Electromagnetic Induction
... • We made electromagnets! • Faraday also figured out that moving a magnetic field through electrical wires created current. • This is called induced current! ...
... • We made electromagnets! • Faraday also figured out that moving a magnetic field through electrical wires created current. • This is called induced current! ...
Physics 121 Exam Sheet - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... implies a cause-effect relation between the two forces which are associated with any interaction. In reality, neither force of a force pair is more fundamental than the other and neither should be viewed as the cause of the other. All forces occur in pairs. There are no isolated forces. Fundamental ...
... implies a cause-effect relation between the two forces which are associated with any interaction. In reality, neither force of a force pair is more fundamental than the other and neither should be viewed as the cause of the other. All forces occur in pairs. There are no isolated forces. Fundamental ...
Strain Sensors 14th June, 2013 Kaustubh Shinde and Obi Igwe
... electromagnetic fields causes caner, but that there is established evidence showing that RF electromagnetic fields may increase a person’s body temperature or may heat body tissues and may stimulate nerve and muscle tissues.” • SAR (specific absorption rate), is the measure of the amount of electrom ...
... electromagnetic fields causes caner, but that there is established evidence showing that RF electromagnetic fields may increase a person’s body temperature or may heat body tissues and may stimulate nerve and muscle tissues.” • SAR (specific absorption rate), is the measure of the amount of electrom ...
Wednesday, Apr. 26, 2006
... Charging capacitor. A 30-pF air-gap capacitor has circular plates of area A=100cm2. It is charged by a 70-V battery through a 2.0-W resistor. At the instant the battery is connected, the electric field between the plates is changing most rapidly. At this instance, calculate (a) the current into the ...
... Charging capacitor. A 30-pF air-gap capacitor has circular plates of area A=100cm2. It is charged by a 70-V battery through a 2.0-W resistor. At the instant the battery is connected, the electric field between the plates is changing most rapidly. At this instance, calculate (a) the current into the ...
V - barransclass
... Electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular: • to each other, and • to the direction of propagation. ...
... Electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular: • to each other, and • to the direction of propagation. ...
Equation sheet #1
... Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one electron -e=-1.60 x10-19 C ___________ ...
... Constants and equations for exam 1. You may detach this page if you wish. ________________________________________________________________________________ Coulumb’s Law constant k=8.99 x109 N m2/C2 Permittivity of free space 0=8.85 x10-12 C2/N m2 Charge of one electron -e=-1.60 x10-19 C ___________ ...
18_12_2012 - Physics.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
... Which one of the following actions produces attractive forces? ____ (a) bringing the north poles of two magnets together (b) ...
The Failure of E=mc2 - Infinite Energy Magazine
... expended to drive the pendulum was, however, only 25.6 kJ. This meant E=mc2 overestimated the Maxwell field energy impinging on the pendulum by a factor of more than 2,000. Hence, Einstein’s law failed to comply with experiment. ...
... expended to drive the pendulum was, however, only 25.6 kJ. This meant E=mc2 overestimated the Maxwell field energy impinging on the pendulum by a factor of more than 2,000. Hence, Einstein’s law failed to comply with experiment. ...
L11 radiation
... frequency f of the wave? (b) What are the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic part of the wave? (c) What are k and ω? (d) What is the intensity? (e) If the wave falls upon a perfectly absorbing sheet of area 1.85 m2, at what rate is momentum delivered to the sheet and what is the radiation ...
... frequency f of the wave? (b) What are the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic part of the wave? (c) What are k and ω? (d) What is the intensity? (e) If the wave falls upon a perfectly absorbing sheet of area 1.85 m2, at what rate is momentum delivered to the sheet and what is the radiation ...
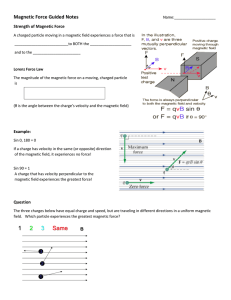
Magnetic Force Guided Notes
... The three charges below have equal charge and speed, but are traveling in different directions in a uniform magnetic field. Which particle experiences the greatest magnetic force? ...
... The three charges below have equal charge and speed, but are traveling in different directions in a uniform magnetic field. Which particle experiences the greatest magnetic force? ...
0117 Lecture Notes - AP Physics 1 Equations to
... AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, this product. Let me be clear about what I mean by “memorize”: I mean you should have the equation memorized, know what it means and know when you can use it. This is a lot more than ...
... AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, this product. Let me be clear about what I mean by “memorize”: I mean you should have the equation memorized, know what it means and know when you can use it. This is a lot more than ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.