Problems and solutions on Magnetism
... Solution: Since the particle is positively charged, use the right hand rule. In this case, start with the thumb of the right hand in the direction of v and the palm facing the direction of F. The fingers will point in the direction of B. The results are (a) ...
... Solution: Since the particle is positively charged, use the right hand rule. In this case, start with the thumb of the right hand in the direction of v and the palm facing the direction of F. The fingers will point in the direction of B. The results are (a) ...
Lecture 13
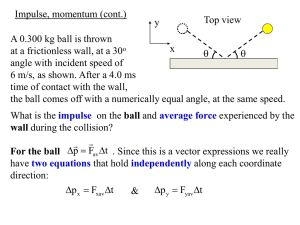
... change in translational kinetic energy of that object (as long as this energy does not go into internal energy…compressed spring, for instance) Wnet W KE ...
... change in translational kinetic energy of that object (as long as this energy does not go into internal energy…compressed spring, for instance) Wnet W KE ...
Rotation
... Equation (8) is the rotational analogue of the momentum principle for translational motion: force = rate of change of momentum For single particles the angular-momentum equation offers no advantage over the momentum equation. However, it is invaluable in the treatment of systems of particles and, in ...
... Equation (8) is the rotational analogue of the momentum principle for translational motion: force = rate of change of momentum For single particles the angular-momentum equation offers no advantage over the momentum equation. However, it is invaluable in the treatment of systems of particles and, in ...
Animation principles
... • Slow in and slow out. For example, a bouncing ball moves faster as it approaches or leaves the ground and slower as it approaches leaves its maximum position. The implementation is usually achieved by using splines to control the path of an object. The various spline parameters can be adjusted to ...
... • Slow in and slow out. For example, a bouncing ball moves faster as it approaches or leaves the ground and slower as it approaches leaves its maximum position. The implementation is usually achieved by using splines to control the path of an object. The various spline parameters can be adjusted to ...
6 Div, grad curl and all that
... Mathematically the divergence of ~v is just ∂i vi = ∂v ∂x + ∂y + ∂z . Consider the volumes inside A and A0 , A = ∂V and A0 = ∂V 0 (the symbol “∂” here means “the boundary of”). Remembering that we’re thinking of ~v as a current density for now, let’s ask ourselves how much how much comes out, passin ...
... Mathematically the divergence of ~v is just ∂i vi = ∂v ∂x + ∂y + ∂z . Consider the volumes inside A and A0 , A = ∂V and A0 = ∂V 0 (the symbol “∂” here means “the boundary of”). Remembering that we’re thinking of ~v as a current density for now, let’s ask ourselves how much how much comes out, passin ...
Six simple machines have many uses.
... You also can think of a wedge that cuts objects in terms of how it changes the pressure on a surface. The thin edges of a wedge provide a smaller surface area for the input force to act on. This greater pressure makes it easier to break through the surface of an object. A sharp knife can cut through ...
... You also can think of a wedge that cuts objects in terms of how it changes the pressure on a surface. The thin edges of a wedge provide a smaller surface area for the input force to act on. This greater pressure makes it easier to break through the surface of an object. A sharp knife can cut through ...