fourth nine weeks
... location, sonar) pre-assessment to determine student’s readiness to learn. Agree/disagree statements Chapter 13, lesson 1 and Chapter 14, lesson 1 Students will demonstrate their understanding of sound and light waves through various lab and center stations, including but not limited to practicing w ...
... location, sonar) pre-assessment to determine student’s readiness to learn. Agree/disagree statements Chapter 13, lesson 1 and Chapter 14, lesson 1 Students will demonstrate their understanding of sound and light waves through various lab and center stations, including but not limited to practicing w ...
Science 9: Unit D – Electrical Principles and Technologies
... An electric motor works through electromagnetism. An electric current is passed into a circuit. The circuit passes through a coil of wire making an electromagnet. When the electromagnet is activated by electricity it becomes a magnet and reacts with permanent magnets on the motor. The magnets re ...
... An electric motor works through electromagnetism. An electric current is passed into a circuit. The circuit passes through a coil of wire making an electromagnet. When the electromagnet is activated by electricity it becomes a magnet and reacts with permanent magnets on the motor. The magnets re ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field affects magnetic materials (including, but not limited to, a compass, iron filings, and paper clips). ...
... Surrounding a magnet is a magnetic field that____________ ______ ____________ , a push or pull, without actually touching an object. Evidence of a magnetic field can be found in how the field affects magnetic materials (including, but not limited to, a compass, iron filings, and paper clips). ...
electric current
... because 7. What is a current that consists of charges that move back and forth in a circuit? 8. The relationship between electricity and magnetism is called 9. A generator uses motion in a magnetic field ...
... because 7. What is a current that consists of charges that move back and forth in a circuit? 8. The relationship between electricity and magnetism is called 9. A generator uses motion in a magnetic field ...
Electricity and Magnetism
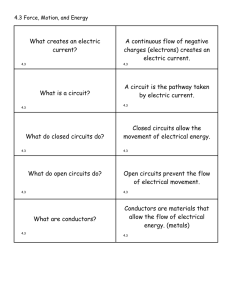
... Conductors are made of materials that electricity can flow through easily. These materials are made up of atoms whose electrons can move away freely. ...
... Conductors are made of materials that electricity can flow through easily. These materials are made up of atoms whose electrons can move away freely. ...
Name_______________________Test Date
... source. For example, Christmas lights that remain lit when one bulb goes out is an example of a parallel circuit. A series circuit can have more than one receiver but all receivers will turn off when the wires are disconnected from the battery (or power source). The distance between a magnet and ano ...
... source. For example, Christmas lights that remain lit when one bulb goes out is an example of a parallel circuit. A series circuit can have more than one receiver but all receivers will turn off when the wires are disconnected from the battery (or power source). The distance between a magnet and ano ...
What is energy
... How do materials with different charges react to each other? How do materials with the same charge react to each other? Define circuit. Define what a load on a circuit is. Define conductor. Define insulator. Define resistance. Define voltage. Define current. What units are used measure power? What u ...
... How do materials with different charges react to each other? How do materials with the same charge react to each other? Define circuit. Define what a load on a circuit is. Define conductor. Define insulator. Define resistance. Define voltage. Define current. What units are used measure power? What u ...
Current Electricity
... Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move around the circuit; measured in Ohms (Ω) ...
... Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move around the circuit; measured in Ohms (Ω) ...
Physics Lecture #33 - WordPress for academic sites @evergreen
... Mon. Mar. 2 – Physics Lecture #33 Maxwell’s Equations – the Unification of Electricity and Magnetism I 1. The Equations of Electricity and Magnetism 2. Changing Electric Fields are Accompanied by Magnetic Fields – or – how Maxwell Modified Ampere 3. The Displacement Current 4. Fields from Moving Cha ...
... Mon. Mar. 2 – Physics Lecture #33 Maxwell’s Equations – the Unification of Electricity and Magnetism I 1. The Equations of Electricity and Magnetism 2. Changing Electric Fields are Accompanied by Magnetic Fields – or – how Maxwell Modified Ampere 3. The Displacement Current 4. Fields from Moving Cha ...
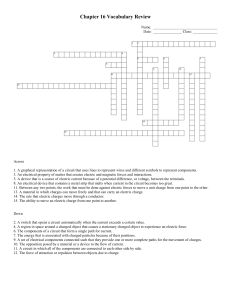
Chapter 16 Vocabulary Review Name: Date: Class: ______ Across
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
ELI `THE GREAT`
... balloon on your head and then touch someone and electrocute them. And make there hair stick up. • The forces of attraction between charged particles caused by static electricity are used in air pollution control, xerography and automobile painting. ...
... balloon on your head and then touch someone and electrocute them. And make there hair stick up. • The forces of attraction between charged particles caused by static electricity are used in air pollution control, xerography and automobile painting. ...
Faraday`s Law of Induction
... During the 1820s Faraday sought to discover how to make electricity from magnetism. He achieved success with the device pictured above on 29 August 1831. When he passed an electric current through one coil he induced an electric current in the other coil, which flowed for a very brief period of time ...
... During the 1820s Faraday sought to discover how to make electricity from magnetism. He achieved success with the device pictured above on 29 August 1831. When he passed an electric current through one coil he induced an electric current in the other coil, which flowed for a very brief period of time ...
Electricity and Magnetism Review Name: Directions: Answer the
... 1. Current electricity is the continuous flow of electrons through a conductor. 2. Materials that are a cross between conductors and insulators such as diodes and transistors are called semiconductors. 3. _____static electricity____ is the buildup of electrons on an object. 4. The interactions/prope ...
... 1. Current electricity is the continuous flow of electrons through a conductor. 2. Materials that are a cross between conductors and insulators such as diodes and transistors are called semiconductors. 3. _____static electricity____ is the buildup of electrons on an object. 4. The interactions/prope ...
Discovering Electricity
... (called ilektron in ancient Greek) with a piece of fur then the amber would attract light objects such as feathers. It took some time before anyone was able to explain the principles behind this phenomenon. ...
... (called ilektron in ancient Greek) with a piece of fur then the amber would attract light objects such as feathers. It took some time before anyone was able to explain the principles behind this phenomenon. ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.