By Erik,Brianna,michael,wyatt
... The properties or effects of magnetic fields. There is magnetism in credit cards, phones, and the earth. On Earth one needs a sensitive needle to find magnetic forces, and out in space they are usually a lot weaker. But beyond the dense atmosphere, such forces have a much bigger role, and a region ...
... The properties or effects of magnetic fields. There is magnetism in credit cards, phones, and the earth. On Earth one needs a sensitive needle to find magnetic forces, and out in space they are usually a lot weaker. But beyond the dense atmosphere, such forces have a much bigger role, and a region ...
Two Identical charges, each -8.00 X 〖10〗^(
... rotated in magnetic field. To increase the voltage many coils are connected in series. When current to be delivered by the generator is to be increased, coils are connected in parallel. The energy consumed in rotating coils is converted into electrical energy in the form of current passing through t ...
... rotated in magnetic field. To increase the voltage many coils are connected in series. When current to be delivered by the generator is to be increased, coils are connected in parallel. The energy consumed in rotating coils is converted into electrical energy in the form of current passing through t ...
Intro to EMR and Wave Equation
... •In a vacuum, all EMR travel at the speed of light regardless of frequency •19th century physics theory said all waves had to travel through something, the medium that EMR moved was called the ether (a transparent substance that filled all space) •Experiments were done to measure the speed of light ...
... •In a vacuum, all EMR travel at the speed of light regardless of frequency •19th century physics theory said all waves had to travel through something, the medium that EMR moved was called the ether (a transparent substance that filled all space) •Experiments were done to measure the speed of light ...
$doc.title
... Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the exam and turn in at the fron ...
... Please write down your name and student # on both the exam and the scoring sheet. After you are finished with the exam, please place the scoring sheet inside the exam and turn in at the fron ...
Purdue University PHYS 221 FINAL EXAM (orange) 12/17/03
... Both E and B must be zero in that region. E must be zero, but B might be non-zero in that region. E and B might both be non-zero, but they must be mutually perpendicular. d) B must be zero, but E might be non-zero in that region. e) E and B might both be non-zero, but they must point in the opposite ...
... Both E and B must be zero in that region. E must be zero, but B might be non-zero in that region. E and B might both be non-zero, but they must be mutually perpendicular. d) B must be zero, but E might be non-zero in that region. e) E and B might both be non-zero, but they must point in the opposite ...
Q- (a) A positive ion of mass m and charge q, initially at rest is
... potential energy of charge q1 when the potential is change by V is given by qV Thus the loss in electrostatic potential energy when the charge is accelerated through a potential difference V is qV. As there is no non-conservative force is to be considered, the total energy of the system remains cons ...
... potential energy of charge q1 when the potential is change by V is given by qV Thus the loss in electrostatic potential energy when the charge is accelerated through a potential difference V is qV. As there is no non-conservative force is to be considered, the total energy of the system remains cons ...
Digital Design - Oakland University
... motion of the source. This theory predicts seemingly unusual effects such as the measured length of moving bodies and time intervals being dependent on the frame of reference being used for the measurement. ...
... motion of the source. This theory predicts seemingly unusual effects such as the measured length of moving bodies and time intervals being dependent on the frame of reference being used for the measurement. ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... An electric current can produce magnetism, which in turn can produce an electric current. Interactions between electric and magnetic fields can be observed in everyday objects like, motors, generators, and transformers. ...
... An electric current can produce magnetism, which in turn can produce an electric current. Interactions between electric and magnetic fields can be observed in everyday objects like, motors, generators, and transformers. ...
[2011 question paper]
... The spins interact via (i) nearest neighbour ferromagnetic interactions with coupling J1 and (ii) next-to-nearest neighbour anti-ferromagnetic interactions (favouring antialigned spins) with coupling J2 . (a) For a one-dimensional system of three spins with a Hamiltonian of the above form, find the ...
... The spins interact via (i) nearest neighbour ferromagnetic interactions with coupling J1 and (ii) next-to-nearest neighbour anti-ferromagnetic interactions (favouring antialigned spins) with coupling J2 . (a) For a one-dimensional system of three spins with a Hamiltonian of the above form, find the ...
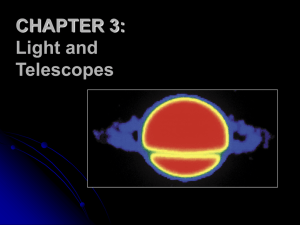
CHAPTER 3: Light and Telescopes
... Particle Properties of Light Radiating matter emits light in discrete chunks of energy called QUANTA (photon) When atoms are excited they can jump up energy levels- when they move back down they give off photons with energy equal to the amount it needs to loose Energy(photon) = hc/ λ h= (plan ...
... Particle Properties of Light Radiating matter emits light in discrete chunks of energy called QUANTA (photon) When atoms are excited they can jump up energy levels- when they move back down they give off photons with energy equal to the amount it needs to loose Energy(photon) = hc/ λ h= (plan ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 18. Define Poynting vector. Derive an expression for it? 19. Discuss the theory of propagation of plane electromagnetic waves when normally incident on the boundary of the two medium. 20. Obtain an expression for the power radiated from a electric dipole? ...
... 18. Define Poynting vector. Derive an expression for it? 19. Discuss the theory of propagation of plane electromagnetic waves when normally incident on the boundary of the two medium. 20. Obtain an expression for the power radiated from a electric dipole? ...
Magnetism & electromagnetic
... composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typically composed of billions of a ...
... composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when placed in a magnetic field. These domains are typically composed of billions of a ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.











![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)