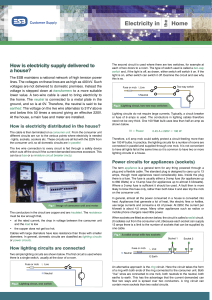
Electric Force and Field Practice Problems
... electroscope. He brings two charged rods without touching the electroscope. The positively charged rod causes the leaves to move further apart and the negatively rod causes leaves to move closer to each other. What type of the electric charge was initially on the electroscope? (A) positive (B) negat ...
... electroscope. He brings two charged rods without touching the electroscope. The positively charged rod causes the leaves to move further apart and the negatively rod causes leaves to move closer to each other. What type of the electric charge was initially on the electroscope? (A) positive (B) negat ...
Thesis - Docjava.com
... Another small problem with the PI is the handling of the current at the corners of rectangular loops. Because PI only models linear partitions, the current at the corner of a rectangular loop is modeled as if it continues on in a straight path, without making the turn around the corner. A more accur ...
... Another small problem with the PI is the handling of the current at the corners of rectangular loops. Because PI only models linear partitions, the current at the corner of a rectangular loop is modeled as if it continues on in a straight path, without making the turn around the corner. A more accur ...
Chapter 21 - KFUPM Faculty List
... We have seen that there is a relationship between the net amount of charge inside a closed surface and the electric flux through that surface. For the special cases of a closed surface in the shape of rectangular box and charge distribution made up of point charges or infinite sheets, we have found ...
... We have seen that there is a relationship between the net amount of charge inside a closed surface and the electric flux through that surface. For the special cases of a closed surface in the shape of rectangular box and charge distribution made up of point charges or infinite sheets, we have found ...
Physics chapter 1 electric charges and fields exercise
... compared to the magnitude of electric charge. Hence, quantization of electric charge is of no use on macroscopic scale. Therefore, it is ignored and it is considered that electric charge is continuous. www.tiwariacademy.com Question 1.5: www.tiwariacademy.com When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk c ...
... compared to the magnitude of electric charge. Hence, quantization of electric charge is of no use on macroscopic scale. Therefore, it is ignored and it is considered that electric charge is continuous. www.tiwariacademy.com Question 1.5: www.tiwariacademy.com When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk c ...
JJ Thomson and “Hidden” - Physics Department, Princeton University
... On p. 348 of [8] Thomsom remarked, in effect, that the argument of sec. 3.1 suggests the field momentum is associated with the magnetic dipole,17 while the argument of sec. 3.2 suggests it is associated with the electric charge. He then noted that if the Ampèrian magnetic dipole were a small permanen ...
... On p. 348 of [8] Thomsom remarked, in effect, that the argument of sec. 3.1 suggests the field momentum is associated with the magnetic dipole,17 while the argument of sec. 3.2 suggests it is associated with the electric charge. He then noted that if the Ampèrian magnetic dipole were a small permanen ...
Document
... Electromagnetic field A changing magnetic field always produces an electric field, and conversely, a changing electric field always produces a magnetic field. This interaction of electric and magnetic forces gives rise to a condition in space known as an electromagnetic field. The characteristics of ...
... Electromagnetic field A changing magnetic field always produces an electric field, and conversely, a changing electric field always produces a magnetic field. This interaction of electric and magnetic forces gives rise to a condition in space known as an electromagnetic field. The characteristics of ...
AP Physics 2 Course Planning and Pacing Guide
... • Identify the physics principle(s) pertaining to the situation and write it down using an acronym (such as N2L for Newton’s second law). • Include a physical representation in the form of a sketch and/or free-body diagram or graph. • Identify the given quantities and the unknowns. ...
... • Identify the physics principle(s) pertaining to the situation and write it down using an acronym (such as N2L for Newton’s second law). • Include a physical representation in the form of a sketch and/or free-body diagram or graph. • Identify the given quantities and the unknowns. ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.