1 Newton`s Laws
... Newton’s 3rd Law When an object exerts a force on a second object (action), the second objects exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object (reaction). To every action there is an equal and ...
... Newton’s 3rd Law When an object exerts a force on a second object (action), the second objects exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object (reaction). To every action there is an equal and ...
Definitions
... Newton defined time and space as follows: “Absolute, true, and mathematical time, of itself and from its own nature, flows equably without relation to anything external…” “Absolute space, in its own nature, without relation to anything external, remains always similar and immovable.” As the 19th Cen ...
... Newton defined time and space as follows: “Absolute, true, and mathematical time, of itself and from its own nature, flows equably without relation to anything external…” “Absolute space, in its own nature, without relation to anything external, remains always similar and immovable.” As the 19th Cen ...
Document
... 2. Pressure, volume and temperature are the same for both gases. Thus the number of moles is also the same. For statement 2, since the temperatures are the same, so the average KE is the same for both gases. Hydrogen being lighter, has higher rms speed. For statement 3, hydrogen moves faster, so hyd ...
... 2. Pressure, volume and temperature are the same for both gases. Thus the number of moles is also the same. For statement 2, since the temperatures are the same, so the average KE is the same for both gases. Hydrogen being lighter, has higher rms speed. For statement 3, hydrogen moves faster, so hyd ...
PDF version
... University of Virginia Hertz Finds Maxwell's Waves: and Something Else The most dramatic prediction of Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism, published in 1865, was the existence of electromagnetic waves moving at the speed of light, and the conclusion that light itself was just such a wave. This cha ...
... University of Virginia Hertz Finds Maxwell's Waves: and Something Else The most dramatic prediction of Maxwell's theory of electromagnetism, published in 1865, was the existence of electromagnetic waves moving at the speed of light, and the conclusion that light itself was just such a wave. This cha ...
Assignment 5.
... Questions 1 - 3 count for 95% of the marks and Question 4 for 5%. Q1: The atmospheric electric field is uniform with a magnitude of 100 V m-1 between the ionosphere and the ground. Assume that the ionosphere and the ground are both perfect conductors, and that the ionosphere is at a height of 120 km ...
... Questions 1 - 3 count for 95% of the marks and Question 4 for 5%. Q1: The atmospheric electric field is uniform with a magnitude of 100 V m-1 between the ionosphere and the ground. Assume that the ionosphere and the ground are both perfect conductors, and that the ionosphere is at a height of 120 km ...
The principle of constancy of the speed of Light in free-space
... associated with the properties of free-space will have the same value in any reference frame. One might ask that and are regarded as universal constants for long; so what is new in the above statement? In that case we wish to refer the work of Sumner [4] where permittivity of free-space is co ...
... associated with the properties of free-space will have the same value in any reference frame. One might ask that and are regarded as universal constants for long; so what is new in the above statement? In that case we wish to refer the work of Sumner [4] where permittivity of free-space is co ...
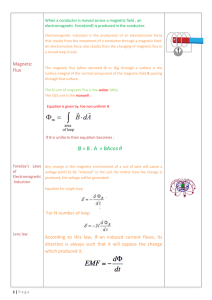
Magnetism
... element could have the same chemical properties but different masses, called isotopes The masses of positive ions can be measured precisely by using a mass spectrometer ...
... element could have the same chemical properties but different masses, called isotopes The masses of positive ions can be measured precisely by using a mass spectrometer ...
Maxwell`s Equations 1.The concept of displacement current was a
... 8.Maxwell’s Equation describes the interrelationship among electric field,electric charge, magnetic field,and: Ans:D A) Plasmic field B) Electron Pulse c) Tiberium Charge D)None of the above 9.What is electromagnetism ? Ans:B A) A current that repels quasi-metals such as vibranium. ...
... 8.Maxwell’s Equation describes the interrelationship among electric field,electric charge, magnetic field,and: Ans:D A) Plasmic field B) Electron Pulse c) Tiberium Charge D)None of the above 9.What is electromagnetism ? Ans:B A) A current that repels quasi-metals such as vibranium. ...
abc - Southern Methodist University
... 1. Two charges of +2q and −5q are placed on a line. The distance between the two charges is d. (a) There is a point on the line where the strength of the electric field due to the two charges is zero. Describe where the point is, relative to the positions of the two charges. (b) Is there any point n ...
... 1. Two charges of +2q and −5q are placed on a line. The distance between the two charges is d. (a) There is a point on the line where the strength of the electric field due to the two charges is zero. Describe where the point is, relative to the positions of the two charges. (b) Is there any point n ...
Ch 17 Introduction to electricity
... 2. Electromagnets= iron core wrapped with electrical wire in which an electric current runs through the wire • When the electric current is turned on it is a strong magnet • When the electric is off the object the magnetic field stops ...
... 2. Electromagnets= iron core wrapped with electrical wire in which an electric current runs through the wire • When the electric current is turned on it is a strong magnet • When the electric is off the object the magnetic field stops ...
Maxwell`s Equations is the Most Basic for Satellite Communications
... introduce to the public at that time, it was able to draw the Faraday’s Fig. 3 Michael Faraday. talent into a research. Such an open lecture may be that the present independent administrative research institution in Japan should learn. Faraday studied a magnetic field around a direct current, establ ...
... introduce to the public at that time, it was able to draw the Faraday’s Fig. 3 Michael Faraday. talent into a research. Such an open lecture may be that the present independent administrative research institution in Japan should learn. Faraday studied a magnetic field around a direct current, establ ...
PPT
... Ch. 22: Electric fields, field maps, fields due to various charge geometries, point charges and dipoles in an electric field Ch. 23: Electric flux, Gauss’s Law for electric fields, Coulomb’s Law from Gauss’s Law, isolated charged conductors, considerations of symmetry Ch. 24: Electric potential ener ...
... Ch. 22: Electric fields, field maps, fields due to various charge geometries, point charges and dipoles in an electric field Ch. 23: Electric flux, Gauss’s Law for electric fields, Coulomb’s Law from Gauss’s Law, isolated charged conductors, considerations of symmetry Ch. 24: Electric potential ener ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.