b) Explain the smoothing of rectified output voltage by capacitor by
... b) State the conditions to observe interference of light. c) State the conditions of constructive and destructive ...
... b) State the conditions to observe interference of light. c) State the conditions of constructive and destructive ...
Lecture_10
... Moving in a Magnetic Field Example 27-5: Magnetic force on a proton. A magnetic field exerts a force of 8.0 x 10-14 N toward the west on a proton moving vertically upward at a speed of 5.0 x 106 m/s (a). When moving horizontally in a northerly direction, the force on the proton is zero (b). Determin ...
... Moving in a Magnetic Field Example 27-5: Magnetic force on a proton. A magnetic field exerts a force of 8.0 x 10-14 N toward the west on a proton moving vertically upward at a speed of 5.0 x 106 m/s (a). When moving horizontally in a northerly direction, the force on the proton is zero (b). Determin ...
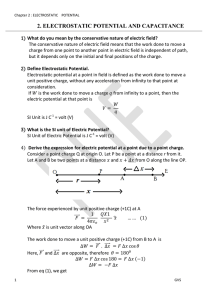
2. electrostatic potential and capacitance
... charges are separated (even when there is no external field). Such molecules have a permanent (or intrinsic) dipole moment. Examples of non-polar molecules are HCl and molecule of water (H2O). 29) What happens when Dielectrics are placed in an electric field? Both polar and non-polar dielectrics dev ...
... charges are separated (even when there is no external field). Such molecules have a permanent (or intrinsic) dipole moment. Examples of non-polar molecules are HCl and molecule of water (H2O). 29) What happens when Dielectrics are placed in an electric field? Both polar and non-polar dielectrics dev ...
SESSION 9: ELECTROSTATICS Key Concepts X
... a way that at any point on the line, a small positive point charge placed at that point will experience a force in the direction of the tangent of the line. CONSERVATION OF CHARGE The Law of Conservation of Charge states that charges cannot be created nor destroyed, but are merely transferred from o ...
... a way that at any point on the line, a small positive point charge placed at that point will experience a force in the direction of the tangent of the line. CONSERVATION OF CHARGE The Law of Conservation of Charge states that charges cannot be created nor destroyed, but are merely transferred from o ...
Grade 9 Science Exam Review
... Below is a list of content that is fair game for the exam. All the material can be found in your booklets, assignments, past tests and textbook. Please use the review questions posted as well as make a few of your own with the outline provided. ...
... Below is a list of content that is fair game for the exam. All the material can be found in your booklets, assignments, past tests and textbook. Please use the review questions posted as well as make a few of your own with the outline provided. ...
Chapter22 - LSU Physics
... As the rod slides, the light bulb uses energy. Where does the energy come from??? It comes from the force pushing the rod to the right! ...
... As the rod slides, the light bulb uses energy. Where does the energy come from??? It comes from the force pushing the rod to the right! ...
The Two Kinds of Electric Charge
... just the electric current, which is necessarily unidirectional in order to bring about this effect. This can be reconciled with the bi-directional Fechner hypothesis of 1845 if we consider that positive particles are pushed along with the aether flow, whereas negative particles eat their way in the ...
... just the electric current, which is necessarily unidirectional in order to bring about this effect. This can be reconciled with the bi-directional Fechner hypothesis of 1845 if we consider that positive particles are pushed along with the aether flow, whereas negative particles eat their way in the ...
magnetism - ScienceScene
... Make a statement regarding the affect of magnetism upon the production of electricity. ...
... Make a statement regarding the affect of magnetism upon the production of electricity. ...
SYLLABUS CLASS-VIII - e-CTLT
... reacts almost instantly to stop the flow of electricity in the circuit and thereby stopping heat production. ...
... reacts almost instantly to stop the flow of electricity in the circuit and thereby stopping heat production. ...
Document
... Some special cases of electromagnetics: Electrostatics: charges at rest Magnetostatics: charges in steady motion (DC) Electromagnetic waves: waves excited by charges in time-varying motion ...
... Some special cases of electromagnetics: Electrostatics: charges at rest Magnetostatics: charges in steady motion (DC) Electromagnetic waves: waves excited by charges in time-varying motion ...
The electric field
... 1. Finding the total charge in a region when you know the electric field outside that region 2. Finding the total flux out of a region when the charge is known a) It can also be used to find the flux out of one side in symmetrical problems b) In such cases, you must first argue from symmetry that th ...
... 1. Finding the total charge in a region when you know the electric field outside that region 2. Finding the total flux out of a region when the charge is known a) It can also be used to find the flux out of one side in symmetrical problems b) In such cases, you must first argue from symmetry that th ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.