Physics 112 Magnetism
... – Pieces of Magnetite, also called lodestone (Fe3O4), were known by Greeks to exert both forces of attraction and repulsion on each other. ...
... – Pieces of Magnetite, also called lodestone (Fe3O4), were known by Greeks to exert both forces of attraction and repulsion on each other. ...
E-field and Electric Potential Practice Problems
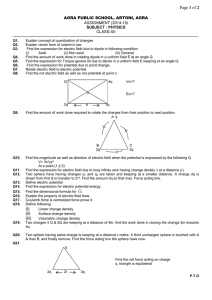
... (C) The electric potential inside a conductor is always zero. (D) The electric field at the surface of a conductor is tangent to the surface. (E) The surface of a conductor is always an equipotential surface. 4. Which of the following represents the magnitude, of the potential V as function of r, th ...
... (C) The electric potential inside a conductor is always zero. (D) The electric field at the surface of a conductor is tangent to the surface. (E) The surface of a conductor is always an equipotential surface. 4. Which of the following represents the magnitude, of the potential V as function of r, th ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle
... ELECTROMAGNETS 1. Strip the plastic covering from the two ends of the wire. (This may already be done for you.) 2. Make ten tight wraps around the middle of the nail, starting about 5 centimeters from the end of the wire. 3. Place the D cells in the battery holders. Connect the cells together with ...
... ELECTROMAGNETS 1. Strip the plastic covering from the two ends of the wire. (This may already be done for you.) 2. Make ten tight wraps around the middle of the nail, starting about 5 centimeters from the end of the wire. 3. Place the D cells in the battery holders. Connect the cells together with ...
Electric Circuits
... circuits and resistor circuits using this intuitive and easy-touse module. Students will discover and retain key concepts such as Ohm's law, Kirchoff's laws, current, voltage, and series and parallel circuits. ...
... circuits and resistor circuits using this intuitive and easy-touse module. Students will discover and retain key concepts such as Ohm's law, Kirchoff's laws, current, voltage, and series and parallel circuits. ...
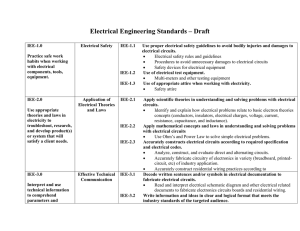
Electrical Engineering Standards
... Identify and explain how electrical problems relate to basic electron theories concepts (conductors, insulators, electrical charges, voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, and inductance). Apply mathematical concepts and laws in understanding and solving problems with electrical circuits ...
... Identify and explain how electrical problems relate to basic electron theories concepts (conductors, insulators, electrical charges, voltage, current, resistance, capacitance, and inductance). Apply mathematical concepts and laws in understanding and solving problems with electrical circuits ...
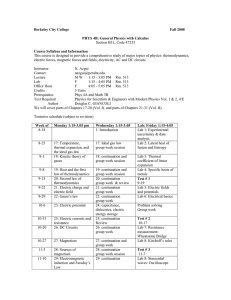
Berkeley City College
... assigned chapter(s) ahead. Group work and/or homework assignments will take place during discussion session. These assignments will not be collected or graded. 2) Laboratory : details will given during lab session. ...
... assigned chapter(s) ahead. Group work and/or homework assignments will take place during discussion session. These assignments will not be collected or graded. 2) Laboratory : details will given during lab session. ...
KHS Trial 2009 - Kotara High School
... Discuss reasons for the need for transformers by certain electrical appliances used in households. 3 ...
... Discuss reasons for the need for transformers by certain electrical appliances used in households. 3 ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Lecture 1 Electric Charge
... Electrostatic smoke precipitator model • Negatively charged central wire has electric field that varies as 1/r (strong electric field gradient). Field induces a dipole moment on the smoke particles. The positive end gets attracted more to the wire • In the meantime a corona discharge is created. Th ...
... Electrostatic smoke precipitator model • Negatively charged central wire has electric field that varies as 1/r (strong electric field gradient). Field induces a dipole moment on the smoke particles. The positive end gets attracted more to the wire • In the meantime a corona discharge is created. Th ...
ELECTROMAGETISM AND INDUCTION
... 1. Relation between magnetism and electricity, production of induced e.m.f & current, Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction 2. Direction of induced e.m.f and current, Lenz’s law, Self inductance ...
... 1. Relation between magnetism and electricity, production of induced e.m.f & current, Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction 2. Direction of induced e.m.f and current, Lenz’s law, Self inductance ...
Ch 17: Electric Potential
... Joule is very large for dealing w/electrons, atoms and molecules eV is energy required to move 1 e- through a potential difference of 1V 1 eV = qe V = (1.6 x 10-19 C)(1.0 V) 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
... Joule is very large for dealing w/electrons, atoms and molecules eV is energy required to move 1 e- through a potential difference of 1V 1 eV = qe V = (1.6 x 10-19 C)(1.0 V) 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J ...
Teaching Faraday`s law of electromagnetic induction in
... acting on a charge q that moves with the speed of the circuit. Thus, the Lorentz force naturally follows from the definition of the rate of flux change d⌽ / dt as a complete derivative. There are cases where Faraday’s law of induction is applied not to circuits, but to extended bodies, such as a Far ...
... acting on a charge q that moves with the speed of the circuit. Thus, the Lorentz force naturally follows from the definition of the rate of flux change d⌽ / dt as a complete derivative. There are cases where Faraday’s law of induction is applied not to circuits, but to extended bodies, such as a Far ...
PHYS 212 – MT3 Spring 2013 Sample 1 Solutions
... induced CW (positive) current to oppose that change. Now as it exits region B and enters region C not only is it losing an external field out but it is gaining an external field into the page, so the rate of change of the external flux is TWICE as high as it was before, so the current will be in the ...
... induced CW (positive) current to oppose that change. Now as it exits region B and enters region C not only is it losing an external field out but it is gaining an external field into the page, so the rate of change of the external flux is TWICE as high as it was before, so the current will be in the ...
History of electromagnetic theory

For a chronological guide to this subject, see Timeline of electromagnetic theory.The history of electromagnetic theory begins with ancient measures to deal with atmospheric electricity, in particular lightning. People then had little understanding of electricity, and were unable to scientifically explain the phenomena. In the 19th century there was a unification of the history of electric theory with the history of magnetic theory. It became clear that electricity should be treated jointly with magnetism, because wherever electricity is in motion, magnetism is also present. Magnetism was not fully explained until the idea of magnetic induction was developed. Electricity was not fully explained until the idea of electric charge was developed.