Transformer Lab Preparation. Explain the working of a transformer.
... secondary coil, a current is sourced through the primary coil. This is not a constant current, but an alternating current. As a consequence the generated magnetic field is also not constant but varying as a function of the time. And then of course Faraday’s law will do the job. In order to make sure ...
... secondary coil, a current is sourced through the primary coil. This is not a constant current, but an alternating current. As a consequence the generated magnetic field is also not constant but varying as a function of the time. And then of course Faraday’s law will do the job. In order to make sure ...
Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... Drawing field lines/lines of force How to analyze impacts of one thing on another How to solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law How to design, construct and evaluate a prototype Prior knowledge: Inverse function/ reciprocal (math function) Opposite charges attract Negative charges rep ...
... Drawing field lines/lines of force How to analyze impacts of one thing on another How to solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law How to design, construct and evaluate a prototype Prior knowledge: Inverse function/ reciprocal (math function) Opposite charges attract Negative charges rep ...
PHYS 632 Lecture 11: Magnetism of Matter: Maxwell`s
... (b) Evaluate M for N = 100, a = 1.0 cm, b = 8.0 cm, and l = 30 cm. (a) The flux over the loop cross section due to the current i in the wire is ...
... (b) Evaluate M for N = 100, a = 1.0 cm, b = 8.0 cm, and l = 30 cm. (a) The flux over the loop cross section due to the current i in the wire is ...
The Electrical Nature of Matter
... • There are two kinds of electric charge_____________________________. • A substance that is has no charge is called ________________________. • When 2 neutral substances are _________________; one substance becomes positively charged and the other negatively charged. • ____________objects attract _ ...
... • There are two kinds of electric charge_____________________________. • A substance that is has no charge is called ________________________. • When 2 neutral substances are _________________; one substance becomes positively charged and the other negatively charged. • ____________objects attract _ ...
Printable Activities
... Magnetism As regards electricity, electric forces are not all there is, we also deal with magnetic forces. These two are directly related to one another. The effect of magnetic forces is readily observed in magnets. By means of these forces, magnets attract certain metals and other magnets. Magnetic ...
... Magnetism As regards electricity, electric forces are not all there is, we also deal with magnetic forces. These two are directly related to one another. The effect of magnetic forces is readily observed in magnets. By means of these forces, magnets attract certain metals and other magnets. Magnetic ...
Magnetic Field and High-Voltage Power Lines
... We hope this information will be useful to you. Please feel free to contact us with other questions or to share your comments. Sincerely, Hydro-Québec employee ...
... We hope this information will be useful to you. Please feel free to contact us with other questions or to share your comments. Sincerely, Hydro-Québec employee ...
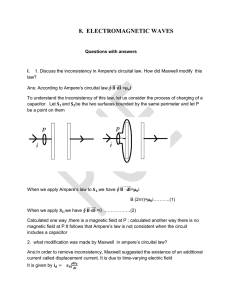
8. electromagnetic waves
... 2. what modification was made by Maxwell in ampere’s circuital law? Ans:In order to remove inconsistency, Maxwell suggested the existence of an additional current called displacement current. It is due to time-varying electric field It is given by ...
... 2. what modification was made by Maxwell in ampere’s circuital law? Ans:In order to remove inconsistency, Maxwell suggested the existence of an additional current called displacement current. It is due to time-varying electric field It is given by ...
4-03 IOT - The 9 Core Technologies
... charged, while the atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged. This type of electricity is called 'static' electricity, because it is not moving, but is stationary. ...
... charged, while the atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged. This type of electricity is called 'static' electricity, because it is not moving, but is stationary. ...
Motion of Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field
... 27.2 Magnetic force on a moving charge • The magnetic force F on a moving charged particle with a velocity v in a magnetic field B at an angle q is given by ...
... 27.2 Magnetic force on a moving charge • The magnetic force F on a moving charged particle with a velocity v in a magnetic field B at an angle q is given by ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.