. The same is true for the electrons - o ...
... The spiralling particles are themselves current loops and generate their own magnetic induction. Consider that generated by the ions. With reference to Fig. 4.1 it is clear that inside the orbit, the induction is into the page, i.e. opposite the direction of B. The same is true for the electrons - o ...
13 particle accelerators
... A charged particle with charge e moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B experiences a force F, where F = qv × B. ...
... A charged particle with charge e moving with velocity v in a magnetic field B experiences a force F, where F = qv × B. ...
Final Exam Review
... A force acting on an object does no work if a. a machine is used to move the object. b. the force is not in the direction of the object’s motion. c. the force is greater than the force of friction. d. the object accelerates ...
... A force acting on an object does no work if a. a machine is used to move the object. b. the force is not in the direction of the object’s motion. c. the force is greater than the force of friction. d. the object accelerates ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
... A proton moves with a speed of 1.0x105 m/s through the Earth’s magnetic field, which has a value of 55µT at a particular location. When the proton moves eastward, the magnetic force is a maximum, and when it moves northward, no magnetic force acts upon it. What is the magnitude and direction of the ...
... A proton moves with a speed of 1.0x105 m/s through the Earth’s magnetic field, which has a value of 55µT at a particular location. When the proton moves eastward, the magnetic force is a maximum, and when it moves northward, no magnetic force acts upon it. What is the magnitude and direction of the ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Even in classical mechanics we can consider processes in which the interaction is localized in space and time, so that the locality condition (2.1) is satisfied and we can avoid the inconsistencies discussed above, related to Newton’s second law. These are typically collisions in which two or more p ...
... Even in classical mechanics we can consider processes in which the interaction is localized in space and time, so that the locality condition (2.1) is satisfied and we can avoid the inconsistencies discussed above, related to Newton’s second law. These are typically collisions in which two or more p ...
newton`s second law - Otterbein University
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...
... the harder you push on a cart, the faster it goes. However, according to Newton, the force merely changes the velocity. It is the acceleration, not the velocity, that is proportional to the force. Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a mu ...