PHET Magnetism
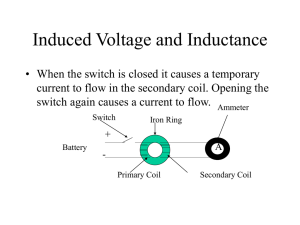
... 2. Select the “pickup coil” tab. 3. Make the light bulb light. Describe what you have to do to keep the light bulb glowing. 4. To make the bulb light you must have moving electrons. What do you have to do with the magnet to make the electrons move? 5. A generator “makes” electricity. Click on the “g ...
... 2. Select the “pickup coil” tab. 3. Make the light bulb light. Describe what you have to do to keep the light bulb glowing. 4. To make the bulb light you must have moving electrons. What do you have to do with the magnet to make the electrons move? 5. A generator “makes” electricity. Click on the “g ...
E6 MAGNETISM: FIELDS AND FORCES
... Electricity and magnetism - a historical perspective As separate phenomena, electricity and magnetism have been known for thousands of years. By the early 19th Century Volta's invention of the battery had made substantial electric currents available to experimenters. A remarkable connection between ...
... Electricity and magnetism - a historical perspective As separate phenomena, electricity and magnetism have been known for thousands of years. By the early 19th Century Volta's invention of the battery had made substantial electric currents available to experimenters. A remarkable connection between ...
Lesson 11. Topic “ Magnetism” Grammar material: The Present
... well-known English physicist (1540-1603). He carried out various important experiments on electricity and magnetism and wrote a book where he put together all that was known about magnetism. He proved that the earth itself was a great magnet. Reference must be made here to Galileo, the famous Italia ...
... well-known English physicist (1540-1603). He carried out various important experiments on electricity and magnetism and wrote a book where he put together all that was known about magnetism. He proved that the earth itself was a great magnet. Reference must be made here to Galileo, the famous Italia ...
Electromagnet - Cascades Science Center Foundation
... Electromagnets are used in all sorts of machines, from door bells, MRI machines to giant scrap yard cranes. Electricity and magnetism are closely related phenomena. A current passing through a coil will give rise to a magnetic field. When the electric current passes through the wire round around the ...
... Electromagnets are used in all sorts of machines, from door bells, MRI machines to giant scrap yard cranes. Electricity and magnetism are closely related phenomena. A current passing through a coil will give rise to a magnetic field. When the electric current passes through the wire round around the ...
- SlideBoom
... Ampere’s force law describes an “action at a distance” analogous to Coulomb’s law. In Coulomb’s law, it was useful to introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by w ...
... Ampere’s force law describes an “action at a distance” analogous to Coulomb’s law. In Coulomb’s law, it was useful to introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by w ...
Ch 18 ppt: Electromagnetism
... Kinds of Magnets • Atoms and Domains Some magnets, called ferromagnets, are made of iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary and Permanent Magnets Temporary magnets are made from material ...
... Kinds of Magnets • Atoms and Domains Some magnets, called ferromagnets, are made of iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary and Permanent Magnets Temporary magnets are made from material ...
3D Finite Element Analysis for Arcing Chamber Optimization
... Due to the physical model asymmetry, the threedimensional modeling of magnetostatic field was necessary. In a three-dimensional case it is described by elliptic equation Laplace-Poisson. Magnetic energy functional of magnetostatic field has a following expression [6]: ⎧⎛ B ...
... Due to the physical model asymmetry, the threedimensional modeling of magnetostatic field was necessary. In a three-dimensional case it is described by elliptic equation Laplace-Poisson. Magnetic energy functional of magnetostatic field has a following expression [6]: ⎧⎛ B ...
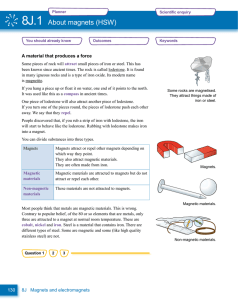
8J.1 About magnets (HSW)
... becomes magnetised. A piece of iron used in this way is called a core. The strength of an electromagnet is increased when an iron core is used. ...
... becomes magnetised. A piece of iron used in this way is called a core. The strength of an electromagnet is increased when an iron core is used. ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.