Manipulation of charged particles in discharge tubes
... electron is constant and hence its acceleration is also constant. The motion of the electron is similar to that of a projectile where the constant force of gravity acts upon the object. We will consider two cases for the motion of an electron in a uniform electric field: (i) ...
... electron is constant and hence its acceleration is also constant. The motion of the electron is similar to that of a projectile where the constant force of gravity acts upon the object. We will consider two cases for the motion of an electron in a uniform electric field: (i) ...
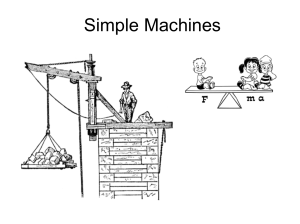
Length of the input arm
... A simple machine does work with only one movement. Simple machines can be combined to form more complex machines We tend to think of machines as motorized devices with many moving parts. In physics, a machine can be a simple item, like a shovel or a screw top lid ...
... A simple machine does work with only one movement. Simple machines can be combined to form more complex machines We tend to think of machines as motorized devices with many moving parts. In physics, a machine can be a simple item, like a shovel or a screw top lid ...
CentripetalForce
... Calibration Steps: For all steps in this lab you will want the support string to be in a vertical plane as you rotate the vertical rod so that the centripetal force is provided solely by the spring. You may also need to adjust the length of the support string so that the spring connecting the bob to ...
... Calibration Steps: For all steps in this lab you will want the support string to be in a vertical plane as you rotate the vertical rod so that the centripetal force is provided solely by the spring. You may also need to adjust the length of the support string so that the spring connecting the bob to ...
IntroTHT_2e_SM_Chap01
... 1-10C Pound-mass lbm is the mass unit in English system whereas pound-force lbf is the force unit. One pound-force is the force required to accelerate a mass of 32.174 lbm by 1 ft/s 2. In other words, the weight of a 1-lbm mass at sea level is 1 lbf. ...
... 1-10C Pound-mass lbm is the mass unit in English system whereas pound-force lbf is the force unit. One pound-force is the force required to accelerate a mass of 32.174 lbm by 1 ft/s 2. In other words, the weight of a 1-lbm mass at sea level is 1 lbf. ...
Chapter 5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In our study of kinematics, we saw that if the acceleration, initial position, and velocity of a body are known, then the future position and velocity of the moving body can be completely described. But one of the things left out of that discussion, was the cause of the body’s acceleration. If a pie ...
... In our study of kinematics, we saw that if the acceleration, initial position, and velocity of a body are known, then the future position and velocity of the moving body can be completely described. But one of the things left out of that discussion, was the cause of the body’s acceleration. If a pie ...
Instructor: Deb Prinkey - Mount Vernon City Schools
... thus illustrating that static friction is variable and kinetic friction a constant. Friction lab: Inquiry-based lab in which students determine the coefficients of static and kinetic friction for a friction block and a cart track using a variety of methods. Angled and flat ramps, pulleys, and mass k ...
... thus illustrating that static friction is variable and kinetic friction a constant. Friction lab: Inquiry-based lab in which students determine the coefficients of static and kinetic friction for a friction block and a cart track using a variety of methods. Angled and flat ramps, pulleys, and mass k ...
Document
... THEORETICAL BACKGROUND: An object executes Uniform Motion, that is, it moves straight with constant velocity (or remains at rest), unless other bodies exert a finite resultant force on the object. This statement is known as Ist Newton’s Law of motion. Thus, in order to realize Uniform Motion it is c ...
... THEORETICAL BACKGROUND: An object executes Uniform Motion, that is, it moves straight with constant velocity (or remains at rest), unless other bodies exert a finite resultant force on the object. This statement is known as Ist Newton’s Law of motion. Thus, in order to realize Uniform Motion it is c ...
A 2012 PH READ INSTRUCTIONS ON THE LEFT
... from 200 K to 400 K by either of the following two processes P1 and P2: P1: bringing it in contact with a reservoir at 400 K. P2: bringing it first in contact with a reservoir at 300 K till equilibrium is reached, and then bringing it in contact with another reservoir at 400 K. Calculate the change ...
... from 200 K to 400 K by either of the following two processes P1 and P2: P1: bringing it in contact with a reservoir at 400 K. P2: bringing it first in contact with a reservoir at 300 K till equilibrium is reached, and then bringing it in contact with another reservoir at 400 K. Calculate the change ...
Systems of Particles
... • Although f ij and f ji are equal and opposite, the work of these forces will not, in general, cancel out. • If the forces acting on the particles are conservative, the work is equal to the change in potential energy and T1 V1 T2 V2 which expresses the principle of conservation of energy for ...
... • Although f ij and f ji are equal and opposite, the work of these forces will not, in general, cancel out. • If the forces acting on the particles are conservative, the work is equal to the change in potential energy and T1 V1 T2 V2 which expresses the principle of conservation of energy for ...
Table of Contents
... Dynamics problems involving Newton’s second law of motion often involve second order linear differential equations as illustrated in the derivation of Equation (1) for a particle attached to a light spring. For an understanding of simple harmonic motion it is sufficient to investigate the solution o ...
... Dynamics problems involving Newton’s second law of motion often involve second order linear differential equations as illustrated in the derivation of Equation (1) for a particle attached to a light spring. For an understanding of simple harmonic motion it is sufficient to investigate the solution o ...
Appendix D. Hints and Answers to Exercises
... stress on his neck bones and muscles. Initially, the horizontal forces on the passenger’s head were very small. When the car was struck from behind, the car and the passenger’s body began moving forward. His head remained at rest in accordance with the First Law of Motion. Thus, his body and head we ...
... stress on his neck bones and muscles. Initially, the horizontal forces on the passenger’s head were very small. When the car was struck from behind, the car and the passenger’s body began moving forward. His head remained at rest in accordance with the First Law of Motion. Thus, his body and head we ...