Electromagnetism_HW... - Jaclyn Kuspiel Murray
... You connect both ends of a copper wire, with a total resistance of 0.10 Ω, to the terminals of a galvanometer. The galvanometer has a resistance of 895 Ω. You then move a 10.0-cm segment of the wire upward at 1.4 m/s through a 2.0 10-2 T magnetic field. What current will the ...
... You connect both ends of a copper wire, with a total resistance of 0.10 Ω, to the terminals of a galvanometer. The galvanometer has a resistance of 895 Ω. You then move a 10.0-cm segment of the wire upward at 1.4 m/s through a 2.0 10-2 T magnetic field. What current will the ...
magnetic field
... attracted to the south pole of a magnet. Opposite poles of magnets attract each other. • A compass needle points north because the magnetic pole of Earth that is closest to the geographic North Pole is a magnetic south pole. ...
... attracted to the south pole of a magnet. Opposite poles of magnets attract each other. • A compass needle points north because the magnetic pole of Earth that is closest to the geographic North Pole is a magnetic south pole. ...
What is a Magenit? - Spring Branch ISD
... stones and were used as compass, many natural magnets are made up of iron, nickel, and cobalt • Magnets can also be man made by using electricity, these magnets are called electromagnets ...
... stones and were used as compass, many natural magnets are made up of iron, nickel, and cobalt • Magnets can also be man made by using electricity, these magnets are called electromagnets ...
18_12_2012 - Physics.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
Exercise 4 (Electromagnetism)
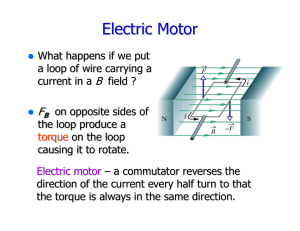
... (b) Assume the magnetic field is perpendicular to the current in the wire. By Fleming’s left hand rule, the magnetic force on the coil points to left. ...
... (b) Assume the magnetic field is perpendicular to the current in the wire. By Fleming’s left hand rule, the magnetic force on the coil points to left. ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
Exam No. 02 (Fall 2013) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... (b) Find the dipole moment of the charge density by evaluating Z d3 r r ρ(r). ...
... (b) Find the dipole moment of the charge density by evaluating Z d3 r r ρ(r). ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.