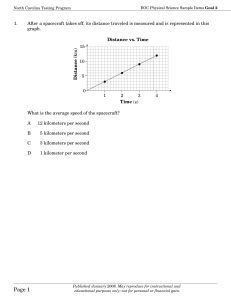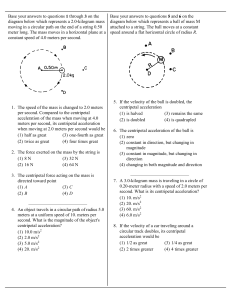
Circular Review with Ans - Physics 12
... 57. A satellite orbits the Earth in a circular orbit. Which statement best explains why the satellite does not move closer to the center of the Earth? (1) The gravitational field of the Earth does not reach the satellite's orbit. (2) The Earth's gravity keeps the satellite moving with constant veloc ...
... 57. A satellite orbits the Earth in a circular orbit. Which statement best explains why the satellite does not move closer to the center of the Earth? (1) The gravitational field of the Earth does not reach the satellite's orbit. (2) The Earth's gravity keeps the satellite moving with constant veloc ...
CH6-10 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... 17. A small object with a momentum of magnitude 5.0 kgúm/s approaches head-on a large object at rest. The small object bounces straight back with a momentum of magnitude 4.0 kgúm/s. What is the magnitude of the small object's momentum change? a) 9.0 kgúm/s b) 5.0 kgúm/s c) 4.0 kgúm/s d) 1.0 kgúm/s 1 ...
... 17. A small object with a momentum of magnitude 5.0 kgúm/s approaches head-on a large object at rest. The small object bounces straight back with a momentum of magnitude 4.0 kgúm/s. What is the magnitude of the small object's momentum change? a) 9.0 kgúm/s b) 5.0 kgúm/s c) 4.0 kgúm/s d) 1.0 kgúm/s 1 ...
ELECTRIC CHARGE, FORCE AND FIELD
... Then F2 is along the direction of r̂ 12 if Q1 and Q2 have the same sign F2 is opposite to ...
... Then F2 is along the direction of r̂ 12 if Q1 and Q2 have the same sign F2 is opposite to ...
Unit 4 – Chapter 7: Oscillatory Motion Requires a Set of Conditions
... Mechanical Resonance – when a periodic force is applied to an oscillating object. Amplitude of oscillation could increase and cause harm. A bridge could break from the wind. Ringing a church bell. ...
... Mechanical Resonance – when a periodic force is applied to an oscillating object. Amplitude of oscillation could increase and cause harm. A bridge could break from the wind. Ringing a church bell. ...
mechanical advantage and combustion
... pulley lifting a weight designated as “A.” The tension in each line connecting these two pulleys is calculated as A/3. This yields an MA of 3. ...
... pulley lifting a weight designated as “A.” The tension in each line connecting these two pulleys is calculated as A/3. This yields an MA of 3. ...
Horizontal Kinematics - The Woodlands High School
... A driver traveling at 90 km/hr sees the lights of a barrier 40 m ahead. It takes the driver 0.75 seconds to apply the brakes. Once braking begins, the car slows at a maximum rate of 10 m/s2. a. Does the car hit the barrier? [yes, at 14m/s, or overshoots by 10m] b. At the moment the driver notices th ...
... A driver traveling at 90 km/hr sees the lights of a barrier 40 m ahead. It takes the driver 0.75 seconds to apply the brakes. Once braking begins, the car slows at a maximum rate of 10 m/s2. a. Does the car hit the barrier? [yes, at 14m/s, or overshoots by 10m] b. At the moment the driver notices th ...
SHM Part 1 - Ask Physics
... Q. A uniform thin cylindrical disk of mass M and radius R is attached to two identical massless springs of spring constant k which are fixed to the wall as shown in the figure. The springs are attached to the axle of the disk symmetrically on either side at a distance d from its centre. The axle is ...
... Q. A uniform thin cylindrical disk of mass M and radius R is attached to two identical massless springs of spring constant k which are fixed to the wall as shown in the figure. The springs are attached to the axle of the disk symmetrically on either side at a distance d from its centre. The axle is ...